The News At BC Hydro
VANCOUVER -- - Barring any last-minute glitches, a deal to transfer the so-called back-office operations of B.C. Hydro to a new company set up by international consulting firm Accenture will close soon.
Propaganda, mainly from opponents of the highly politicized corporate restructuring, has created a tense atmosphere for more than 1,600 employees affected by the agreement, which transfers billing, accounting, customer service, human resources, information technology and similar functions to Accenture Business Services of B.C.
Accenture says the company, which it expects will be up and running by April 1, will pursue a potential $58-billion market for administrative and support services at utilities throughout North America.
Although it recommended its members ratify the arrangement, the Office and Professional Employees International Union opposes it in principle and has called for a public inquiry on the future of B.C. Hydro. The union says it advised members to accept the Accenture transition -- and 90 per cent did so -- to ensure compliance with the collective agreement and because employees were offered few alternatives.
Ironically, Accenture says the deal hinged on the new company having a trained staff well-versed in the ways of B.C. Hydro. Had the union urged its members to reject the agreement, it would have scuttled the transaction.
However noble its motives, the union has been drawn into a campaign of disinformation being waged by critics of Liberal government policies.
The principal weapon in this effort is corporate character assassination.
Accenture, they argue, is really Andersen Consulting, an arm of Arthur Andersen, the disgraced and defunct document-shredding auditor of Enron Corp., the energy company that precipitated a widespread accounting scandal from which the US business and investment community has yet to recover.
The fact is that Accenture has never been an arm or leg or any other body part of Arthur Andersen LLP; neither was it involved in its accounting or auditing practice. Andersen Consulting was formed as a separate legal entity which has operated independently since 1989, a status confirmed by the Securities and Exchange Commission in 1990.
In fact, Andersen Consulting had to pay Arthur Andersen millions in royalties annually while the accounting firm proceeded to set up its own consulting business to compete with its namesake.
After nearly a decade of conflict and acrimony, Andersen Consulting launched a process in 1997 that culminated in August 2000 with an arbitration ruling from the International Chamber of Commerce in Paris that severed any contractual ties between the two, finding that Arthur Andersen had violated the intent of their agreement.
Andersen Consulting had to pay US$1 billion for its freedom, far less than the $14 billion Arthur Andersen had demanded. At the time, analysts said that although Andersen Consulting came out the winner, it lost a major asset -- it was forced to surrender the "prestigious" Andersen name.
Another line of attack critics employ is to charge that Accenture is based in an offshore tax haven in order to shield income from countries where it does business. Media reports often refer to "Bermuda-based Accenture," suggesting something nefarious.
Indeed, Accenture is based in Bermuda, an international centre of banking and insurance for more than 50 years. The reason it is headquartered there has as much to do with geography as with tax policies.
With 2,500 partners in 47 different countries, Accenture found the partnership model unworkable. The nature of the beast is that a partnership pays out all of its money to the partners at year end. There is no money for growth and acquisitions and no access to capital markets. Accenture needed a corporate structure.
When Accenture's partners established the umbrella company, they debated the location of a head office. The Europeans didn't want to be in North America, the North Americans didn't want to be in Europe and the Asian partners felt they didn't have the force of numbers to influence the outcome. On Bermuda, they were able to reach a consensus.
The island's tax policies are favourable to business. There is no corporate tax. Accenture pays taxes in every country it operates. By setting up the holding company in Bermuda, it avoids the double taxation that it would be subject to if it established headquarters in the same jurisdiction as one of its operating entities.
Accenture bashers perpetuate the myth that the company is banned from doing business in California. Not true. The treasurer of the state of California compiled a list of a dozen companies he believed had relocated from the United States through corporate inversion, a term that refers to re-incorporating overseas in order to reduce taxes on income earned from foreign sources.
Stanley Works, Ingersoll-Rand, Seagate Technology, Foster Wheeler and Fruit of the Loom were among companies on the list. So, mistakenly, was Accenture. Accenture had never been a US corporation and did not relocate.
In any case, the treasurer's list had no effect on the business of any of these companies in California. Subsequently, the state legislature considered a law banning companies that had done a corporate inversion from doing business in California. The legislation was never passed and no such law has ever been enacted.
Accenture critics like to cite the NDP-appointed Ontario provincial auditor who has found fault with a welfare-delivery system the company installed nearly four years ago. But his allegations of high costs and performance failures fly in the face of results of an independent third-party audit of the system that concluded it has delivered $692 million in savings. It further confirmed projected savings of $300 million a year over five years.
What's more, installing the new system was a benefits-based deal, meaning Accenture was paid on performance and measurable savings. No savings, no payment.
Accenture transformed a hodge-podge of eight separate systems that did not share data or operate in real time into one the Ontario government says has been an unqualified success, delivered on time and within budget (Accenture shaved $20 million from the $285 million the Ontario government had allocated). Since it was installed, the new welfare system has handled 3.8 million callers through an automated telephone system.
B.C. Hydro has one of the highest debt burdens of all utilities in Canada, with a debt-to-capital ratio of 80 per cent, according to Dominion Bond Rating Service Ltd., the Toronto-based debt-rating agency. It has not invested in any significant new generating capacity in more than a decade.
The utility also has one of the highest government levy burdens, with 60 to 90 per cent of annual operating earnings returned to the government through taxes, water-rental fees, debt guarantees, fees and dividend payments.
B.C. Hydro is a low-cost producer of electricity, but that's not the reason power costs to consumers are low. The government has imposed a rate freeze since 1997 and, in fact, rates have not increased since 1993. When they do, as they must, critics will inevitably blame Accenture.
Related News
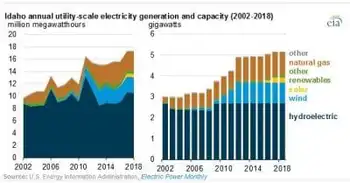
Idaho gets vast majority of electricity from renewables, almost half from hydropower
BOISE - Idaho Renewable Energy 2018 saw over 80% in-state utility-scale power from hydropower, wind, solar, biomass, and geothermal, per EIA, with imports declining as Snake River Plain resources and Hells Canyon hydro lead.
Key Points
Idaho produced over 80% in-state power from renewables in 2018, led by hydropower, wind, solar, and biomass.
✅ Hydropower supplies about half of capacity; Hells Canyon leads.
✅ Wind provides nearly 20% of capacity along the Snake River Plain.
✅ Utility-scale solar surged since 2016; biomass and geothermal add output.
More than 80% of Idaho’s in-state utility-scale electricity generation came from renewable…




