Control Transformer Explained

Substation Relay Protection Training
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our OSHA 4474 Fact Sheet – Establishing Boundaries Around Arc Flash Hazards

- Understand the difference between arc flash and electric shock boundaries
- Learn who may cross each boundary and under what conditions
- Apply voltage-based rules for safer approach distances
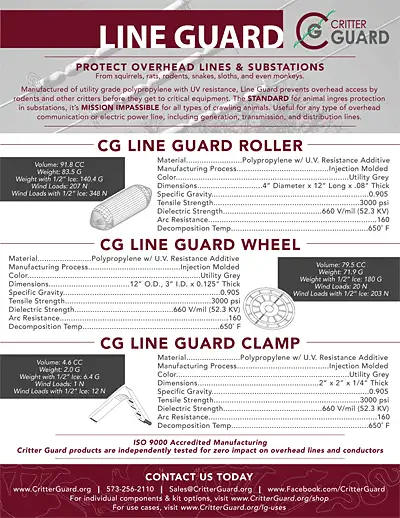
A control transformer provides a stable voltage to control circuits in industrial and commercial applications. It ensures reliable performance of contactors, relays, and motor starters by stepping down line voltage for safe, consistent control system operation.
What is a Control Transformer?
A control transformer is a type of transformer used to supply voltage to control devices in electrical systems.
✅ Provides consistent voltage for control circuits and devices
✅ Supports relays, contactors, timers, and PLCs
✅ Ideal for industrial machines and automation systems
Electrical Transformer Maintenance Training
Substation Maintenance Training
Request a Free Training Quotation
It is designed to provide a stable voltage for control circuits in various applications. This equipment reduces the supply voltage to a lower, more manageable level, suitable for controlling machinery and other electrical devices. Typically, the primary voltage is high, while the secondary voltage is lower, providing the necessary power for systems without compromising safety. Unlike a current transformer, which is used for measurement and protection, a control transformer focuses on delivering reliable voltage for circuits.
The working principle of these units is straightforward. When alternating current flows through the primary winding, it creates a magnetic field that induces a current in the secondary winding. This induced current has a lower voltage, specifically tailored to the needs of control circuits, ensuring consistent and reliable operation of the equipment. For a broader context on energy regulation, see our overview of what is a transformer, which explains how these devices manage voltage in power and systems.
Understanding The Control Transformer
Control transformers are specifically designed to step down the higher voltage from the main power supply to a lower, safer voltage level suitable for control circuits. These circuits are responsible for operating various devices such as relays, contactors, solenoids, and other equipment. Many industrial facilities also pair control transformers with dry type transformers, which offer durability and safety in environments where oil-filled designs are not suitable.
Test Your Knowledge About Electrical Transformers!
Think you know Electrical Transformers? Take our quick, interactive quiz and test your knowledge in minutes.
- Instantly see your results and score
- Identify strengths and areas for improvement
- Challenge yourself on real-world electrical topics
These devices typically operate at lower voltages, usually between 24V and 240V. Control power transformers provide the necessary voltage transformation to ensure the safe and efficient operation of these types of circuits. Discover how step down transformers safely reduce voltage, a principle commonly applied in most control transformer designs for circuit protection.
Construction and Design
Control power transformers are typically constructed with a laminated steel core and two or more windings. The primary winding is connected to the main power supply, while the secondary winding provides the lower voltage output for the circuits.
The design considers various factors, including the required secondary voltage, power rating, and insulation requirements. They are often designed to withstand harsh industrial environments and offer protection against short circuits and overloads.
Key Features and Benefits
They offer several features and benefits that make them indispensable in industrial settings:
-
Safety: The primary function is to provide a safe voltage level for circuits, protecting personnel and equipment from electrical hazards.
-
Reliability: These units are designed to be rugged and reliable, ensuring consistent power delivery to circuits even in demanding conditions.
-
Efficiency: They are engineered to be highly efficient, minimizing energy losses and reducing operating costs.
-
Versatility: They are available in a wide range of voltage and power ratings, making them suitable for various industrial applications.
-
Compact Design: Many units are designed to be compact and space-saving, making them easy to install in confined spaces.
Key Differences Between a Control Transformer and a Power Transformer
While both types serve to transfer electrical energy from one circuit to another, they are distinct in their applications and design. Control power transformers are primarily used to supply power to circuits, whereas power transformers are designed for high-voltage transmission and distribution in electrical grids. Understand different types of devicess to see how they fit into the broader equipment ecosystem, including power, potential, and isolation types.
One key difference lies in the voltage regulation. They offer better voltage regulation, which is crucial for sensitive circuits that require a stable and precise secondary voltage. In contrast, power transformers are optimized for efficiency and capacity, often dealing with much higher power levels.
Additionally, they are designed to handle inrush currents that occur when control devices, such as relays and solenoids, are activated. This ability to manage sudden surges in current makes them ideal for industrial environments where control stability is paramount. If you’re comparing applications, our page on power transformers contrasts with control transformers by focusing on high-voltage transmission and grid distribution.
Typical Applications
Control transformers are widely used in various industrial settings. Some of the typical applications include:
-
Machine Tool: These units provide stable voltage to control circuits in machine tools, ensuring precise operation and safety.
-
HVAC Systems: These systems utilize electrical components to power circuits that regulate temperature and airflow in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.
-
Lighting: In commercial and industrial lighting systems, they help manage the circuits for switching and dimming lights.
-
Motors: They are essential in motor centers, providing the necessary voltage for relays and contactors that start and stop motors.
For comparison, an isolation transformer provides electrical separation and safety, whereas a control transformer specializes in stable voltage regulation for control equipment.
Selecting the Right One
Choosing the appropriate device requires careful consideration of several factors:
-
Voltage Requirements: Determine the primary and secondary voltage levels needed for your application. The secondary voltage should match the requirements of the circuit.
-
Power Rating: Assess the power demand of the circuit and select a unit that can handle the load. The power rating is usually specified in volt-amperes (VA).
-
Inrush Current: Consider the inrush current capacity, especially if the circuit includes components such as relays or solenoids that draw high currents at startup.
-
Environmental Conditions: Ensure the unit is suitable for the operating environment, considering factors such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to dust or chemicals.
-
Regulation and Efficiency: Choose a unit that offers good voltage regulation and efficiency to ensure reliable performance.
For a more detailed look at specialized devices, visit our page on the potential transformer, which also converts voltage but for measurement purposes.
FREE EF Electrical Training Catalog
Download our FREE Electrical Training Catalog and explore a full range of expert-led electrical training courses.

- Live online and in-person courses available
- Real-time instruction with Q&A from industry experts
- Flexible scheduling for your convenience
Common Issues and Troubleshooting Steps
Despite their robustness, they can encounter issues. Some common problems include:
-
Overheating: This can occur due to excessive load or poor ventilation. To address this, ensure the device is not overloaded and that it has adequate cooling.
-
Voltage Fluctuations: Inconsistent secondary voltage can result from poor connections or a failing unit. Check all connections and replace the equipment if necessary.
-
Short Circuits: A short circuit in the circuit can cause the unit to fail. Inspect the circuit for faults and repair any damaged components.
-
Noise: Unusual noises often indicate loose laminations or hardware. Tighten any loose parts and ensure the device is securely mounted.
A control transformer is vital in industrial settings, providing stable and reliable voltage to circuits. Understanding their working principles, applications, and differences from power transformers is crucial for selecting the right equipment for your needs. By addressing common issues and following proper troubleshooting steps, you can ensure the longevity and efficiency of your industrial systems, maintaining their smooth operation. Discover how transformer systems operate in real-world applications with our comprehensive resource on what is a transformer, which explains their design, function, and industrial applications.
Related Articles