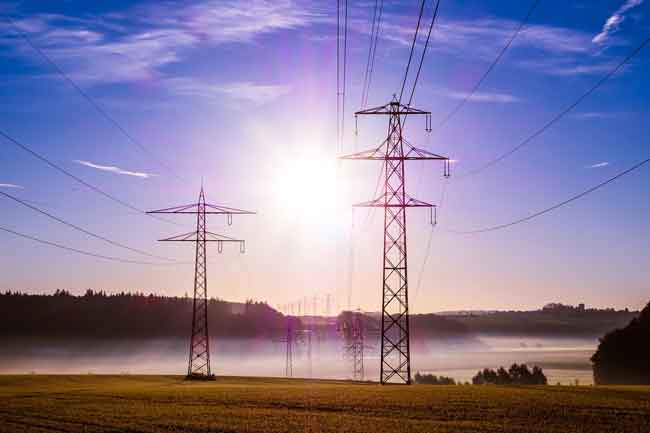
Norway opens worldÂ’s first osmotic power plant
State-owned utility Statkraft's prototype plant, which for now will produce a tiny 2-4 kilowatts of power or enough to run a coffee machine, will enable Statkraft to test and develop the technology needed to drive down production costs.
The plant is driven by osmosis that naturally draws fresh water across a membrane and toward the seawater side. This creates higher pressure on the seawater side, driving a turbine and producing electricity.
"While salt might not save the world alone, we believe osmotic power will be an interesting part of the renewable energy mix of the future," Statkraft Chief Executive Baard Mikkelsen told reporters.
Statkraft, Europe's largest producer of renewable energy with experience in hydropower that provides nearly all of Norway's electricity, aims to begin building commercial osmotic power plants by 2015.
The main issue is to improve the efficiency of the membrane from around 1 watt per square meter now to some 5 watts, which Statkraft says would make osmotic power costs comparable to those from other renewable sources.
The prototype, on the Oslo fjord and about 60 km (40 miles) south of the Norwegian capital, has about 2,000 square meters of membrane.
Future full-scale plants producing 25 MW of electricity, enough to provide power for 30,000 European households, would be as large as a football stadium and require some 5 million square meters of membrane, Statkraft said.
Once new membrane "architecture" is solved, Statkraft believes the global production capacity for osmotic energy could amount to 1,600-1,700 TWh annually, or about half of the European Union's total electricity demand.
Europe's osmotic power potential is seen at 180 TWh, or about 5 percent of total consumption — which could help the bloc reach renewable energy goals set to curb emissions of heat-trapping gases and limit global warming.
Osmotic power, which can be located anywhere where clean fresh water runs into the sea, is seen as more reliable than more variable wind or solar energy.
A summit in Copenhagen next month is due to agree on a UN pact to combat climate change by promoting clean energies and a shift from fossil fuels that a UN scientific panel blames for stoking heatwaves, floods, droughts and rising seas.
Related News

Energy Ministry may lower coal production target as Chinese demand falls
JAKARTA - The Energy and Mineral Resources (ESDM) Ministry is considering lowering the coal production target this year as demand from China has shown a significant decline since the start of the outbreak of the novel coronavirus in the country late last year, a senior ministry official has said.
The ministry’s coal and mineral director general Bambang Gatot Ariyono said in Jakarta on March 12 that the decline in the demand had also caused a sharp drop in coal prices on the world market, which could cause the country’s miners to reduce their production.
The 2020 minerals and coal mining program and…