Electrical Grounding For Telecommunications Systems Course Outline
Instructor
Pablo Diaz, P. Eng, Electrical Grounding Consultant, The Electricity Forum
DAY ONE
OVERVIEW
- Grounding concepts for the telecommunications industry
- How the telecommunications industry developed the concept of "Single Point Ground" system
- Utilization of banks of batteries and their grounding in a telecommunication site
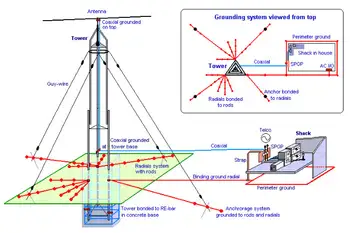
- How to ground telecommunications towers.
- How to ground equipment and communications antennas installed on a communications tower
- Proper ground resistance values required by the telecommunications industry
- The most common grounding electrodes utilized in a telecommunications site
- Proper grounding and bonding of equipment installed in a telecommunications rack.
- The "Master Ground Bar' and other auxiliary copper bars used in the telecommunications industry and their proper grounding.
- Review of four Case Histories performed in cellular and digital microwave sites
SESSION 1: TELECOMMUNICATIONS GROUNDING OVERVIEW
- Grounding- Definitions
- Grounding methods used in the telecommunications industry
- Grounding practices for cellular and digital microwave sites
- System grounding for transformers used in a communications site
- Telecommunications single point grounding
- Why the telecommunications industry uses a solid grounding system
- Impedance grounding for a telecommunication tower
- Why ground circuits and systems
- Grounding systems options for a telecommunications site
- Grounded systems
- The telecommunications industry TIA/EIA cabling grounding
SESSION 2: GROUNDING ELECTRODE SYSTEM
- Grounding Electrodes: Construction And Installation
- Ground Resistance and Resistivity
- Grounding Electrode Conductor
- Electrical Grounding and Corrosion
- Materials-Splicing
- Installation and Protection
- Sizing the grounding Electrode Conductor
SESSION 3: SYSTEM GROUNDING
- Circuit grounding
- Why Systems and Circuits are grounded
- Grounded Conductor
- Direct Current Systems
- Alternating-Current System
- Systems less than 50 Volts
- Grounding of Transformers
- Grounding for Telecommunications Site
SESSION 4: TOWER INSTALLATIONS
- Self-Supporting Tower Installations
- Bonding the Tower Ground to the Central Office Ground
- Pole Mounted Antennas
- Antenna Towers Mounted on Top of Buildings
- Antennas and Connecting Coaxial Transmission Lines and Waveguides
- Protection of Radio Equipment
- Guyed Tower Installation
- Pole Mounted Installation
- Building Mounted Installation
SESSION 5: TELECOMMUNICATIONS ELECTRICAL BONDING SYSTEM
- Equipment Bonding and Grounding
- Rack Bonding
- Major Requirements: Leakage Current, Proper Sizing
- Generators
- Transformers
- UPS systems: Online, Standby, Line Interactive, Alternative
- Installation
- Sizing the Equipment grounding
- Identification of the Equipment grounding Conductor
- Electric Shock
- Grounding and electric Shock
SESSION 6: TELECOMMUNICATIONS STAND-BY/EMERGENCY GENERATORS
- Separately Derived Systems (SDS)
- When an Emergency Generator is not a SDS
- Main Bonding Jumper
- Portable generators
- Vehicle Mounted Generators
DAY TWO
SESSION 7: LIGHTNING PROTECTION SYSTEM FOR A TELECOMMUNICATIONS SITE
- The Phenomenon of Lightning
- Development of Lightning Flash
- Flash Parameters
- Lightning- Characteristics
- Electrical Effects
- Basic Protection Requirements
- Protection Systems
- Electro-Geometric Method
- Tower Lightning Protection System
- Rolling sphere Concept
- Lightning Protection system Specifications
SESSION 8: TELECOMMUNICATIONS INDUSTRY GROUNDING PRACTICES
- Telecommunication Site Grounding
- Single Point Ground System
- Grounding Subsystems
- Exterior Ground Ring
- Exterior Structural Metal Elements
- Interior Ground ring- Halo Ground
- Master Ground Bar
- Cable entrance Ground Bar
- Telecommunications Closets
- Cable Trays or Raceways
- Low Frequency Networks
- High frequency Networks
- Waveguides Grounding
- Racks, Cabinets and Enclosures
- Central Office Battery System
SESSION 9: GROUNDING AGAINST ELECTROMAGNETIC INTERFERENCE (EMI/ESD/RFI)
- Electronic Equipment Grounding
- Introduction and Definitions
- Telecommunication Rooms and Closets
- Data Processing Equipment Grounding
- Electronic Security Equipment Grounding
- EMI (Electromagnetic Interference)
- Inductive, Capacitive and Radiation Coupling
- RFI (Radio frequency Interference)
- Electrostatic Discharge
- Shields grounding
- Cable Shielding and Grounding
- Coaxial Cables
- Telephone Lines
SESSION 10: TELECOMMUNICATIONS EQUIPMENT PROTECTION
- System Reference Zero
- Detection of a faulty Neutral-Ground System
- Sizing Wiring to meet Computer Industry Standards
- Grounding line Treatment Devices
- Transient Overvoltage Protector Grounding
- Gas Tubes
- Metal Oxide Varistors
- Silicon Avalanche Diodes
- Data Lines Grounding- RS232
CASE HISTORIES 4 case histories included: Four Telecommunications Case Histories will be reviewed and analyzed.
STANDARDS AND CODES REFERNCES FOR THIS COURSE
- National Electrical Code/IEEE Standards/ANSI Stds, Industry STDS
- Canadian Standards Association:
- CSA Grounding and Bonding (C22.1 E98, Section 10)
- CSA Protection and Control (C22.1 E98, Section 14)
- CSA Installation of Electrical Equipment (C22.1 E98, Section 26)
- CSA Electrical Communication Equipment (C22.1 E98, Section 60)
- Canadian Electrical Code:
- Bonding and Grounding of Electrical Equipment (C22.2 No. 0.4 EM1982 R1993)
- Grounding and Bonding Equipment (C22.2 No. 41 EM1987 R1993) (C22.2 No. 0.4 EM1982 R1993)
- NEC National Electrical Code
REFERENCES
- Communications:
- TIA/EIA - 568: Commercial Building Telecommunications Cabling Standard
- TIA/EIA - 607: Commercial Building Grounding and Bonding Requirements for Telecommunications
- ISO/IEC IS 11801: Generic Cabling for Customer Premises
- BICSI: BICSI Telecommunications Cabling Installation Manual
- BICSI: BICSI Customer-Owned Outside Plant Design Manual (CO-OSP)
Review of expectations
Questions and Answers
COURSE TIMETABLE
Both Days:
Start: 8:00 a.m.
Coffee Break: 10:00 a.m.
Lunch: 12:00 noon
Restart: 1:15 p.m.
Finish: 4:30 p.m.