What is Electrical Arcing?
By R.W. Hurst, Editor

NFPA 70e Training - Arc Flash
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 6 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our OSHA 3873 Fact Sheet – Minimum Approach Distance and Training Requirements

- Calculate MAD using voltage and overvoltage values
- Ensure proper communication between host and contract employers
- Meet OSHA training requirements for qualified electrical workers
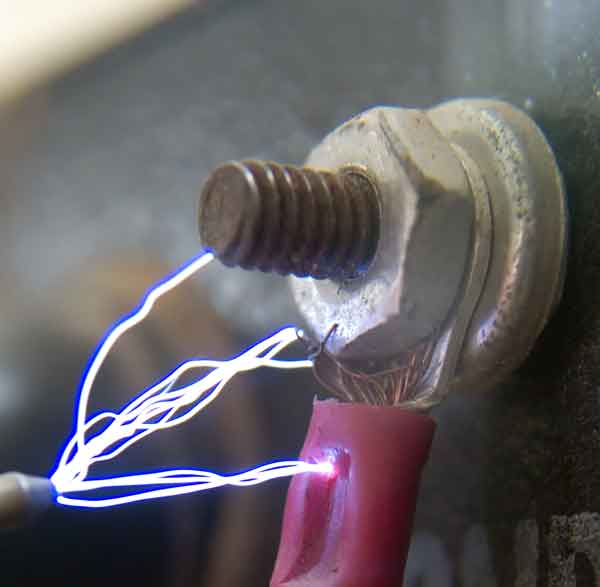
Electrical arcing is a discharge of electricity through the air between conductors, creating intense heat and light. It occurs due to gaps, faults, or damaged insulation and can lead to equipment failure, fire hazards, and arc flash injuries in power systems.
What is Electrical Arcing?
Electrical arcing is a dangerous phenomenon in electric power systems that can lead to serious safety hazards and equipment damage.
✅ Creates intense heat and light from high-voltage discharge
✅ Often results from damaged insulation or conductor gaps
✅ Can cause arc flash, fires, or system failure
It is a phenomenon that occurs when electricity flows through an unintended path, creating a short spark that can cause significant damage to systems and pose serious safety risks. Understanding what causes it, recognizing its examples, and knowing how to prevent it are crucial for ensuring the safety and efficiency of systems. For root causes and prevention, see What Causes Electrical Arcing, which outlines the physical conditions that trigger arc events.
Various factors can cause this, often related to the condition and integrity of components. Here are some common causes:
-
Damaged Circuits: Over time, circuits in a panel can experience wear and tear, resulting in damaged insulation or broken wires. This damage can create an unintended path for electricity flow, resulting in an arc.
-
Loose Connections: Poorly connected wires in outlets or at connection points in a panel can create gaps that allow electricity to arc across them.
-
Corrosion: Moisture and other environmental factors can cause corrosion, weakening connections and increasing the likelihood of an arc.
-
High Voltage: It is more likely to occur in high-voltage systems, where the potential for a significant electrical discharge is greater.
-
Faulty Equipment: Malfunctioning or poorly maintained equipment, such as circuit breakers or outlets, can also lead to an arc.
To explore the broader context of safety, our Arc Flash Hazard article covers key risks, consequences, and mitigation strategies.
Sign Up for Electricity Forum’s Arc Flash Newsletter
Stay informed with our FREE Arc Flash Newsletter — get the latest news, breakthrough technologies, and expert insights, delivered straight to your inbox.
An arc flash is a sudden and dangerous release of energy caused by an electrical fault, often triggered by a short circuit or a conductor gap that allows electricity to jump through the air. This high-energy event produces a high voltage discharge, intense heat, and pressure waves that can cause serious injury or damage. A malfunctioning circuit breaker or poor maintenance can fail to interrupt the fault current in a timely manner, allowing the arc to sustain and escalate. These events represent a severe electrical hazard, especially in industrial or high-voltage environments. Proper safety procedures and regular system inspections are crucial in mitigating the risk of arc-related incidents.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an Example of Electrical Arcing?
One common example of this occurs in arc furnaces, which are used in industrial settings to melt metals. In an arc furnace, an arc is intentionally created between electrodes and the metal being processed, generating intense heat required for melting.
Another example is the arc lamp, where an electric arc between electrodes produces bright light. These lamps are used in high-intensity illumination applications, such as movie projectors and searchlights.
However, electrical arcing can also occur unintentionally and pose risks. For instance, an arc flash can occur in a panel when a short circuit creates a sudden release of energy, leading to a potentially explosive event that can cause serious injuries and fires. A comprehensive Arc Flash Analysis can help quantify incident energy levels and determine safe working distances.
How Do You Stop Electrical Arcing?
One of the common causes of electrical arcing is damaged wiring, which can occur due to age, rodent activity, or physical damage. It may also occur in a circuit panel where loose connections or corroded terminals are present. Overloaded outlets are another frequent culprit, as excessive current can heat up wires and cause insulation breakdown. Routine inspection is essential for identifying potential risks early, such as scorch marks, buzzing sounds, or flickering lights—all of which are signs of electrical arcing. Addressing these issues promptly helps prevent fire hazards and ensures a safer power system.
Preventing it involves several proactive measures to ensure the safety and reliability of systems:
-
Regular Maintenance: Conduct routine equipment inspections and maintenance to identify and address potential issues before they cause an arc. This includes checking for damaged circuits and replacing worn-out components.
-
Tight Connections: Ensure all connections are secure and free from corrosion. Loose or corroded connections should be tightened or replaced to prevent an arc.
-
Proper Insulation: Use appropriate insulation materials to cover wires and connections. Damaged insulation should be promptly repaired or replaced to prevent short circuits.
-
Use of Protective Devices: Install protective devices, such as circuit breakers and arc-fault circuit interrupters (AFCIs), to detect and interrupt unintended electricity flow, thereby preventing arcs and potential fires.
-
Avoid Overloading Circuits: Ensure that systems are not overloaded with excessive current, which can increase the risk of an arc. Distribute loads evenly across circuits.
Follow our 7 Steps to Arc Flash Analysis guide to perform a compliant and effective hazard assessment.
What is Electrical Arcing and is it Safe?
It is generally not safe and poses several risks, including:
-
Fires: It can generate intense heat, which can ignite surrounding materials and lead to fires. This is a significant hazard, particularly in residential and commercial settings.
-
Damage to Equipment: It can cause severe damage to equipment, resulting in costly repairs and downtime. It can also lead to the failure of critical systems.
-
Personal Injury: Arc flashes can cause serious injuries to individuals working near panels or equipment. The intense energy release can result in burns, hearing damage, and other injuries.
While intentional arcing in controlled environments, such as arc furnaces or arc lamps, is managed through safety protocols, unintentional arcing in systems must be avoided through diligent maintenance and protective measures. Equip workers with the right knowledge and protection through our 70E Training, based on the NFPA 70E standard.
Electricity Today T&D Magazine Subscribe for FREE

- Timely insights from industry experts
- Practical solutions T&D engineers
- Free access to every issue
It is a hazardous phenomenon that occurs when electricity flows through an unintended path, creating a short spark that can lead to significant damage and safety risks. Understanding the causes of it, such as damaged circuits, loose connections, and high voltage, is essential for preventing it. Examples of an arc, like those found in arc furnaces and arc lamps, highlight both its industrial applications and potential dangers. By implementing regular maintenance, securing connections, using proper insulation, and installing protective devices like circuit breakers and AFCIs, you can effectively prevent electrical arcing and ensure the safety of your systems. See the real-world consequences of arcing events in our Arc Flash Video, which shows how fast and destructive an arc can be.
Related Articles