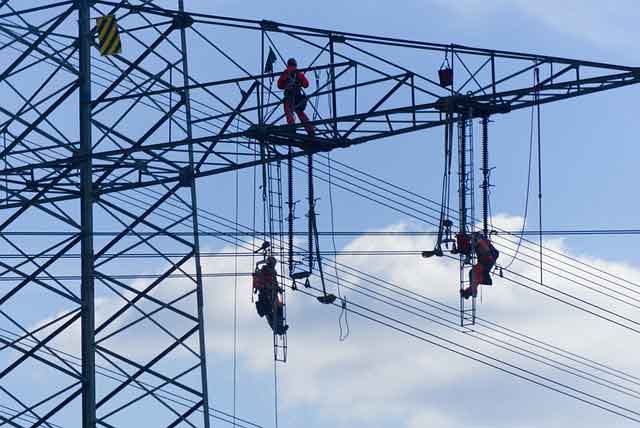
Electricity alert ends after Alberta forced to rely on reserves to run grid

Electrical Testing & Commissioning of Power Systems
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Alberta Power Grid Level 2 Alert signals AESO reserve power usage, load management, supply shortage from generator outages, low wind, and limited imports, urging peak demand conservation to avoid blackouts and preserve grid reliability.
Key Points
An AESO status where reserves power the grid and load management is used during supply constraints to prevent blackouts.
✅ Triggered by outages, low wind, and reduced import capacity
✅ Peak hours 4 to 7 pm saw conservation requests
✅ Several hundred MW margin from Level 3 load shedding
Alberta's energy grid ran on reserves Wednesday, after multiple factors led to a supply shortage, a scenario explored in U.S. grid COVID response discussions as operators plan for contingencies.
At 3:52 p.m. Wednesday, the Alberta Electric System Operator issued a Level 2 alert, meaning that reserves were being used to supply energy requirements and that load management procedures had been implemented, while operators elsewhere adopted Ontario power staffing lockdown measures during COVID-19 for continuity. The alert ended at 6:06 p.m.
"This is due to unplanned generator outages, low wind and a reduction of import capability," the agency said in a post to social media. "Supply is tight but still meeting demand."
AESO spokesperson Mike Deising said the intertie with Saskatchewan had tripped off, and an issue on the British Columbia side of the border, as seen during BC Hydro storm response events, meant the province couldn't import power.
"There are no blackouts … this just means we're using our reserve power, and that's a standard procedure we'll deploy," he said.
AESO had asked that people reduce their energy consumption between 4 and 7 p.m., similar to Cal ISO conservation calls during grid strain, which is typically when peak use occurs.
Deising said the system was several hundred MWs away from needing to move to an alert Level 3, with utilities such as FortisAlberta precautions in place to support continuity, which is when power is cut off to some customers in order to keep the system operating. Deising said Level 2 alerts are fairly rare and occur every few years. The last Level 3 alert was in 2013.
According to the supply and demand report on AESO's website, the load on the grid at 5 p.m. was 10,643 MW.
That's down significantly from last week, when a heat wave pushed demand to record highs on the grid, with loads in the 11,700 MW range, contrasting with Ontario demand drop during COVID when many stayed home.
A heat warning was issued Wednesday for Edmonton and surrounding areas shortly before 4 p.m., with temperatures above 29 C expected over the next three days, with many households seeing residential electricity use up during such periods.