What is the Function of Transformer?
By Howard Williams, Assocaite Editor

Substation Maintenance Training
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our OSHA 4475 Fact Sheet – Being Aware of Arc Flash Hazards

- Identify root causes of arc flash incidents and contributing conditions
- Apply prevention strategies including LOTO, PPE, and testing protocols
- Understand OSHA requirements for training and equipment maintenance
The function of a transformer is to convert voltage levels in AC circuits, enabling efficient transmission, distribution, and utilization of electrical energy while improving safety, reducing losses, and supporting reliable performance in power systems.
What is the function of a transformer?
✅ Converts voltage levels in AC circuits for efficient energy transfer
✅ Enables safe power transmission and distribution in electrical systems
✅ Reduces energy losses and supports stable performance in applications
Transformers are essential electrical devices that play a crucial role in the transmission and distribution of electrical energy. By converting alternating current (AC) and adjusting voltage levels, they ensure efficient and safe delivery of power over long distances. Our Utility Transformers Channel offers in-depth guides on types, applications, and best practices for maintaining these transformers.
A transformer is designed to change the voltage levels of alternating current (AC) in electrical systems. Its primary function is to convert AC from one voltage level to another, either by increasing the voltage (step up) or decreasing it (step down). This voltage transformation is achieved through electromagnetic induction, allowing for efficient energy transfer and minimizing losses during transmission. The AC transformer is the most common form, since only alternating current can create the changing magnetic field required for induction. There’s no such thing as a “DC transformer” — DC-DC converters fill that role in direct current systems.
Why Do We Need to Change Voltage Levels in Electrical Systems?
Changing voltage levels in electrical systems is necessary for several reasons:
-
Transmission Efficiency: High voltage is used to transmit electrical energy over long distances because it reduces the current, thereby minimizing energy losses due to resistance in the lines.
-
Safety and Compatibility: Electrical devices require specific voltage levels to operate safely. Stepping down the transmission voltage makes electricity compatible with homes, businesses, and industrial equipment.
-
Grid Management: Different parts of the electrical grid operate at various voltage levels. Transformers enable the interconnection of these sections while maintaining a stable and reliable power supply.
Modern condition monitoring enables the early detection of transformer faults, thereby improving lifespan and performance.
Electricity Today T&D Magazine Subscribe for FREE

- Timely insights from industry experts
- Practical solutions T&D engineers
- Free access to every issue
How Do Transformers Work?
Transformers work on the principle of electromagnetic induction, discovered by Michael Faraday. When AC flows through the primary winding, it creates a changing magnetic field in the core. This field induces a voltage in the secondary winding, proportional to the turns ratio.
-
An alternating current in the primary winding creates a changing magnetic field.
-
The field induces a voltage in the secondary winding.
-
The turns ratio determines whether voltage is stepped up or stepped down.
This allows electrical energy to transfer efficiently between circuits, adjusting voltage without moving parts and while maintaining electrical isolation. The process conserves energy: as voltage increases, current decreases, and vice versa.
Voltage Transformation and Turns Ratio
The turns ratio — the relationship between the number of turns in the primary and secondary coils — determines the output voltage.
-
Step-Up Transformers: Increasing the number of turns in the secondary raises the voltage for efficient long-distance transmission.
-
Step-Down Transformers: Fewer turns in the secondary, lower voltage for safe local distribution.
For example, doubling the number of secondary turns doubles the output voltage, while halving the turns halves it. This simple yet powerful principle enables transformers to optimize voltage regulation, conserve energy, and ensure reliable performance across transmission and distribution networks.
The Anatomy of a Transformer
Transformers contain several essential components that work together for safe and efficient performance:
-
Core: Laminated silicon steel directs magnetic flux while minimizing eddy currents and hysteresis losses.
-
Primary Winding: Connected to the power source, generating the magnetic field.
-
Secondary Winding: Receives the induced voltage and supplies the load.
-
Insulation: Oil, resin, or paper systems prevent shorts and manage heat.
-
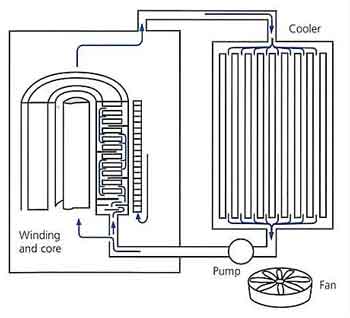
Cooling Mechanisms: Oil cooling or air/cast resin cooling dissipates heat during operation.
-
Components, including bushings, tap changers, and protective devices, help regulate performance under load.
Explore the Construction of a Transformer to understand how cores, windings, and insulation work together for efficient voltage transformation.
Types of Transformers and Their Applications
Transformers come in many forms, each serving specialized roles in electrical systems:
-
Step-Up Transformers: Increase generator voltage for efficient long-distance transmission.
-
Step-Down Transformers: Reduce voltage for safe use in residential, commercial, and light industrial applications.
-
Isolation Transformers: Provide electrical isolation between circuits, improving safety and reducing noise in sensitive electronics.
-
Autotransformers: Use a single winding to deliver variable voltage adjustments in compact, efficient designs.
-
Current Transformers (CTs): Scale high currents for safe measurement and protection.
-
Potential Transformers (PTs): Reduce high voltages to measurable levels for meters and relays.
-
Instrument Transformers: Combined CTs and PTs for substation monitoring and relay protection.
-
Dry-Type Transformers: Air- or resin-cooled, fire-safe for indoor or institutional applications.
Together, these categories support efficient power transmission, safe distribution, reliable metering, and industrial voltage control.
What Are the Key Advantages of Using Transformers in Electrical Systems?
They offer several key advantages in electrical systems:
-
Key Advantages of Transformers
Transformers deliver several critical benefits to modern electrical systems:
-
Efficient Power Transmission: Stepping up the voltage reduces I²R losses across long distances.
-
Safety: Provides electrical isolation, protecting users and equipment from dangerous voltages.
-
Flexibility: Supports multiple voltage levels across different parts of the grid and in industrial control systems.
-
Cost-Effectiveness: No moving parts → low maintenance, long service life.
-
Voltage Regulation: Maintains a stable output even when load conditions fluctuate.
-
Energy Efficiency: With advanced core design and insulation, transformers can achieve efficiencies above 98%.
The function of a transformer is to convert AC and adjust voltage levels to ensure efficient, safe, and reliable transmission of electrical energy. By leveraging electromagnetic induction, high-efficiency materials, and specialized designs, transformers minimize losses, protect equipment, and ensure the continued operation of global power systems. From step-up units in power plants to step-down devices in neighbourhoods and isolation transformers in sensitive electronics, they remain indispensable to both the electrical grid and industrial applications.
Sign Up for Electricity Forum’s Utility Transformers Newsletter
Stay informed with our FREE Utility Transformers Newsletter — get the latest news, breakthrough technologies, and expert insights, delivered straight to your inbox.