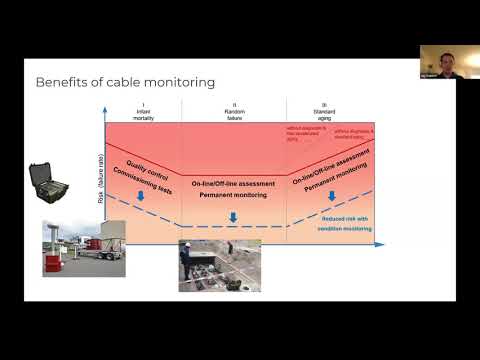
Hydrogen Detection System - Technology and Placement

A hydrogen detection system is an essential tool in environments where hydrogen H2 gas is used or stored, such as battery rooms or industrial facilities. H is a highly flammable and lighter than air gas, making it crucial to detect even the smallest leaks early. Without proper detection, the concentration of H can quickly reach dangerous levels, posing a risk of explosion or fire. H2 gas detectors help prevent these hazards by providing real-time monitoring, ensuring that the levels of H2 gas stay within safe thresholds. For electrical workers, understanding how H2 gas detection systems work and where to install detectors is vital for maintaining safety and preventing accidents in the workplace. With advancements in gas sensor technology, the use of reliable H2 gas monitors helps protect personnel and equipment, making them indispensable in any setting where H is present.
Electrical Transformer Maintenance Training
Substation Maintenance Training
Request a Free Training Quotation
A hydrogen detection system is designed to continuously monitor the presence of H2 gas in various environments, particularly in areas like battery rooms or industrial facilities where H2 gas is used or stored. The system typically incorporates different types of gas sensors, such as electrochemical sensors, catalytic bead sensors, or metal oxide sensors, depending on the specific application and sensitivity requirements. These sensors detect changes in the concentration of H and trigger alarms if the gas levels exceed safe thresholds. Additionally, the system is often integrated with ventilation systems to automatically disperse accumulated gas when dangerous levels are detected. The design also includes real-time monitoring and alarm mechanisms that alert workers to potential hazards, allowing for immediate action. By leveraging reliable H2 gas detection technologies, a network of sensors ensures safety, accuracy, and compliance with safety standards in environments where H2 gas is present.
What are the detection techniques for hydrogen?
There are several key technologies used in hydrogen detection to ensure accurate and timely monitoring. One of the most widely used methods is the electrochemical sensor, which operates by reacting H with an electrolyte to produce an electrical current proportional to the concentration of hydrogen. This method is highly sensitive and accurate, making it ideal for battery rooms and other critical areas where H levels need to be closely monitored.
Another common technique is the use of catalytic bead sensors, which consist of two heated beads—one coated with a catalyst. When H2 gas comes into contact with the catalyst, it causes a change in resistance between the beads, indicating the presence of H. Catalytic bead sensors are known for their durability and reliability, making them popular in industrial settings.
In addition, metal oxide sensors detect H by measuring changes in electrical resistance as the gas interacts with a metal oxide surface. This technology is also reliable and efficient for continuous monitoring in areas with H2 gas risks.
Optical sensors and thermal conductivity sensors are also used, with optical sensors leveraging light absorption or emission to detect H molecules. While they are less common, they are used in specific high-sensitivity applications.
Which hydrogen gas detector will be used for hydrogen detection?
The selection of a H2 gas detector depends on the environment and specific application. Electrochemical sensors are ideal for battery rooms due to their accuracy and ability to detect even low concentrations of H. These sensors offer reliable, long-term performance and are suited for areas where H is frequently generated.
For broader industrial settings where durability and longevity are crucial, catalytic bead sensors are commonly chosen. Their robustness allows them to withstand challenging environments, making them a dependable option in hydrogen gas detection systems.
For portable applications, a portable hydrogen gas detector is the best choice, enabling workers to carry out detection tasks on the go, ensuring safety in any part of the facility.
What is the safest method to detect hydrogen gas?
The safest method for H2 gas detection involves using high-quality, certified gas detection systems that incorporate both electrochemical and catalytic bead sensors for comprehensive coverage. These hydrogen detectors can continuously monitor levels of H2 gas and trigger alarms when thresholds are breached, allowing workers to take immediate action. Additionally, integrating the H2 gas detectors with a facility’s ventilation system ensures that when h2 gas concentrations rise to dangerous levels, the system automatically activates ventilation to disperse the gas.
Regular maintenance and calibration are essential to keep the gas detection systems functioning correctly. It is also important for workers to undergo regular training in handling hydrogen and emergency protocols to ensure proper safety measures are in place.
Where should a hydrogen detector be placed?
Placement of H2 gas detectors is critical to ensuring effective detection. In battery rooms, where H is frequently produced, the detectors should be installed at the highest points because H2 gas is lighter than air and will naturally rise. Placing detectors near the ceiling will allow for early detection of accumulating gas.
In industrial environments, a hydrogen gas monitor should be installed near hydrogen storage tanks, pipelines, and processing areas where levels of H2 gas could become dangerous. It is also important to place detectors in confined spaces where H might accumulate and pose an explosive risk.
Finally, integrating H2 gas detection systems with the building’s ventilation ensures that in the event of a gas leak, the ventilation system can quickly disperse the gas, maintaining safe working conditions.
Using a network of H2 sensors is crucial in environments where H is present, as it can help prevent serious accidents by detecting dangerous levels of H2 gas early. Different technologies, such as electrochemical sensors, catalytic bead sensors, and metal oxide sensors, ensure reliable detection, while proper placement in battery rooms and industrial areas enhances safety. For electrical workers, understanding the role of H2 gas detection and the safe use of detectors is key to maintaining a secure working environment.
On-Site Training
Interested in cost effective, professional on-site electrical training?
We can present an Electrical Training Course to your electrical engineering and maintenance staff, on your premises, tailored to your specific equipment and requirements. Click on the link below to request a Free quotation.
EF PARTNER MEDIA
Videos
Product Showcases
Shared Media