Benefits of Industry-Standard Networks Explained
By Stancho Djiev, Ph.D., Technical University Sofia, Bulgaria
Download Our OSHA 3875 Fact Sheet – Electrical PPE for Power Industry Workers

- Follow rules for rubber gloves, arc-rated PPE, and inspection procedures
- Learn employer obligations for testing, certification, and training
- Protect workers from arc flash and electrical shock injuries
Benefits of industry networks include collaboration, knowledge sharing, standards alignment, and vendor partnerships that accelerate innovation in electrical engineering, grid modernization, smart manufacturing, and safety compliance across power systems and automation ecosystems.
What Are the Benefits of Industry Networks?
They enable faster innovation, standards compliance, risk mitigation, and scalable solutions through shared expertise.
✅ Accelerates compliance with IEEE, IEC, UL standards and codes
✅ Improves interoperability across SCADA, PLC, and smart grid systems
✅ Enables supplier benchmarking, risk sharing, and joint R&D
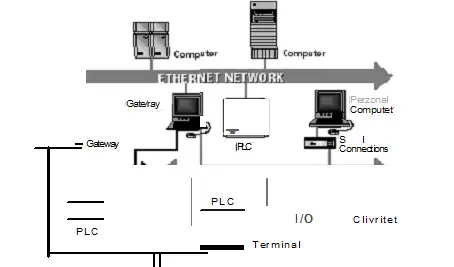
Modern control and business systems require open, digital communications. Industrial networks replace conventional point-to-point RS-232, RS-485, and 4-20 mA wiring between existing measurement devices and automation systems with an all-digital, 2-way communication network. Industrial networking technology offers several major improvements over existing systems. With industry-standard networks, we can select the right instrument and system for the job regardless of the control system manufacturer. Other benefits include:
To understand how device-level buses, controllers, and enterprise systems coordinate, resources like industrial automation communication outline protocol choices, latency tradeoffs, and integration patterns. Selecting between Ethernet, fieldbus, and wireless options benefits from comparing transmission methods for industrial networks with respect to determinism, noise immunity, and distance.
- Reduced wiring -- resulting in lower overall installation and maintenance costs
- Intelligent devices -- leading to higher performance and increased functionality such as advanced diagnostics
- Distributed control -- with intelligent devices providing the flexibility to apply control either centrally or distributed for improved performance and reliability
- Simplified wiring of a new installation, resulting in fewer, simpler drawings and overall reduced control system engineering costs
- Lower installation costs for wiring, marshalling, and junction boxes
Delivering these benefits also depends on choosing switches, gateways, and physical media from a well-architected set of industrial network components that match environmental and reliability requirements. Designers often map sensors, controllers, and supervisory systems across the hierarchical levels of industrial networks to balance real-time control with plantwide visibility.
Sign Up for Electricity Forum’s Building Automation Newsletter
Stay informed with our FREE Building Automation Newsletter — get the latest news, breakthrough technologies, and expert insights, delivered straight to your inbox.
Standard industrial networks offer the capability to meet the expanding needs of manufacturing operations of all sizes. As our measurement and automation system needs grow, industrial networks provide an industry-standard, open infrastructure to add new capabilities to meet increasing manufacturing and production needs. For relatively low initial investments, we can install small computer-based measurement and automation systems that are compatible with large-scale and long-term plant control and business systems. This standards-based approach aligns closely with how a building automation system aggregates HVAC, power, and security data for unified operations. For teams expanding beyond production into facilities integration, understanding what building automation entails helps frame networking requirements and data governance.
As energy costs and sustainability goals rise, leveraging advanced energy management over the same industrial network can drive measurable efficiency gains and carbon reporting accuracy.




