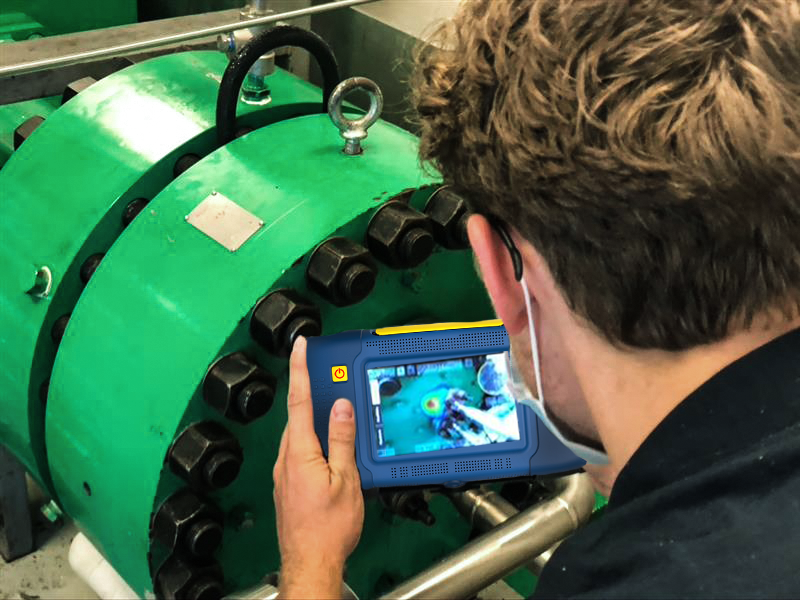
Tackling climate change with machine learning: Covid-19 and the energy transition
Arc Flash Training CSA Z462 - Electrical Safety Essentials
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 6 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Covid-19 Energy Transition and Machine Learning reshape climate change policy, electricity planning, and grid operations, from demand forecasting and decarbonization strategies in Europe to scalable electrification modeling and renewable integration across Africa.
Key Points
How the pandemic reshapes energy policy and how ML improves planning, demand forecasts, and grid reliability in Africa.
✅ Pandemic-driven demand shifts strain grid operations and markets
✅ Policy momentum risks rollback; favor future-oriented decarbonization
✅ ML boosts demand prediction, electrification, and grid reliability in Africa
The impact of Covid-19 on the energy system was discussed in an online climate change workshop that also considered how machine learning can help electricity planning in Africa.
This year’s International Conference on Learning Representations event included a workshop held by the Climate Change AI group of academics and artificial intelligence industry representatives, which considered how machine learning can help tackle climate change and highlighted advances by European electricity prediction specialists working in this field.
Bjarne Steffen, senior researcher at the energy politics group at ETH Zürich, shared his insights at the workshop on how Covid-19 and the accompanying economic crisis are affecting recently introduced ‘green’ policies. “The crisis hit at a time when energy policies were experiencing increasing momentum towards climate action, especially in Europe, and in proposals to invest in smarter electricity infrastructure for long-term resilience,” said Steffen, who added the coronavirus pandemic has cast into doubt the implementation of such progressive policies.
The academic said there was a risk of overreacting to the public health crisis, as far as progress towards climate change goals was concerned.
Lobbying
“Many interest groups from carbon-intensive industries are pushing to remove the emissions trading system and other green policies,” said Steffen. “In cases where those policies are having a serious impact on carbon-emitting industries, governments should offer temporary waivers during this temporary crisis, instead of overhauling the regulatory structure.”
However, the ETH Zürich researcher said any temptation to impose environmental conditions to bail-outs for carbon-intensive industries should be resisted. “While it is tempting to push a green agenda in the relief packages, tying short-term environmental conditions to bail-outs is impractical, given the uncertainty in how long this crisis will last,” he said. “It is better to include provisions that will give more control over future decisions to decarbonize industries, such as the government taking equity shares in companies.”
Steffen shared with pv magazine readers an article published in Joule which can be accessed here, and which articulates his arguments about how Covid-19 could affect the energy transition.
Covid-19 in the U.K.
The electricity system in the U.K. is also being affected by Covid-19, even as the U.S. electric grid grapples with climate risks, according to Jack Kelly, founder of London-based, not-for-profit, greenhouse gas emission reduction research laboratory Open Climate Fix.
“The crisis has reduced overall electricity use in the U.K.,” said Kelly. “Residential use has increased but this has not offset reductions in commercial and industrial loads.”
Steve Wallace, a power system manager at British electricity system operator National Grid ESO recently told U.K. broadcaster the BBC electricity demand has fallen 15-20% across the U.K. The National Grid ESO blog has stated the fall-off makes managing grid functions such as voltage regulation more challenging.
Open Climate Fix’s Kelly noted even events such as a nationally-coordinated round of applause for key workers was followed by a dramatic surge in demand, stating: “On April 16, the National Grid saw a nearly 1 GW spike in electricity demand over 10 minutes after everyone finished clapping for healthcare workers and went about the rest of their evenings.”
Climate Change AI workshop panelists also discussed the impact machine learning could have on improving electricity planning in Africa. The Electricity Growth and Use in Developing Economies (e-Guide) initiative funded by fossil fuel philanthropic organization the Rockefeller Foundation aims to use data to improve the planning and operation of electricity systems in developing countries.
E-Guide members Nathan Williams, an assistant professor at the Rochester Institute of Technology (RIT) in New York state, and Simone Fobi, a PhD student at Columbia University in NYC, spoke about their work at the Climate Change AI workshop, which closed on Thursday. Williams emphasized the importance of demand prediction, saying: “Uncertainty around current and future electricity consumption leads to inefficient planning. The weak link for energy planning tools is the poor quality of demand data.”
Fobi said: “We are trying to use machine learning to make use of lower-quality data and still be able to make strong predictions.”
The market maturity of individual solar home systems and PV mini-grids in Africa mean more complex electrification plan modeling is required, similar to integrating AI data centers into Canada's grids at scale.
Modeling
“When we are doing [electricity] access planning, we are trying to figure out where the demand will be and how much demand will exist so we can propose the right technology,” added Fobi. “This makes demand estimation crucial to efficient planning.”
Unlike many traditional modeling approaches, machine learning is scalable and transferable. Rochester’s Williams has been using data from nations such as Kenya, which are more advanced in their electrification efforts, to train machine learning models to make predictions to guide electrification efforts in countries which are not as far down the track.
Williams also discussed work being undertaken by e-Guide members at the Colorado School of Mines, which uses nighttime satellite imagery and machine learning to assess the reliability of grid infrastructure in India, where new algorithms to prevent ransomware-induced blackouts are also advancing.
Rural power
Another e-Guide project, led by Jay Taneja at the University of Massachusetts, Amherst – and co-funded by the Energy and Economic Growth program on development spending based at Berkeley – uses satellite imagery to identify productive uses of electricity in rural areas by detecting pollution signals from diesel irrigation pumps.
Though good quality data is often not readily available for Africa, Williams added, it does exist.
“We have spent years developing trusting relationships with utilities,” said the RIT academic. “Once our partners realize the value proposition we can offer, they are enthusiastic about sharing their data … We can’t do machine learning without high-quality data and this requires that organizations can effectively collect, organize, store and work with data. Data can transform the electricity sector, as shown by Canadian projects to use AI for energy savings, but capacity building is crucial.”