Checking Insulation Resistance
High Voltage Maintenance Training Online
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our OSHA 4474 Fact Sheet – Establishing Boundaries Around Arc Flash Hazards

- Understand the difference between arc flash and electric shock boundaries
- Learn who may cross each boundary and under what conditions
- Apply voltage-based rules for safer approach distances
Checking insulation resistance ensures safe operation of electrical systems by detecting moisture, degradation, or leakage currents. It’s essential for preventing equipment failure and maintaining high dielectric quality in cables, motors, and switchgear.
Why Are We Checking Insulation Resistance?
Checking insulation resistance is the process of testing electrical insulation to ensure reliability, prevent shock hazards, and maintain system performance. It:
✅ Detects moisture, aging, or breakdown in insulation
✅ Prevents electrical failures and equipment hazards
✅ Commonly used on motors, cables, and switchgear
Regular dielectric resistance testing is a crucial component of maintaining the integrity and safety of electrical insulation systems. This testing helps identify potential issues such as short circuits or degraded non-conductive material that could lead to failures. By performing these tests as part of a preventive maintenance routine, facilities can ensure that their systems operate efficiently and safely. To perform accurate IR testing, it's essential to use a reliable insulation resistance tester designed specifically for assessing the health of dielectric materials in motors, cables, and electrical panels.
What is the purpose of checking insulation resistance in electrical systems?
The primary purpose of conducting an insulation resistance (IR) test is to assess the condition of the electrical insulation protecting conductors and components within a system. Over time, the insulating layer can degrade due to factors such as environmental stress, aging, and exposure to moisture, which can result in short circuits or reduced system efficiency. By identifying potential weaknesses in the insulation, maintenance teams can take proactive measures to prevent unexpected failures and ensure the ongoing reliability of their electrical systems.
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) standard 43, "Recommended Practice for Testing Insulation Resistance of Electric Machinery," advises that all resistance readings be adjusted to a standardized temperature of 40°C (104°F). This consistent temperature provides a reliable baseline, allowing for meaningful historical comparisons over time. Discover the importance of preventive maintenance in prolonging equipment life and preventing costly failures caused by dielectric material breakdown.
Sign Up for Electricity Forum’s Test Equipment Newsletter
Stay informed with our FREE Test Equipment Newsletter — get the latest news, breakthrough technologies, and expert insights, delivered straight to your inbox.
What are the steps when checking insulation resistance?
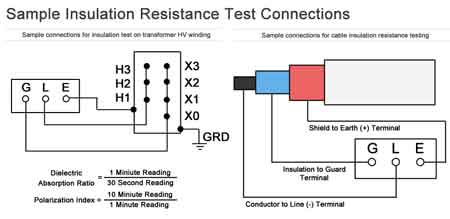
The process of conducting an IR test begins by ensuring that the equipment being tested is de-energized to prevent accidents. After verifying that the system is safe to work on, insulation resistance testers are used to apply a specified test voltage across the dielectric material. The resistance measurements obtained during the test provide valuable insight into the condition of the insulation. Additionally, a polarization index (PI) test may be performed, which involves taking two separate measurements—one after 60 seconds and another after 10 minutes—to assess the dielectric absorption capabilities of the protective coating. The test results are then compared to industry standards or historical data for the specific equipment.
What are acceptable insulation resistance values for different types of electrical equipment?
Acceptable values for an IR test vary depending on the type of equipment and the system voltage. Typically, higher resistance measurements indicate better dielectric quality, with megohm values often used as the benchmark. For example, large industrial motors or high-voltage transformers may require a minimum of 1 megohm per kilovolt of operating voltage. However, the test results need to be interpreted in context, considering factors such as the age of the equipment and the environment in which it operates. As part of a predictive maintenance strategy, our electric motor testing guide explains how insulation resistance measurements can reveal early-stage deterioration in windings.
How often should insulation resistance be checked?
The frequency of insulation resistance testing depends on the critical nature of the equipment and its operating conditions. For critical infrastructure, testing should be performed as part of a regular preventive maintenance schedule, typically once a year or more frequently if the equipment is exposed to harsh environments. High-voltage systems and those operating in wet or dusty conditions may require more frequent testing to ensure the dielectric material remains intact and effective.
Key Factors in Checking Insulation Resistance
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Purpose of IR Testing | Detect degradation, moisture intrusion, aging, and leakage paths |
| Test Instrument | Insulation Resistance Tester |
| IEEE Standard Reference | IEEE Std 43 – Test values normalized to 40°C (104°F) for consistency |
| Minimum Resistance Values | ≥1 MΩ per kV of rated voltage (e.g., 5 kV = 5 MΩ minimum) |
| Test Voltage Range | 500 V to 5,000 V DC (varies by equipment type and voltage class) |
| Test Types | Spot Reading, Time-Resistance Method, Polarization Index (PI) |
| PI Ratio (10-min / 1-min reading) | ≥2.0 (good insulation), 1.0–2.0 (marginal), <1.0 (potential issue) |
| Frequency of Testing | Annually or more often in harsh, high-voltage, or mission-critical systems |
| Environmental Influences | Temperature, humidity, contamination, equipment age |
| Common Applications | Motors, generators, cables, switchgear, transformers |
What factors can affect the accuracy of insulation resistance test results?
Several factors can influence the accuracy of an insulation resistance IR test. Temperature, humidity, and contamination can cause fluctuations in resistance measurements, leading to inaccurate assessments. For instance, moisture can lower the resistance value, suggesting degradation when the actual issue is environmental in nature. Similarly, the age of the equipment and the condition of the dielectric material can also impact test outcomes. Properly accounting for these variables during testing ensures that the test results accurately reflect the insulation's condition. IR testing is just one of many procedures outlined in our comprehensive electrical testing resource, which covers the key tools and methods used in field diagnostics.
Insulation resistance testing is a critical component of electrical system maintenance. By regularly performing IR tests and carefully analyzing the test results, maintenance teams can identify potential issues before they result in costly failures. Ensuring that equipment is properly de-energized and following standardized procedures for testing helps achieve accurate and reliable measurements, ultimately improving the longevity and safety of the electrical system.
Related Articles








