Kaspersky Lab Discovers Russian Hacker Infrastructure

Arc Flash Training CSA Z462 - Electrical Safety Essentials
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 6 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Crouching Yeti APT targets energy infrastructure with watering-hole attacks, compromising servers to steal credentials and stage intrusions; Kaspersky Lab links the Energetic Bear group to ICS threats across Russia, US, Europe, and Turkey.
Key Points
Crouching Yeti APT, aka Energetic Bear, is a threat group that targets energy firms using watering-hole attacks.
✅ Targets energy infrastructure via watering-hole compromises
✅ Uses open-source tools and backdoored sshd for persistence
✅ Scans global servers to stage intrusions and steal credentials
A hacker collective known for attacking industrial companies around the world have had some of their infrastructure identified by Russian security specialists.
Kaspersky Lab said that it has discovered a number of servers compromised by the group, belonging to different organisations based in Russia, the US, and Turkey, as well as European countries.
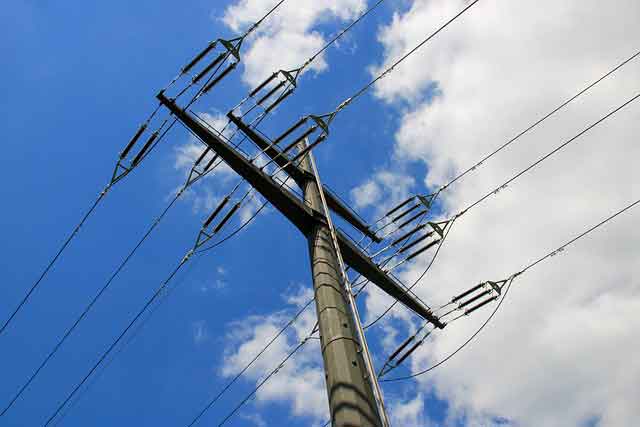
The Russian-speaking hackers, known as Crouching Yeti or Energetic Bear, mostly focus on energy facilities, as seen in reports of infiltration of the U.S. power grid targeting critical infrastructure, for the main purpose of stealing valuable data from victim systems.
Hacked servers
Crouching Yeti is described as an advanced persistent threat (APT) group that Kaspersky Lab has been tracking since 2010.
#google#
Kaspersky Lab said that the servers it has compromised are not just limited to industrial companies. The servers were hit in 2016 and 2017 with different intentions. Some were compromised to gain access to other resources or to be used as intermediaries to conduct attacks on other resources.
Others, including those hosting Russian websites, were used as watering holes.
It is a common tactic for Crouching Yeti to utilise watering hole attacks where the attackers inject websites with a link redirecting visitors to a malicious server.
“In the process of analysing infected servers, researchers identified numerous websites and servers used by organisations in Russia, US, Europe, Asia and Latin America that the attackers had scanned with various tools, possibly to find a server that could be used to establish a foothold for hosting the attackers’ tools and to subsequently develop an attack,” said the security specialists in a blog posting.
“The range of websites and servers that captured the attention of the intruders is extensive,” the firm said. “Kaspersky Lab researchers found that the attackers had scanned numerous websites of different types, including online stores and services, public organisations, NGOs, manufacturing, etc.
Kaspersky Lab said that the hackers used publicly available malicious tools, designed for analysing servers, and for seeking out and collecting information. The researchers also found a modified sshd file with a preinstalled backdoor. This was used to replace the original file and could be authorised with a ‘master password’.
“Crouching Yeti is a notorious Russian-speaking group that has been active for many years and is still successfully targeting industrial organisations through watering hole attacks, among other techniques,” explained Vladimir Dashchenko, head of vulnerability research group at Kaspersky Lab ICS CERT.
Russian government?
“Our findings show that the group compromised servers not only for establishing watering holes, but also for further scanning, and they actively used open-sourced tools that made it much harder to identify them afterwards,” he said.
“The group’s activities, such as initial data collection, the theft of authentication data, and the scanning of resources, are used to launch further attacks,” said Dashchenko. “The diversity of infected servers and scanned resources suggests the group may operate in the interests of the third parties.”
This may well tie into a similar conclusion from a rival security vendor.
In 2014 CrowdStrike claimed that the ‘Energetic Bear’ group was also tracked in Symantec's Dragonfly research and had been hacking foreign companies on behalf of the Russian state.
The security vendor had said the group had been carrying out attacks on foreign companies since 2012, with reports of breaches at U.S. power plants that underscored the campaign, and there was evidence that these operations were sanctioned by the Russian government.
Last month the United States for the first time publicly accused Russia in a condemnation of Russian grid hacking of attacks against the American power grid.
Symantec meanwhile warned last year of a resurgence in cyber attacks on European and US energy companies, including reports of access to U.S. utility control rooms that could result in widespread power outages.
And last July the UK’s National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) acknowledged it was investigating a broad wave of attacks on companies in the British energy and manufacturing sectors.