DC Motor Speed Control
Motor Control Training
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our OSHA FS3529 Fact Sheet – Lockout/Tagout Safety Procedures

- Learn how to disable machines and isolate energy sources safely
- Follow OSHA guidelines for developing energy control programs
- Protect workers with proper lockout devices and annual inspections
DC motor speed control adjusts rotational speed using voltage variation, PWM, or feedback systems. Essential for automation, robotics, and precise motor performance. Ensures efficient torque control and enhances application reliability.
What is: DC Motor Speed Control?
DC motor speed control is the method of regulating the speed of a direct current motor to suit specific application needs.
✅ Enables precise control for automation, conveyors, and robotics
✅ Uses methods like PWM, voltage regulation, and feedback loops
✅ Improves energy efficiency and extends motor lifespan
Electric Motor Testing Training
Request a Free Training Quotation
Understanding how to regulate the speed of these motors precisely is essential for optimizing performance, efficiency, and safety across a wide range of applications. Let's delve into the core concepts, equipping electricians with the knowledge to manage and troubleshoot these systems effectively. From the fundamentals of Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) to the intricacies of feedback adjustment and torque management, readers will gain valuable insights into the factors that influence motor speed and the techniques for achieving precise control. To understand how speed regulation fits into broader motor systems, see our guide on electric motor control, which covers the fundamentals of managing torque, current, and direction.
Comparison of DC Motor Speed Modulation Methods
| Control Method | How It Works | Advantages | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage Control | Adjusts the supply voltage to vary motor speed | Simple, low cost, easy to implement | Small DC fans, toys, low-power systems |
| Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) | Modulates the duty cycle of voltage pulses | High efficiency, minimal power loss, precise regulation | Robotics, automation, EVs, CNC machines |
| Armature Resistance Control | Inserts a variable resistor in the armature circuit | Basic speed variation, low-tech option | Educational setups, legacy systems |
| Field Flux Control | Alters the field current to change the speed and torque characteristics | Useful for wide speed ranges, and torque regulation is possible | Industrial drives, hoists, elevators |
| Closed-Loop Feedback | Uses encoders or tachometers to maintain the desired speed | High accuracy, adaptive to load changes | Servo systems, robotics, precision tools |
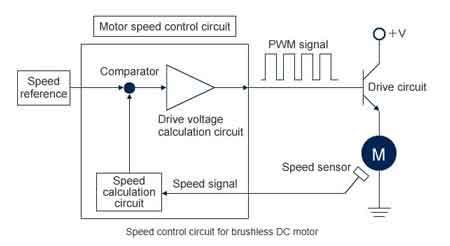
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation)
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) reigns supreme as the most common and efficient method for adjusting the speed of DC motors. Instead of providing a constant flow of power, PWM delivers a series of rapid on-off pulses. By adjusting the width of these pulses, the average voltage delivered can be precisely controlled, thus regulating speed. This technique offers numerous advantages, including high efficiency, minimal heat generation, and the ability to achieve fine-grained speed adjustments. When precise speed control is needed in HVAC or industrial systems, consider the role of a variable frequency drive (VFD) in optimizing AC motor performance.
Electricity Today T&D Magazine Subscribe for FREE

- Timely insights from industry experts
- Practical solutions T&D engineers
- Free access to every issue
Motor Drivers/Controllers
Think of motor drivers/controllers as the translators between the PWM signal and the DC motor itself. These electronic circuits receive the PWM signal and convert it into the appropriate voltage and current levels required to drive the motor. They often incorporate features like direction modulation, current limiting, and protection against overloads, ensuring safe and reliable operation. Selecting the right motor driver depends on factors such as size, voltage requirements, and the specific application's demands. For deeper insight into how motor structure affects control strategies, visit our page on electric motor design and its influence on speed and torque behavior.
Feedback Control
Maintaining a consistent DC motor speed under varying conditions requires constant adjustments, much like driving a car at a steady speed on a hilly road without a speedometer. Feedback modulation mechanisms, such as encoders or tachometers, provide the necessary information to achieve this stability. These devices measure the actual speed and feed this data back to the controller, which then dynamically adjusts the PWM signal to compensate for any deviations. This ensures accurate and stable speed regulation, even when faced with fluctuating loads or other external factors.
Torque Control
While speed often takes center stage, controlling torque is equally crucial in many applications. Torque, the rotational force produced, directly impacts a motor's ability to accelerate, overcome inertia, and handle varying loads. Managing torque alongside speed is particularly important in applications like robotics, where precise movements and force control are essential. Advanced speed control systems often incorporate torque modulation features, allowing for fine-tuned management of both parameters.
Types of DC Motors
DC motors come in various forms, each with unique characteristics that influence their speed control requirements. Brushed DC motors, with their internal commutators and brushes, are relatively simple but require periodic maintenance. Brushless DC motors, on the other hand, offer higher efficiency and longevity but necessitate more complex control electronics. Understanding the nuances of different motor types is vital for selecting the appropriate speed management strategy. For instance, permanent magnet DC motors, known for their high efficiency and compact size, are commonly found in applications where precise speed control is paramount.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does a DC motor speed regulation work?
It regulates the voltage or current supplied, thereby adjusting its speed. This is often achieved through techniques like Pulse Width Modulation (PWM), where the controller varies the width of voltage pulses to adjust the average voltage delivered. If you’re just starting to explore the field, our overview of how electric motors work offers a solid foundation for understanding speed modulation principles.
What are the common methods of controlling DC motor speed?
Besides PWM, other methods include using variable resistors (rheostats), voltage regulators, and specialized motor driver circuits. However, PWM has become the most prevalent due to its efficiency and precision.
What factors affect the speed of a DC motor?
Several factors influence DC motor speed, including the applied voltage, the load, and the motor's internal characteristics (such as the strength of the magnetic field and the number of windings).
What are the advantages of using PWM?
PWM offers several advantages:
-
High Efficiency: Minimal energy is wasted as heat, leading to greater efficiency.
-
Precise Modulation: Allows for fine-grained speed adjustments.
-
Reduced Motor Stress: Smooth speed transitions minimize wear and tear.
Can DC motor speed modulation affect torque, and how can it be managed?
Yes, some constant speed control methods in ac motors can inadvertently reduce torque, especially at lower speeds. To mitigate this, advanced controllers incorporate torque regulation features that allow for independent management of both speed and torque, ensuring optimal performance across the entire speed range.
Test Your Knowledge About Motors and Drives!
Think you know Motors and Drives? Take our quick, interactive quiz and test your knowledge in minutes.
- Instantly see your results and score
- Identify strengths and areas for improvement
- Challenge yourself on real-world electrical topics
It is crucial for optimizing motor performance in industrial settings. By understanding techniques like PWM, motor drivers, and feedback modulation, electricians can ensure precise and efficient operation. Recognizing the interplay between speed and torque is also vital for applications demanding accurate motion tuning. This knowledge empowers electricians to manage and troubleshoot diverse DC motor systems effectively, maximizing their performance and lifespan. Enhancing system performance goes beyond speed adjustment—proper electric motor maintenance ensures long-term reliability and efficiency.
Related Articles








