US Electricity Demand Stagnation reflects decoupling from GDP as TVA's IRP revises outlook, with energy efficiency, distributed generation, renewables, and cheap natural gas undercutting coal, reshaping utility business models and accelerating grid modernization.
Key Points
US electricity demand stagnation is flat load growth driven by efficiency, DG, and decoupling from GDP.
✅ Flat sales pressure IOU profits and legacy baseload investments.
✅ Efficiency and rooftop solar reduce load growth and capacity needs.
✅ Utilities must pivot to services, DER orchestration, and grid software.
The US electricity sector is in a period of unprecedented change and turmoil, with emerging utility trends reshaping strategies across the industry today. Renewable energy prices are falling like crazy. Natural gas production continues its extraordinary surge. Coal, the golden child of the current administration, is headed down the tubes.
In all that bedlam, it’s easy to lose sight of an equally important (if less sexy) trend: Demand for electricity is stagnant.
Thanks to a combination of greater energy efficiency, outsourcing of heavy industry, and customers generating their own power on site, demand for utility power has been flat for 10 years, with COVID-19 electricity demand underscoring recent variability and long-run stagnation, and most forecasts expect it to stay that way. The die was cast around 1998, when GDP growth and electricity demand growth became “decoupled”:
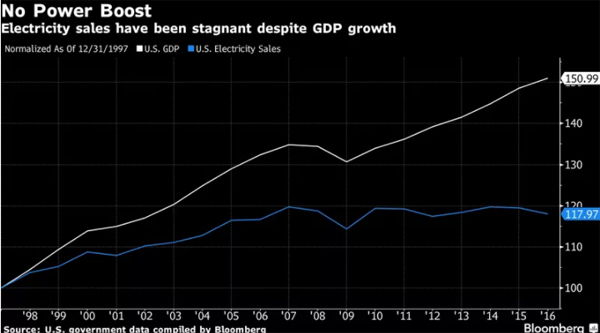
This historic shift has wreaked havoc in the utility industry in ways large and small, visible and obscure. Some of that havoc is high-profile and headline-making, as in the recent requests from utilities (and attempts by the Trump administration) to bail out large coal and nuclear plants amid coal and nuclear industry disruptions affecting power markets and reliability.
Some of it, however, is unfolding in more obscure quarters. A great example recently popped up in Tennessee, where one utility is finding its 20-year forecasts rendered archaic almost as soon as they are released.
Falling demand has TVA moving up its planning process
Every five years, the Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA) — the federally owned regional planning agency that, among other things, supplies electricity to Tennessee and parts of surrounding states — develops an Integrated Resource Plan (IRP) meant to assess what it requires to meet customer needs for the next 20 years.
The last IRP, completed in 2015, anticipated that there would be no need for major new investment in baseload (coal, nuclear, and hydro) power plants; it foresaw that energy efficiency and distributed (customer-owned) energy generation would hold down demand.
Even so, TVA underestimated. Just three years later, the Times Free Press reports, “TVA now expects to sell 13 percent less power in 2027 than it did two decades earlier — the first sustained reversal in the growth of electricity usage in the 85-year history of TVA.”
TVA will sell less electricity in 10 years than it did 10 years ago. That is bonkers.
This startling shift in prospects has prompted the company to accelerate its schedule. It will now develop its next IRP a year early, in 2019.
Think for a moment about why a big utility like TVA (serving 9 million customers in seven states, with more than $11 billion in revenue) sets out to plan 20 years ahead. It is investing in extremely large and capital-intensive infrastructure like power plants and transmission lines, which cost billions of dollars and last for decades. These are not decisions to make lightly; the utility wants to be sure that they will still be needed, and will still pay off, for many years to come.
Now think for a moment about what it means for the electricity sector to be changing so fast that TVA’s projections are out of date three years after its last IRP, so much so that it needs to plunge back into the multimillion-dollar, year-long process of developing a new plan.
TVA wanted a plan for 20 years; the plan lasted three.
The utility business model is headed for a reckoning
TVA, as a government-owned, fully regulated utility, has only the goals of “low cost, informed risk, environmental responsibility, reliability, diversity of power and flexibility to meet changing market conditions,” as its planning manager told the Times Free Press. (Yes, that’s already a lot of goals!)
But investor-owned utilities (IOUs), which administer electricity for well over half of Americans, face another imperative: to make money for investors. They can’t make money selling electricity; monopoly regulations forbid it, raising questions about utility revenue models as marginal energy costs fall. Instead, they make money by earning a rate of return on investments in electrical power plants and infrastructure.
The problem is, with demand stagnant, there’s not much need for new hardware. And a drop in investment means a drop in profit. Unable to continue the steady growth that their investors have always counted on, IOUs are treading water, watching as revenues dry up
Utilities have been frantically adjusting to this new normal. The generation utilities that sell into wholesale electricity markets (also under pressure from falling power prices; thanks to natural gas and renewables, wholesale power prices are down 70 percent from 2007) have reacted by cutting costs and merging. The regulated utilities that administer local distribution grids have responded by increasing investments in those grids, including efforts to improve electricity reliability and resilience at lower cost.
But these are temporary, limited responses, not enough to stay in business in the face of long-term decline in demand. Ultimately, deeper reforms will be necessary.
As I have explained at length, the US utility sector was built around the presumption of perpetual growth. Utilities were envisioned as entities that would build the electricity infrastructure to safely and affordably meet ever-rising demand, which was seen as a fixed, external factor, outside utility control.
But demand is no longer rising. What the US needs now are utilities that can manage and accelerate that decline in demand, increasing efficiency as they shift to cleaner generation. The new electricity paradigm is to match flexible, diverse, low-carbon supply with (increasingly controllable) demand, through sophisticated real-time sensing and software.
That’s simply a different model than current utilities are designed for. To adapt, the utility business model must change. Utilities need newly defined responsibilities and new ways to make money, through services rather than new hardware. That kind of reform will require regulators, politicians, and risky experiments. Very few states — New York, California, Massachusetts, a few others — have consciously set off down that path.
Flat or declining demand is going to force the issue
Even if natural gas and renewables weren’t roiling the sector, the end of demand growth would eventually force utility reform.
To be clear: For both economic and environmental reasons, it is good that US power demand has decoupled from GDP growth. As long as we’re getting the energy services we need, we want overall demand to decline. It saves money, reduces pollution, and avoids the need for expensive infrastructure.
But the way we’ve set up utilities, they must fight that trend. Every time they are forced to invest in energy efficiency or make some allowance for distributed generation (and they must always be forced), demand for their product declines, and with it their justification to make new investments.
Only when the utility model fundamentally changes — when utilities begin to see themselves primarily as architects and managers of high-efficiency, low-emissions, multidirectional electricity systems rather than just investors in infrastructure growth — can utilities turn in earnest to the kind planning they need to be doing.
In a climate-aligned world, utilities would view the decoupling of power demand from GDP growth as cause for celebration, a sign of success. They would throw themselves into accelerating the trend.
Instead, utilities find themselves constantly surprised, caught flat-footed again and again by a trend they desperately want to believe is temporary. Unless we can collectively reorient utilities to pursue rather than fear current trends in electricity, they are headed for a grim reckoning.
Related News












