More radiation meds are on way
SAN LUIS OBISPO, CALIFORNIA - State emergency services officials will order 500,000 adult doses and 300,000 children's doses of emergency potassium iodide to replenish aging supplies of the thyroid protecting pills.
The federal Nuclear Regulatory Commission has given states until April 30 to order more pills. They are to be taken in the event of radiation exposure following an accident or terrorist attack at a commercial nuclear power plant.
The pills will be divided between San Luis Obispo County, which has Diablo Canyon nuclear power plant near Avila Beach, and the communities around San Onofre nuclear generating station in northern San Diego County, said Greg Renick, a spokesman with the state Office of Emergency Services.
Unlike the last time state and federal officials supplied potassium iodide, these pills will not be mailed to households. Instead San Luis Obispo County's pills will be stored locally and shipped to Camp Roberts in the event of a radiation emergency.
The state has designated Camp Roberts as the care and treatment center for evacuees from a Diablo Canyon emergency.
"The pills would be available to those who don't already have them," Renick said.
In 2003, the state and federal governments supplied pills to households in the Diablo Canyon emergency planning zone, areas around the plant that could be irradiated in the event of a radioactive release. The shelf life of those pills is good through 2009.
The NRC authorized a one-time purchase of more tablets, but their distribution was delayed by budget concerns and the difficulties of dealing with 21 different states, said Patricia Milligan, who oversees the NRC's potassium iodide program.
"States are notoriously slow," she said. "Two or three responded right away, and a trickle after that, and some still haven't responded."
California is one of those states that haven't responded, but Renick said his office will meet the April 30 deadline.
How Potassium iodide works:
Potassium iodide is a form of salt that is often added to table salt. The tablets would be taken at the direction of county health officials following a radiological release.
The pills saturate the thyroid gland, preventing it from absorbing radioactive iodine, a common component of radiation releases.
Potassium iodide only protects the thyroid and should not be considered an all-purpose radiation protection pill.
The adult dose of potassium iodide is 130 milligrams, and a child's dose is 65 milligrams. It is especially important that newborns receive the right dose, Milligan said.
Potassium iodide is a stable drug and can be used even after its shelf life expires, Milligan said. Its expiration date is based on the ability of the pills to dissolve within 15 minutes of being swallowed. Expired pills can still be effective if they are crushed before being taken, Milligan said.
Study: Coal plants would foul Dallas-Fort Worth air Feb 11, 2007 - Fort Worth Star-Telegram, Texas Pollution created by new power plants planned for East and Central Texas will harm Dallas-Fort Worth's air quality and probably put Waco and Austin in violation of federal clean-air laws for the first time. Those were the conclusions in a new study conducted by researchers at the University of Texas at Austin.
The study is billed by power plant opponents as the most comprehensive analysis yet of the pollution that would be created by building as many as 16 new power plants.
It's also the first to demonstrate that Waco and Austin, and even the Tyler-Longview area 150 miles southeast of Fort Worth, could be dramatically affected by the power plants' pollution.
Led by David Allen, an air pollution expert who heads UT's Center for Energy and Environmental Resources, the study bolsters arguments by elected leaders, residents and clean-air activists that the new power plants will doom Dallas-Fort Worth, and perhaps much of Central Texas, to years of dirty air.
"This gives us finally what we have been waiting for a long time, which is the evidence to present to the state of Texas about why we cannot afford to build all these coal plants," said Dallas Mayor Laura Miller during a recent news conference.
But energy industry representatives ripped the study, claiming it's not objective. They note that the study was commissioned by the Texas Clean Air Cities Coalition, a group led by Miller and Houston Mayor Bill White that is fighting the new plants.
The study "appears to be motivated by a desire to delay or defeat new coal-fired capacity in Texas," said Scott Segal, director of the Electric Reliability Coordinating Council, an industry trade group. "Undermining electric power in Texas hurts the ability of the state to provide healthy living conditions to its residents."
Some also questioned the motivation of Allen, who plans to testify during public hearings supporting Miller's group and others opposed to the plants.
"The professor who did it is one of their witnesses, and he did this for them," said Tom Kleckner, a spokesman for Dallas-based TXU Corp., which wants to build 11 of the plants.
His study comes as the battle to build the power plants is set to come to a head this month in Austin.
Challenges to state permits that would allow TXU to build six new plants are scheduled to be heard before a state administrative law judge.
State energy experts say the new plants are needed to replenish Texas' dwindling energy reserves, which could reach a critical level by the end of the decade, they say.
Critics say that the state does not face a looming energy crisis and that the proposed power plants won't use the most modern pollution control technology.
Concerns about air quality prompted state Rep. Charles "Doc" Anderson, R-Waco, to file a bill last month calling for a six-month moratorium on building power plants until all environmental and public health impacts are studied.
The controversy has garnered national attention, in part, because of a 2005 executive order by Gov. Rick Perry that directed state environmental regulators to expedite permitting process to build new power plants. That order has contributed to the rush to build plants, which will dramatically increase the state's energy reserves but emit tens of millions of tons a year of pollutants.
Perry has been sued over the executive order, and so has the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality for its handling of the power plant permits.
TXU, the state's largest energy supplier, has been the focus of much of the criticism.
Its $10 billion plant-building plan includes a commitment to reduce pollution companywide by 20 percent in exchange for permission from the state to build the 11 power plants in East and Central Texas.
While industry officials dismiss Allen's work, they point to a state-sponsored computer modeling study done last year that concluded that if TXU follows through on its commitment to cut emissions by 20 percent, then building the 11 plants, and as many as six others, would lower average ozone levels in the nine-county Dallas-Fort Worth area.
But that study also found that on days when the wind blows out of the south and southeast, where many of the plants would be built, ozone levels would increase - in some cases significantly - even with the 20 percent emissions reduction. Even more troubling is that the hardest-hit area on those days would be Frisco in Collin County, the area federal regulators have identified as having the region's worst ozone problem.
"The study confirms our worst fears, that these power plants will have a devastating effect on air quality throughout the state," said Tom "Smitty" Smith, director of the Texas chapter of Public Citizen in Austin.
David Allen, an air pollution specialist at the University of Texas, led the study released that predicts severe air-quality problems if many power plants are built. It's based on computer models of the ozone season in 2002. Highlights include:
Virtually every area in the Dallas-Fort Worth area would be affected by the power plants' pollution, preventing the region from meeting federal ozone standards for years.
Waco, which currently meets federal standards, could soon be in violation of the air-quality standards.
Austin could see all its efforts to lower pollution and stay in compliance with air-quality standards wiped out by power plant pollution.
Pollution from diesel locomotives carrying coal through the Dallas-Fort Worth, Waco and Tyler-Longview areas to the new plants would significantly hamper local ozone-fighting efforts, a conclusion supported by state and regional studies.
Related News
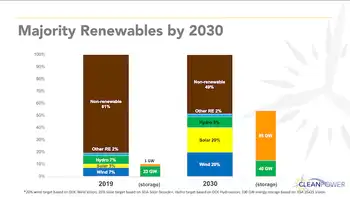
U.S. Renewable and Clean Energy Industries Set Sights on Market Majority
WASHINGTON - Within a decade, more than half of the electricity generated in the U.S. will come from clean, renewable resources supported by energy storage, according to a joint commitment today from the American wind, solar, hydropower, and energy storage industries. The American Wind Energy Association (AWEA), Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA), National Hydropower Association (NHA), and Energy Storage Association (ESA) have agreed to actively collaborate across their industry segments to achieve this target.
The four industries have released a set of joint advocacy principles that will enable them to realize this bold vision of a majority renewables grid. Along with…




