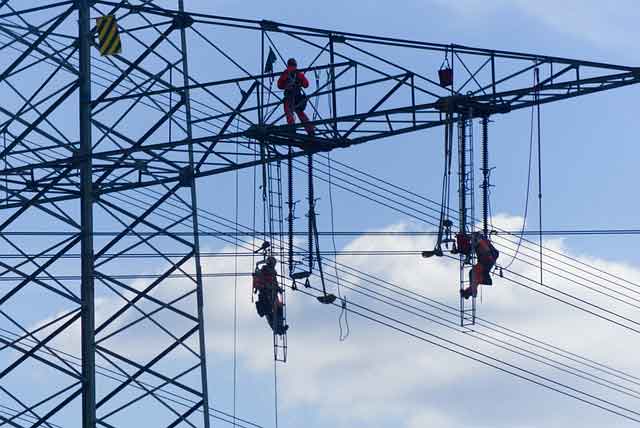
Tougher water limits predicted
Stage 4 would ban outdoor watering and likely place new limits on businesses that have not faced restrictions so far. Households in some communities could face daily limits. Stage 4 measures would be new territory for most Catawba River communities. Charlotte-Mecklenburg had never even banned outdoor lawn watering until Sept. 26.
But Charlotte might not wait until the stage is declared before ordering an end to all outdoor water use, ending exceptions and increasing fines, said Charlotte-Mecklenburg Utilities conservation coordinator Maeneen Klein. "We really have to start looking at worst-case scenarios and how to avoid them," she said.
There's still no word from the Charlotte-based utility about how much water the region has left or when it might run out, if the drought continues. Duke had said making such predictions is not scientific and that other communities, such as Atlanta, Durham and Raleigh, are being inaccurate by announcing how many days of water remain.
But Duke apparently has changed its mind about such forecasts.
Jeff Lineberger, the company's hydro licensing manager, said Duke is working on estimates that "will give a better feel for the remaining available water storage." Bill Holman, a former N.C. environment secretary and now a visiting scholar and water expert at Duke University, said the utility should be able to give an accurate prediction.
Members of the Catawba drought advisory group have met in Huntersville with the N.C. Drought Management Advisory Council. The groups talked about future steps and what has worked in the past, Klein said.
Seventeen N.C. water systems serving hundreds of thousands of residents - including Raleigh, Durham and Monroe - have regular water supplies of less than 100 days given current conditions, according to a recent report to the State Water Infrastructure Commission. Only six systems were in such straits a week ago, said Woody Yonts, chairman of the state's drought advisory council.
An additional 80 of the state's 604 local water systems are vulnerable or being closely monitored by state officials.
"We're in a situation that we've never seen the likes of here," Yonts said.
Downstream, Rock Hill banned all sprinklers and irrigation systems.
"We don't have too much longer before we start having some serious problems," said city Utilities Director Jimmy Bagley. Over the past month, the Catawba has lost 2.25 percent of its water storage a week, Lineberger said. Cities, industries, power plants and evaporation are taking more water than rainfall and tributary streams can replace.
The utility says usable water storage in the Catawba lakes is at less than 37 percent. It has been dropping steadily since May. The optimum level for this time of year is more than 70 percent.
Duke's prognosis: Stage 4 drought status by mid-November to early December if no substantial rain falls. At that point, says the Catawba drought-response plan, usable storage in the reservoirs "can be fully depleted in a matter of weeks or months."
Duke manages the Catawba under a federal hydropower license and controls the level of 11 lakes and flow of water with 13 hydroelectric dams. The water provides the Charlotte region its drinking water and Duke uses it to run and cool its power plants along the river and its lakes.
A drought advisory group including Duke and major water users on the Catawba would make the Stage 4 declaration, which would set a new conservation goal of 20 to 30 percent. Local officials would decide what specific restrictions apply in their communities.
The Stage 3 restrictions now in place across the Catawba basin call for curbing water use by 10 to 20 percent. Some communities have exceeded that goal, Lineberger said.
Charlotte-Mecklenburg Utilities has pumped an average of 24.5 percent less water since those mandatory restrictions took effect Aug. 28, compared with the rest of August.
"What we really need, though, is a bunch of rain," Lineberger said.
"And we need more conservation."
Related News

Data Center Boom Poses a Power Challenge for U.S. Utilities
WASHINGTON - U.S. electric utilities are facing a significant new challenge as the explosive growth of data centers puts unprecedented strain on power grids across the nation. According to a new report from Reuters, data centers' power demands are expected to increase dramatically over the next few years, raising concerns about grid reliability and potential increases in electricity costs for businesses and consumers.
What's Driving the Data Center Surge?
The explosion in data centers is being fueled by several factors:
- Cloud Computing: The rise of cloud computing services, where businesses and individuals store and process data on…