IEA warns fall in global energy investment may lead to shortages
NFPA 70b Training - Electrical Maintenance
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Global Energy Investment Decline risks future oil and electricity supply, says the IEA, as spending on upstream, coal plants, and grids falls while renewables, storage, and flexible generation lag in the energy transition.
Key Points
Multi-year cuts to oil, power, and grid spending that increase risks of future supply shortages and market tightness.
✅ IEA warns underinvestment risks oil supply squeeze
✅ China and India slow coal plant additions; renewables rise
✅ Batteries aid flexibility but cannot replace seasonal storage
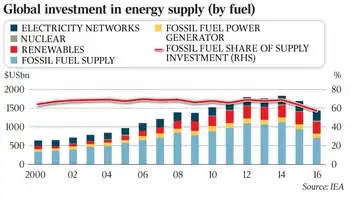
An almost 20 per cent fall in global energy investment over the past three years could lead to oil and electricity shortages, as surging electricity demand persists, and there are concerns about whether current business models will encourage sufficient levels of spending in the future, according a new report.
The International Energy Agency’s second annual IEA benchmark analysis of energy investment found that while the world spent $US1.7 trillion ($2.2 trillion) on fossil-fuel exploration, new power plants and upgrades to electricity grids last year, with electricity investment surpassing oil and gas even as global energy investment was down 12 per cent from a year earlier and 17 per cent lower than 2014.
While the IEA said continued oversupply of oil and electricity globally would prevent any imminent shock, falling investment “points to a risk of market tightness and undercapacity at some point down the line’’.
The low crude oil price drove a 44 per cent drop in oil and gas investment between 2014 and 2016. It fell 26 per cent last year. It was due to falls in upstream activity and a slowdown in the sanctioning of conventional oilfields to the lowest level in more than 70 years.
“Given the depletion of existing fields, the pace of investment in conventional fields will need to rise to avoid a supply squeeze, even on optimistic assumptions about technology and the impact of climate policies on oil demand,’’ the IEA warned in its report released yesterday evening. “The energy transition has barely begun in several key sectors, such as transport and industry, which will continue to rely heavily on oil, gas and coal for the foreseeable future.’’
The fall in global energy spending also reflected declining investment in power generation, particularly from coal plants.
While 21 per cent of global energy investment was made by China in 2016, the world’s fastest growing economy had a 25 per cent decline in the commissioning of new coal-fired power plants, due largely to air pollution issues and investment in renewables.
Investment in new coal-fired plants also fell in India.
“India and China have slammed the brakes on coal-fired generation. That is the big change we have seen globally,’’ said Bruce Mountain a director at CME Australia.
“What it confirms is the pressures and the changes we are seeing in Australia, the restructuring of our energy supply, is just part of a global trend. We are facing the pressures more sharply in Australia because our power prices are very high. But that same shift in energy source in Australia are being mirrored internationally.’’ The IEA — a Paris-based adviser to the OECD on energy policy — also highlighted Australia’s reduced power reserves in its report and called for regulatory change to encourage greater use of renewables.
“Australia has one of the highest proportions of households with PV systems on their roof of any country in the world, and its electricity use in its National Electricity Market is spread out over a huge and weakly connected network,’’ the report said.
“It appears that a series of accompanying investments and regulatory changes are needed, including a plan to avoid supply threats, to use Australia’s abundant wind and solar potential: changing system operation methods and reliability procedures as well as investment into network capacity, flexible generation and storage.’’ The report found that in Australia there had been an increase in grid-scale installations mostly associated with large-scale solar PV plants.
Last month the Turnbull government revealed it was prepared to back the construction of new coal-fired power stations to prevent further shortfalls in electricity supplies, while the PM ruled out taxpayer-funded plants and declared it was open to using “clean coal” technology to replace existing generators.
He also pledged “immediate” action to boost the supply of gas by forcing exporters to divert production into the domestic market.
Since then technology billionaire Elon Musk has promised to solve South Australia’s energy issues by building the world’s largest lithium-ion battery in the state.
But the IEA report said batteries were unlikely to become a “one size fits all” single solution to electricity security and flexibility provision.
“While batteries are well-suited to frequency control and shifting hourly load, they cannot provide seasonal storage or substitute the full range of technical services that conventional plants provide to stabilise the system,’’ the report said.
“In the absence of a major technological breakthrough, it is most likely that batteries will complement rather than substitute conventional means of providing system flexibility. While conventional plants continue to provide essential system services, their business model is increasingly being called into question in unbundled systems.’’















