Arc Flash vs Arc Blast: What's the Difference?
NFPA 70e Training
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 6 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our OSHA 4474 Fact Sheet – Establishing Boundaries Around Arc Flash Hazards

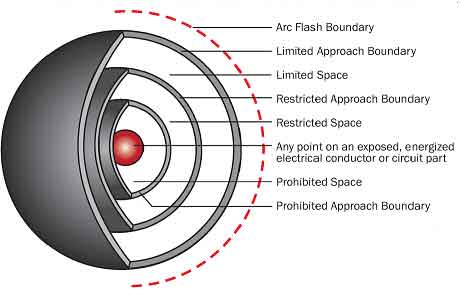
- Understand the difference between arc flash and electric shock boundaries
- Learn who may cross each boundary and under what conditions
- Apply voltage-based rules for safer approach distances
The difference between arc flash and arc blast is that arc flash releases intense heat and light during an electrical fault, while arc blast produces a pressure wave that can hurl objects and injure workers.
Arc Flash vs Arc Blast - What is the Difference?
Arc flash is a high-temperature electrical discharge caused by a fault, while arc blast is the explosive pressure wave that follows the arc. Arc flash causes burns and fire; arc blast causes concussive injuries and flying debris.
✅ Arc flash produces extreme heat, light, and radiation, causing burns and equipment damage
✅ Arc blast creates a powerful pressure wave that can propel debris and damage hearing
✅ Both hazards require PPE, training, and risk assessments under NFPA 70E
Arc flash causes burns; arc blast causes blunt-force trauma and hearing damage. Arc flash causes burns and fire; arc blast causes concussive injuries and flying debris. While both involve the sudden release of energy during a fault, their impacts differ significantly in terms of thermal and pressure effects. Recognizing these differences is essential for ensuring workplace safety, selecting the right personal protective equipment (PPE), and implementing effective risk mitigation strategies. By understanding the unique characteristics of each, professionals can better protect workers, reduce downtime, and enhance the reliability of electrical systems. To better understand the root cause of arc incidents, see our detailed guide on what causes arc flash, including electrical faults and system failures.
Request a Free Training Quotation
Understanding the difference is essential for safeguarding workers and maintaining a safe electrical environment. An electrical explosion primarily generates intense heat and light that can cause severe burns, while the pressure wave is capable of throwing objects and damaging hearing. By recognizing these unique hazards, workers can take tailored precautions to protect themselves. This includes wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as clothing, face shields, and hearing protection, as well as following established safety protocols, including maintaining proper distance and using insulated tools. Comprehensive training and adherence to safety standards further empower workers to minimize risks and respond effectively in high-energy environments. Explore the arc flash boundary page to learn how distance affects risk and how the blast radius differs from thermal exposure zones.
Test Your Knowledge About Arc Flash!
Think you know Arc Flash? Take our quick, interactive quiz and test your knowledge in minutes.
- Instantly see your results and score
- Identify strengths and areas for improvement
- Challenge yourself on real-world electrical topics
Arc Flash
Arc Flash is an energy discharge of light and heat that forms when a fault occurs in an electrical circuit. This results in a tremendous amount of energy being released as current flowing through ionized air. These electrical explosions can reach temperatures hotter than the surface of the sun.
Electrical explosions produce some of the highest temperatures known to occur on Earth - up to 35,000 degrees Fahrenheit at the arc terminals. The intense heat causes the sudden expansion of air. This can result in a blast with very strong air pressure. Learn more about how arc flash PPE requirements protect against thermal hazards, while recognizing that no PPE is currently rated for blast pressure protection.
Think of it this way: arc flash is the cause, and arc blast is the effect. When a short circuit occurs, it can often cause a highly dangerous electrical explosion that generates extremely high temperatures. If you're looking for tools to measure hazard severity, use our interactive arc flash calculator to estimate incident energy and PPE requirements.
Arc Blast
Another item associated with an electrical explosion is the arc blast (AB) energy or pressure. This hazard is not presently covered in NFPA 70E or IEEE Std 1584. This force can be significant and can blow workers away from the explosion, causing falls and injuries that may be more severe than burns. Molten metals and debris travel through the air at tremendous speed and force. In one case, with approximately 100 kA fault level and current of 42 kA, on a 480-V system, an electrician was thrown 25 feet away. Being forced away from the explosion can reduce the electrician’s exposure to heat radiation and molten copper, but can subject the worker to falls or impact injuries. The approximate initial impulse force at 24 inches was calculated to be approximately 260 lb/ft2 as determined from the equation below. The high temperatures and pressure involved in arc events are illustrated in this in-depth article on arc flash blast explosion, which explains both thermal and concussive impacts.
The heat and flames generated by an AB is enough to vaporize metal components, as well as cause life-threatening (or even deadly) burns to personnel in the immediate vicinity. Shrapnel from exploded equipment can turn metal objects into high-speed shrapnel, which threatens to seriously injure or kill workers in the general area of the blast. AB often causes damage to eyesight due to high-intensity light, which can result in both temporary and long-term vision problems. Dive deeper into terminology and effects by reviewing our full arc blast definition, including examples of real-world injuries caused by concussive force.
PPE is not tested for protection from any type of blast pressure, and at this time, there are no accepted calculation methods for determining the hazard of blast pressure for any particular situation.
Arc Flash vs Arc Blast is a vital topic for electrical engineering and maintenance professionals, as it addresses two distinct hazards that pose serious risks in the workplace. While an AF involves intense thermal energy capable of causing severe burns, an AB results from a sudden pressure wave that can lead to equipment damage and life-threatening injuries. Understanding these phenomena is crucial for implementing effective safety measures, selecting the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), and ensuring compliance with industry standards. By grasping the differences between electrical safety managers can enhance safety protocols, protect workers, and improve the reliability of electrical systems. For professionals conducting hazard assessments, our arc flash analysis and 7 steps to arc flash analysis pages provide essential procedures and common mistakes to avoid.
Related Resources