Duke Energy will spend US$25bn to modernise its US grid

NFPA 70b Training - Electrical Maintenance
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
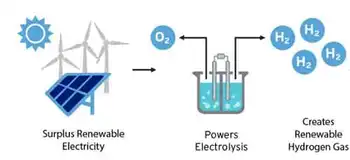
Duke Energy Clean Energy Strategy targets smart grid upgrades, wind and solar expansion, efficient gas, and high-reliability nuclear, cutting CO2, boosting decarbonization, and advancing energy efficiency and reliability for the Carolinas.
Key Points
A plan investing in smart grids, renewables, gas, and nuclear to cut CO2 and enhance reliability and efficiency by 2030.
✅ US$25bn smart grid upgrades; US$11bn renewables and gas
✅ 40% CO2 reduction and >80% low-/zero-carbon generation by 2030
✅ 2017 nuclear fleet 95.64% capacity factor; ~90 TWh carbon-free
The US power group Duke Energy plans to invest US$25bn on grid modernization over the 2017-2026 period, including the implementation of smart grid technologies to cope with the development of renewable energies, along with US$11bn on the expansion of renewable (wind and solar) and gas-fired power generation capacities.
The company will modernize its fleet and expects more than 80% of its power generation mix to come from zero and lower CO2 emitting sources, aligning with nuclear and net-zero goals, by 2030. Its current strategy focuses on cutting down CO2 emissions by 40% by 2030. Duke Energy will also promote energy efficiency and expects cumulative energy savings - based on the expansion of existing programmes - to grow to 22 TWh by 2030, i.e. the equivalent to the annual usage of 1.8 million households.
#google#
Duke Energy’s 11 nuclear generating units posted strong operating performance in 2017, as U.S. nuclear costs hit a ten-year low, providing the Carolinas with nearly 90 billion kilowatt-hours of carbon-free electricity – enough to power more than 7 million homes.
Globally, China's nuclear program remains on a steady development track, underscoring broader industry momentum.
“Much of our 2017 success is due to our focus on safety and work efficiencies identified by our nuclear employees, along with ongoing emphasis on planning and executing refueling outages to increase our fleet’s availability for producing electricity,” said Preston Gillespie, Duke Energy chief nuclear officer.
Some of the nuclear fleet’s 2017 accomplishments include, as a new U.S. reactor comes online nationally:
- The 11 units achieved a combined capacity factor of 95.64 percent, second only to the fleet’s 2016 record of 95.72 percent, marking the 19th consecutive year of attaining a 90-plus percent capacity factor (a measure of reliability).
- The two units at Catawba Nuclear Station produced more than 19 billion kilowatt-hours of electricity, and the single unit at Harris Nuclear Plant generated more than 8 billion kilowatt-hours, both setting 12-month records.
- Brunswick Nuclear Plant unit 2 achieved a record operating run.
- Both McGuire Nuclear Station units completed their shortest refueling outages ever and unit 1 recorded its longest operating run.
- Oconee Nuclear Station unit 2 achieved a fleet record operating run.
The Robinson Nuclear Plant team completed the station’s 30th refueling outage, which included a main generator stator replacement and other life-extension activities, well ahead of schedule.
“Our nuclear employees are committed to providing reliable, clean electricity every day for our Carolinas customers,” added Gillespie. “We are very proud of our team’s 2017 accomplishments and continue to look for additional opportunities to further enhance operations.”