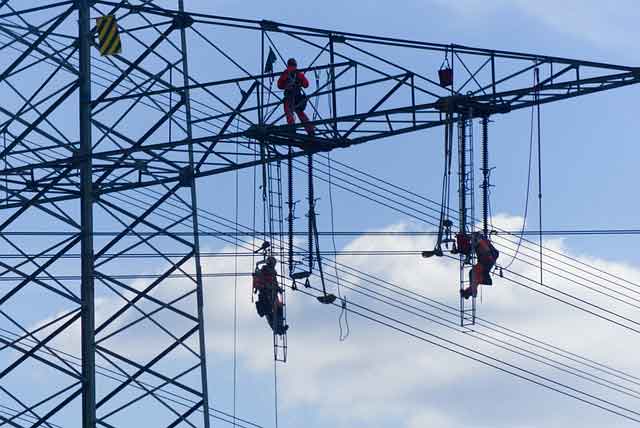
Thar project taps into Pakistan's major coal resource
By Industrial Info Resources
Protective Relay Training - Basic
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
The World Bank, which is focusing on power generation through cost-effective feeds other than oil and hydro, will aid Pakistan in procuring investments from the International Finance Corporation for the project.
The Mines and Minerals Department of Sindh invited expressions of interest from domestic and international players for setting up a joint venture on a 75:25 equity basis.
The government of Sindh will provide 50% of the equity.
Players from Indonesia, China and a few Gulf countries have expressed interest in the joint venture with technical assistance from Germany and Australia. A committee is in the process of scrutinizing the offers and will submit its recommendation to the government shortly.
The Pakistani province of Sindh has an estimated 175 billion metric tons of coal reserves in the Thar region. The quality of coal ranges from lignite-B to sub-bituminous A-C. It is estimated that these coal deposits can be utilized to generate more than 100,000 MW of electricity that will address the country's power requirements for up to several decades.
Last year, the project suffered a setback when Shenhua Corporation (Beijing) withdrew its plans of setting up a $1 billion, 1,000-MW power plant at Thar, citing low tariff rates, security issues, unavailability of a reliable water supply and domestic workload as major concerns. Pakistan's government had turned down Shenhua's demand for a tariff of 5.7 cents per unit. Private players in Pakistan were also unwilling to participate in the project at tariffs lower than 10.5 cents per unit.
Late last year, the Mines and Minerals Department approved a proposal, submitted in 2003 by Cougar Energy Limited, for setting up 400-MW units based on Thar coal, using underground gasification technology. Cougar will commence work at Block III of the Thar coalfield after signing a memorandum of understanding with Pakistan's government and will initially generate 400 MW of power. The capacity of the units will be subsequently enhanced to generate 1,000 MW of power.
Investments of $500 million have already been made by the government in the exploration of three blocks of coal in Sonda and six blocks of coal in Thar. Requisite infrastructure including roads, water supply, communications and electricity has already been set up in the regions leading to the coalfields in Thar and the granite deposits in Nagarparker.
Designs are being drawn up for the construction of an airstrip in the region. Thar Lodge is being constructed to provide accommodation with modern amenities to visiting engineers and investors.
Pakistan has drawn up plans to generate 5,000 MW of electricity under the Thar project and further enhance the project's capacity to generate 20,000 MW. Pakistan is currently grappling with a severe power crisis. The power shortage in the country is presently as high as 3,000 MW and is likely to go up to 4,000 MW within a year. The government plans to install power generation units of 2,200 MW in the current year.
Load management campaigns are being organized to save nearly 500 MW without resorting to unplanned load shedding. The government has also directed the Pakistan Electric Power Company to supply consumers with 10 million energy-saving bulbs at subsidized rates.
Under the Public Sector Development Program for 2008-09, Pakistan's government has allocated $12.8 million for 19 development projects being implemented by the Petroleum and Natural Resources Division. From this, a sum of $7.5 million has been set aside for the Thar project.
An additional allocation of $523,000 has been made for undertaking gasification feasibility studies for this project. The government has also allocated $339,000 for the development of Pakistan's National Coal Policy. A sum of $150,000 has been allocated for the exploration and assessment of coal reserves at Bahlol, Chamalang Dhaka, and parts of the Ghazi coal basin in Baluchistan.
The estimated total cost of this project is $450,000. The government will also spend $60,000 to explore coal reserves in Kotli, Azad Kashmir. This project is expected to cost $298,000.
Presently, coal accounts for only 0.1% of the total power generated in Pakistan, while the world average is 40%. The country aims to increase the amount of coal in its energy mix to 19% by 2030 and to 50% by 2050.