What is an arc flash boundary?
What is an arc flash boundary? It is the NFPA 70E-defined safe working distance where incident energy reaches 1.2 cal/cm², dictating PPE selection, approach limits, arc flash labeling, and electrical safety procedures for energized equipment.
What Is an Arc Flash Boundary?
The arc flash boundary is the NFPA 70E distance where 1.2 cal/cm² incident energy requires PPE and controls.
✅ Defined by NFPA 70E based on incident energy analysis
✅ Requires PPE, signage, and energized work permits inside boundary
✅ Adjusted by fault current, clearing time, and working distance
The term arc flash boundary may sound like technical jargon, but its meaning and evolution have been crucial in shaping modern electrical safety practices. While it’s now a defined safety zone in NFPA 70E and CSA Z462, its origins and significance have a deeper story rooted in the effort to prevent catastrophic workplace injuries. For a plain-language primer on concepts and terminology, the Arc Flash Boundary overview outlines definitions, history, and key safety implications.
Historical Development of the Term
Before the adoption of NFPA 70E, the concept of arc flash hazards received little formal recognition in workplace safety programs. Electrical safety focused primarily on shock hazards, with boundaries defined only in terms of approach distances to energized conductors. To understand how both thermal and shock boundaries are set, see the guide to determining arc flash and electric shock protection boundaries for methodology and examples.
That began to change in the 1990s, as awareness grew around the dangers of arc flash — high-energy explosions caused by electrical faults. Researchers, particularly those involved in IEEE 1584, helped quantify the risks and the amount of incident energy workers could be exposed to during such events. For engineers performing studies, the arc flash boundary calculation resource details equations, assumptions, and data inputs.
With the 2000 publication of NFPA 70E, the arc flash boundary was formally introduced as a critical protection zone — defined as the distance at which a worker could receive 1.2 cal/cm² of incident energy, the threshold for a second-degree burn. In 2015 and later updates, this definition was refined, and emphasis shifted from rigid tables to calculated boundaries based on incident energy analysis, incorporating real-world equipment and system data. When quick lookups are needed, the incident energy boundary table can help verify results and inform PPE selection.
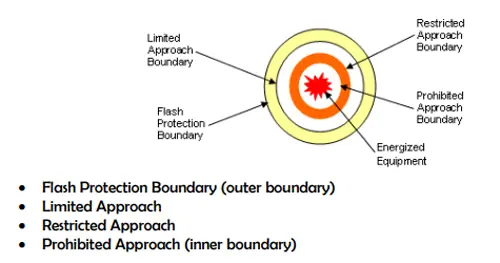
CSA Z462, Canada's parallel standard, adopted similar language and principles, aligning the term across North America and reinforcing its use in both industrial and commercial environments. This alignment also clarifies distinctions from the Limited Approach Boundary, which addresses shock hazards under separate criteria.
Why Does It Matter?
For electrical workers, knowing where the arc flash boundary lies is not theoretical — it’s life-saving. This boundary determines when and where personal protective equipment (PPE) is required and defines safe work distances. It shapes:
-
Job planning and risk assessment
-
The selection of arc-rated clothing and equipment
-
Decisions about energized vs de-energized work
-
Signage, labeling, and physical barriers in the field
In day-to-day tasks like opening panels or performing diagnostics, the arc flash boundary informs whether a worker must don a full arc-rated suit or can proceed with minimal PPE. It also supports supervisors and safety coordinators in enforcing compliant work procedures. For field implementation, the guidance on marking off arc flash boundaries covers labeling, barricades, and temporary controls.
In short, it translates complex hazard calculations into clear, actionable field instructions that protect lives.
Common Misconceptions About Arc Flash Boundaries
Despite its widespread use, the term still carries confusion. Here are a few common misconceptions:
-
“It’s the same as the Limited Approach Boundary.”
False. The Limited Approach Boundary addresses shock hazards. The Arc Flash Boundary relates specifically to thermal energy exposure. -
“All arc flash boundaries are 18 inches.”
Not true. While 18 inches is a common working distance for calculating incident energy, arc flash boundaries vary depending on system voltage, fault current, clearing time, and equipment condition. Practitioners often consult the arc flash boundary chart to visualize how these variables shift distance across equipment types. -
“If I’m outside the arc flash boundary, I don’t need to worry.”
That’s misleading. While PPE may not be required beyond the boundary, awareness and training are still critical. Arc blast pressure, flying debris, and indirect injuries remain possible. -
“Once labeled, a boundary never changes.”
Incorrect. Labels must be updated after system changes, new hazard analyses, or NFPA/CSA standard updates. Assumptions based on outdated data can be dangerous.
The arc flash boundary is more than a technical term — it is a dynamic tool born out of decades of research and tragedy. Its importance continues to grow as electrical systems evolve and safety regulations adapt. By understanding where it came from, what it means, and how to apply it, we can bridge the gap between compliance and true workplace safety.
Would you like a new meta title and description for this updated version?
Visit our Arc Flash Boundary main page for more detailed information on calculating boundaries, protection zones, compliance requirements, and real-world application examples.
Related Articles
On-Site Training
Interested in cost effective, professional on-site electrical training?
We can present an Electrical Training Course to your electrical engineering and maintenance staff, on your premises, tailored to your specific equipment and requirements. Click on the link below to request a Free quotation.
EF PARTNER MEDIA
Product Showcases
Shared Media
















