Dielectric Voltage Withstand Test Explained
Download Our OSHA 3075 Fact Sheet – Understanding Electrical Hazards in the Workplace

- Learn the effects of electric current on the human body
- Understand OSHA safety standards and protective devices
- Discover essential lockout/tagout and grounding practices
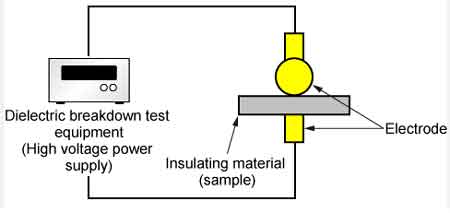
The Dielectric Voltage Withstand Test applies high voltage to verify insulation strength. It ensures transformers, wiring, and switchgear resist breakdown, helping prevent electrical hazards and confirming compliance with essential safety standards.
What is a Dielectric Voltage Withstand Test?
The Dielectric Voltage Withstand Test is a high-voltage insulation test that verifies electrical safety and ensures reliable system performance.
✅ Confirms insulation integrity in equipment
✅ Prevents breakdown under overvoltage conditions
✅ Ensures compliance with safety standards
The Dielectric Voltage Withstand Test is a critical safety procedure that every industrial electrician should be familiar with. This procedure, also known as a hipot test or high potential test, evaluates the effectiveness of electrical insulation in preventing potentially dangerous voltage breakdowns. By understanding the principles and applications of this procedure, industrial electricians can ensure the safety of electrical systems and prevent hazards such as electric shock, short circuits, and equipment damage. This article provides a comprehensive overview, covering its importance, procedures, and key factors to consider. Read on to gain valuable knowledge that will enhance your understanding of electrical safety and best practices.
To prevent dangerous dielectric breakdown in electrical systems, the dielectric withstand test is a required procedure for many applications. It assesses the integrity of insulating materials under high voltage stress, helping to ensure electrical safety and prevent equipment failures. Engineers often use dielectric voltage testing to confirm compliance with safety standards and prevent dangerous breakdowns in electrical equipment.
Dielectric Voltage Withstand Test Parameters and Comparisons
| Parameter | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Test Voltage | High voltage applied above normal operating levels | Confirms insulation can endure electrical stress without failure |
| Duration | Time the voltage is applied (typically 1–60 seconds) | Ensures insulation integrity under sustained conditions |
| Leakage Current | Small current flowing through insulation during the test | Rising leakage indicates deterioration or contamination |
| Breakdown Voltage | Voltage level at which insulation fails and current flows uncontrollably | Key factor in selecting suitable insulating materials |
| Pass/Fail Criteria | Device passes if leakage current remains below safety limit | Defines compliance with IEC, UL, and ISO standards |
| Complementary Tests | Insulation Resistance Test, Line Leakage Test | Provide additional evaluation of insulation health and performance |
| Test Equipment | Hipot testers, insulation resistance testers, ground testers | Accuracy and calibration critical for valid, reliable results |
Insulation Resistance
The Dielectric Voltage Withstand Test is often complemented by the Insulation Resistance Test. While the former focuses on assessing the insulation's ability to withstand high voltages, the Insulation Resistance Test measures the insulation's resistance to current flow at a lower voltage. Together, these procedures provide a comprehensive evaluation of the insulation's integrity, ensuring its ability to prevent electrical leakage and maintain safe operation. The insulation resistance explained page illustrates how this lower-voltage test complements withstand tests to provide a comprehensive view of insulation integrity.
Electricity Today T&D Magazine Subscribe for FREE

- Timely insights from industry experts
- Practical solutions T&D engineers
- Free access to every issue
Hipot Test
The term "Hipot Test" is a common abbreviation for "High Potential Test" and is another name for the Dielectric Voltage Withstand Test. This procedure involves applying a high voltage to the insulation for a specific duration to assess its ability to withstand electrical stress. By exceeding the normal operating voltage, the Hipot Test can reveal hidden defects or weaknesses that might not be apparent during regular use. A reliable hipot tester is essential for applying controlled voltages and measuring leakage current during withstand tests.
Breakdown Voltage
A key parameter in insulation testing is the breakdown voltage. This refers to the voltage level at which the insulating material fails, allowing current to flow through it. Exceeding the breakdown voltage can lead to a rapid increase in current, generating excessive heat and potentially causing a catastrophic failure. Understanding the breakdown voltage of different insulating materials is crucial for selecting appropriate insulation for specific applications and ensuring safe operating conditions.
Safety Standards
Various safety standards and regulations govern its application. Organizations like the IEC, UL, and ISO provide guidelines and specifications for procedures, voltage levels, and durations. Adhering to these standards ensures consistent and reliable practices, promoting electrical safety and preventing potential hazards.
Electrical Safety
The primary purpose is to ensure the electrical safety of devices and components. Identifying insulation weaknesses helps prevent electric shock, short circuits, and other electrical hazards that could pose risks to users or damage equipment. Prioritizing electrical safety through rigorous testing is essential for maintaining a safe operating environment and preventing accidents.
Leakage Current
During the Dielectric Voltage Withstand Test, a small amount of current, known as leakage current, may flow through the insulation. Monitoring this leakage current is crucial as it can indicate the condition of the insulation. An increase in leakage current can signal deterioration or contamination, potentially leading to insulation failure. By setting appropriate limits for leakage current, manufacturers can ensure that insulation meets the required safety standards. Complementary procedures, such as line leakage testing, provide additional insights into insulation health and electrical safety.
Test Equipment
Specialized equipment, such as Hipot testers or insulation resistance testers, is used to conduct the Dielectric Voltage Withstand Test. These devices apply controlled high voltages and measure the resulting leakage current. The accuracy and reliability of the equipment are essential for obtaining valid results and ensuring the effectiveness of the process. A dependable ground tester ensures that grounding systems work correctly, which is critical for accurate and safe dielectric testing.
Applications of Dielectric Voltage Withstand Test
It finds wide applications across various industries and products. From consumer electronics and household appliances to industrial equipment and medical devices, it is crucial to verify the safety and reliability of electrical insulation. Ensuring the integrity of insulation in these diverse applications helps prevent electrical hazards and maintain product performance.
Quality Control
Incorporating the test into quality control procedures is essential for manufacturers of electrical products. By performing this procedure during the production process, manufacturers can identify and reject faulty units before they reach the market. This proactive approach to quality control helps maintain high standards, reduces the risk of product failures, and enhances customer satisfaction. To maintain accuracy, it is vital to calibrate test equipment regularly, ensuring all high-voltage insulation tests deliver valid and reliable results.
Test Your Knowledge About T&D Test Equipment!
Think you know T&D Test Equipment? Take our quick, interactive quiz and test your knowledge in minutes.
- Instantly see your results and score
- Identify strengths and areas for improvement
- Challenge yourself on real-world electrical topics
Failure Analysis
Despite rigorous testing and quality control measures, insulation failures can still occur. When such incidents happen, a thorough failure analysis is conducted to determine the root cause. This analysis may involve examining the failed insulation, analyzing environmental factors, and reviewing historical data. The insights gained from failure analysis contribute to the improvement of insulation design, manufacturing processes, and maintenance practices, ultimately enhancing the reliability and safety of electrical products.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of the Dielectric Voltage Withstand Test?
It aims to evaluate the effectiveness of a device's insulation by applying a high voltage. This helps determine whether the insulation can withstand electrical stress during normal operation, thereby preventing electric shock, short circuits, and product malfunctions.
How is the Dielectric Voltage Withstand Test performed?
A specialized "hipot tester" applies a controlled high voltage to the device and monitors the leakage current. The voltage and duration are predetermined based on safety standards. If the leakage current remains below a predefined limit, the device passes.
What is the difference between the Dielectric Voltage Withstand Test and the Insulation Resistance Test?
It applies a high voltage to check for insulation breakdown, while the Insulation Resistance Test measures resistance to current flow at a lower voltage. They complement each other to provide a complete evaluation of insulation health.
What are the acceptable results or pass/fail criteria?
The device passes if the leakage current during high-voltage application remains below a predefined limit, determined by factors such as operating voltage, insulation material, and intended application.
The Dielectric Voltage Withstand Test is a crucial procedure for ensuring electrical safety and preventing insulation failures in various applications. By applying a high voltage, this test assesses the insulation's ability to withstand electrical stress, helping to prevent hazards such as electric shock and short circuits. Complementary tests, such as the Insulation Resistance Test, provide a comprehensive evaluation of insulation health. Understanding key parameters such as breakdown voltage and leakage current is essential for interpreting test results and ensuring compliance with safety standards. By incorporating it into quality control processes and conducting thorough failure analysis, manufacturers can enhance the reliability and safety of electrical products.












