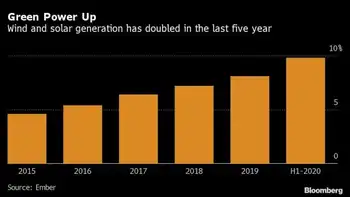
Windfarm Britain means skyrocketing bills
By The Register
CSA Z462 Arc Flash Training - Electrical Safety Essentials
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 6 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
This could have a negative impact on plans for electrification of transport and domestic energy use.
The study is called Impact of Intermittency, and was carried out by consulting group Pöyry for various industry players such as the National Grid and Centrica at a cost of more than £1m. Pöyry modelled the likely effects on the UK electricity market of a large windpower base of the sort needed to meet government carbon targets - assuming no major change in the amount of nuclear power available.
There's a summary of the report for the public, and is probably quite detailed enough for most of us at 30 pages. It says that there's no particular problem for the National Grid as such - the actual electricity transmission network - with large amounts of wind in the 40+ gigawatt capacity range. But the introduction of so many wind turbines will spell disastrous problems for operators of "thermal" plant - that is fossil fuelled, and conceivably nuclear too.
According to James Cox, one of the report's authors: "Our worry at the outset of the study that the very dynamics of variable wind output would challenge the system operators, has moved to concern that the economic environment for thermal plant will be highly challenging.”
Massive unpredictable variations in the amount of energy coming from the wind would combine with the much more regular changes in demand and in possible tidal power projects to produce an energy market described in the study as "volatile". If there were enough thermal plants in existence to cope with rare (but nonetheless certain to occur) events such as nationwide calms during winter evenings, some of these plants would almost never be in use. They'd sometimes go years without running for more than a few hours.
In order for energy companies to build those thermal plants, necessary to avoid power cuts, they'd need to be sure that they could charge enormous, outrageous prices during the brief periods when they were actually in operation. According to the report's authors:
“In our opinion, it is likely that the sort of price 'spikes' needed to reward the risks for such plant will stretch the market design to its utmost... Equally a market with spiky and volatile prices is one where the risk of operation is greatly increased: it is unlikely to send clear economic signals to new investors.”
In other words, nobody would want to build and maintain a power station with no reliable idea how much it would get used from one year to the next (the report reveals that the UK's annual wind output could be expected to vary by no less than 13 per cent). A certainty of enormous rewards when the kit was finally needed would be required in investors' minds - but there could be no such certainty. The spot electricity price would need to soar to such levels as to introduce even more risk, in the form of government intervention to protect energy distributors from going bust and consumers suffering from vicious price surges.
As things stand, then, it will be more or less impossible to get the necessary contingency plants built - nobody would provide the capital for them. Thus, when the inevitable early-evening winter calms hit in the 2030s, the required amount of thermal backup power stations will simply not be there. Up to a certain point the National Grid can "manage demand" without causing power cuts by fiddling with the supply voltage, so delivering less power to users without cutting any of them off, but it has been known to crash right through this safety net even with the comparatively manageable power stations of today.
So we're talking power cuts on a fairly routine basis, if nothing else changes and the planned levels of wind farms appear.
We're also, already, talking about very serious electricity price increases simply to make those wind farms happen: the only reason they ever get built is the government's Renewables Obligation Certificates (ROC) scheme. By cranking up the ROC system, the government can drive more wind into the market; this process is already underway, and set to continue for a long time. ROCs are often misleadingly described as a "subsidy", but they cost the Treasury nothing: their effect is to pay renewables plants a guaranteed minimum sum of extra money for every unit of power they put into the grid, on top of the market price, and pass the costs of this on to the consumer via the distributing companies.
This means that the seemingly crazy idea of negative electricity prices actually becomes meaningful with ROCs and windfarms. At times of high wind and low demand the wind farms would have more electricity on hand than the grid wanted, and they would be competing to get their juice onto the grid: not so much for its price, but to obtain valuable ROCs.
It would become worth their while at such times, up to a certain point, for windfarmers to actually pay the distributing companies to take their electricity, in order to get ROCs. The spot electricity price could indeed go negative at times. Sadly this isn't good news for electricity bills; consumers pay for the ROCs too.
Obviously the thermal power stations would have been undercut off the grid well before the price reached zero, worsening their profitability. There wouldn't just be a few gas stations switching on and off on a fairly regular schedule as we see today: the entire thermal sector - perhaps even including nuclear - would be dropping in and out of play unpredictably, running their machinery perhaps for just a few hours at a time. This would not only result in lost revenue, but drive up maintenance and operating costs and increase breakdowns - so requiring more plants offline and under repair, at more expense. Again, prices would have to rise.
All in all, the whole thermal system - which would have to remain of a size to power the UK unaided by renewables - would be enormously more expensive for consumers than it is now. Added to the significant expense of the windfarms and other renewables, this would mean swinging price rises.
Some have suggested that problems might be mitigated by "interconnector" power lines between national energy markets, bringing in power from places where the wind is blowing to places where it isn't and so smoothing out the troublesome surges. Pöyry are fairly blunt about this:
“Interconnectors cannot be the 'golden bullet'... we note that if interconnectors remove price differentials between markets the commercial case for building them can be challenging.” "There's no such thing as cheap green power - that is a myth," Pöyry's Phil Hare told the BBC.
This notion of seriously increased electricity prices might cast some doubt on the desirability of electric cars and railways, with unfortunate consequences for low-carbon transport. (Perhaps not so much in the case of cars, owing to the enormous taxes on motor fuel.) Expensive electricity would also tend to make domestic users favour gas and heating oil over electricity even more than they do now. (A kilowatt-hour of gas is already much cheaper than one of 'leccy, which is why we tend do everything we can with it: hot water, heating, cooking. A normal home already uses significantly more kWh of gas or oil than of 'leccy as a result.)
Gas-powered fridges, gas-powered air conditioning, combined-heat-and-power microgen plants, increased industrial use of gas and other such things might come into vogue with a vengeance in the future Windfarm Britain, further worsening our national carbon burden and gas-supply problems.
It's also worthy of note that experts believe that the fossil sector would become significantly dirtier than is now projected under these circumstances, as fuel-efficient but capital-intensive combined cycle gas turbines (CCGTs) would be replaced by tougher, cheaper, carbon-spewing gear more able to stand being thrashed on and off all the time. That's why the Renewable Energy Foundation's Dr John Constable, commenting on the new report, told the Beeb:
"Less ambitious levels of wind would almost certainly result in a system which is not only just as clean but is also more robust and affordable."
Amazingly, given all this, Beeb environment correspondent Roger Harrabin has lately chosen to report:
“A major obstacle to wind was demolished when a study from National Grid last week concluded that the electricity distribution grid could cope with on-off wind energy without spending a lot on back-up fossil fuel power stations.”
This conclusion countered a key argument used by opponents of wind power, who suggested that the UK would still need to build extra fossil fuel power stations in order to bridge the gap between demand and supply when the wind did not blow.
A study to be published by consultants Poyry will suggest that by 2030 wind will be the dominant source of electricity for the UK.
Actually the Pöyry study says no such thing - even in the Windfarm Britain scenario envisaged by the government, a majority of 'leccy would come from thermal sources rather than renewable (and part of the renewables would be tidal rather than wind, but pass on). The report also says, as we have seen, that massive extra costs over and above those of the windfarms themselves will hit the thermal sector if the lights are to be kept on.
But Harrabin of the BBC goes on undaunted:
“The [Pöyry] study amplifies a recent paper from National Grid itself stating that a move towards wind power would not necessitate widespread investment in expensive back-up power plants fuelled by gas or coal.”
This is a key finding which helps remove one of the main barriers to the advance of wind...
Harrabin does eventually admit that Windfarm Britain is going to cost a lot, though it's hard to see where he thinks all the extra cash on the electricity bill - over and above that for the windfarms' ROC money - is going, if not to "expensive back-up power plants fuelled by gas or coal".
Anyway, it's all the government's fault, it seems.
Politicians are still reluctant to pass on this message to the public.
They are, as witness their ongoing pretence that the ROC scheme is somehow a "subsidy" rather than a tax levied on electricity users.
But consider Harrabin's headline - "Wind 'can revolutionize UK power'" (Who's he quoting? Himself?) and his opening lines:
“Research from analysts Poyry says that the UK can massively expand wind power by 2030 without suffering power cuts or a melt-down of the National Grid.”
No it doesn't. And then:
“The cost of electricity would then be determined not by consumer demand, but by how hard the wind is blowing.” When it is windy power will be so cheap that other forms of generation will be unable to compete, the report says.
But the power won't be cheap to users even when it's windy, thanks to the ROC system. And when it isn't windy, power will be so expensive it'll make your eyes water. Overall, your electricity bill will be a great deal higher than it now is.
It's not just politicians who are reluctant to tell the expensive truth about wind power, it seems. Perhaps Harrabin was afraid of another bitchslap from the orthodox greens if he reported the news himself.