What is SCADA?
By R.W. Hurst, Editor
_1752206400.jpg)
Download Our OSHA 4475 Fact Sheet – Being Aware of Arc Flash Hazards

- Identify root causes of arc flash incidents and contributing conditions
- Apply prevention strategies including LOTO, PPE, and testing protocols
- Understand OSHA requirements for training and equipment maintenance
SCADA is a utility-grade system that enables real-time grid monitoring, remote control, fault detection, and substation automation. It improves electric utility reliability, safety, and performance through centralized supervision and smart data collection.
What is SCADA?
SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) :
✅ Monitors and controls the electric grid in real time using data from substations, breakers, transformers, and field sensors.
✅ Enables remote operations so utilities can issue commands, respond to alarms, and reconfigure the system without on-site intervention.
✅ Improves reliability, safety, and efficiency by automating processes, logging historical data, and supporting predictive analytics.
Key Functions of SCADA in Utilities
In today’s power systems, real-time control, automation, and visibility are not optional—they’re essential. SCADA systems make this possible. For electric utilities, SCADA serves as the digital nervous system, connecting control centers with field equipment spread across substations, switchyards, feeders, and beyond. It turns dispersed infrastructure into a responsive, manageable network.
Rather than being a single tool or software, SCADA is a layered ecosystem. It integrates sensors, control logic, data communication, human-machine interfaces (HMI), and centralized supervision. This orchestration allows utility operators to make informed decisions, respond instantly to failures, and maintain system stability at all times. See How Does SCADA Work, for a complete description of how this technology is used.
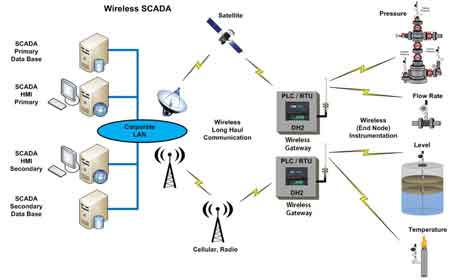
At the heart of every SCADA system is a set of operational capabilities that allow it to fulfill its core mission: monitor and control the power grid effectively. These functions go beyond passive observation—they enable dynamic responses, predictive planning, and precise execution. They are what make SCADA systems active participants in grid operations, not just silent observers.
Electricity Today T&D Magazine Subscribe for FREE

- Timely insights from industry experts
- Practical solutions T&D engineers
- Free access to every issue
-
Real-Time Monitoring: Continuously gathers data such as voltage, current, frequency, breaker position, and transformer temperatures across the network.
-
Remote Control: Allows operators to open/close breakers, switch circuits, change setpoints, and reset alarms from the control center.
-
Alarm Management: Detects abnormal or unsafe conditions and triggers alerts for immediate response.
-
Event Logging and Data Archiving: Records time-stamped operational data and events for analysis, troubleshooting, and compliance.
-
System Diagnostics: Detects and diagnoses communication failures, equipment faults, or sensor malfunctions to support rapid maintenance.
SCADA systems also play a vital role in industrial automation by connecting control equipment across large utility and manufacturing environments. These systems rely on both local control at field sites and centralized coordination via remote terminal units (RTUs). Modern SCADA software integrates seamlessly with user interfaces to provide real-time data visualization and control, enabling operators to manage complex processes efficiently. Through wireless communication, SCADA platforms can transmit data between remote assets and control centers, ensuring reliability, scalability, and rapid response in mission-critical applications.
SCADA System Components and Their Functions
| Component | Description | Function in SCADA System |
|---|---|---|
| Control Equipment | Devices such as breakers, valves, switches, and relays | Executes commands received from RTUs or PLCs |
| Industrial Automation | Use of control systems for industrial processes | Improves operational efficiency and reduces manual intervention |
| Local Control | On-site decision-making via PLCs or embedded logic | Enables rapid response without relying on central systems |
| Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) | Field devices that collect data and send control signals to equipment | Interface between field sensors/actuators and SCADA master station |
| SCADA Software | Centralized applications for monitoring, command execution, and logging | Manages data visualization, alarms, trending, and control logic |
| User Interfaces | HMIs (Human-Machine Interfaces) and dashboards | Allow operators to interact with system data and issue commands |
| Wireless Communication | Radio, cellular, or satellite links between remote sites and control centers | Enables real-time remote control and data transmission |
SCADA Architecture Overview
Understanding SCADA means understanding its structure. SCADA architecture isn’t just about connecting devices; it’s about building a system that supports scalability, cybersecurity, and seamless integration across operational tiers. Each component plays a distinct role, contributing to a chain of data flow and control that supports mission-critical decisions.
-
Field Devices (Level 0): Sensors and actuators gather raw process data and execute mechanical actions such as opening a breaker or adjusting voltage tap changers.
-
Control Devices (Level 1): RTUs and PLCs collect, preprocess, and transmit data from field devices. RTUs are optimized for remote or harsh environments, while PLCs are more common in plant-based automation.
-
Supervisory Systems (Level 2): The SCADA server, HMI, and master station run applications that collect data, visualize grid conditions, issue control commands, and manage alarms.
-
Enterprise Systems (Level 3): Often includes integration with Historian databases, outage management systems (OMS), GIS, and other IT/OT platforms for long-term analysis and decision-making.

Benefits of SCADA in the Electric Power Industry
The deployment of SCADA transforms how utilities manage both routine operations and emergency conditions. Beyond the technology, the real value lies in the measurable improvements to grid reliability, safety, and cost-effectiveness. These systems are not only reactive—they are predictive, proactive, and increasingly intelligent.
-
Increased Reliability: Continuous monitoring ensures faults are detected early and power can be rerouted or isolated before causing widespread outages.
-
Operational Efficiency: Reduces the need for manual intervention and site visits, especially for remote substations or feeders.
-
Improved Safety: Enables technicians to interact with high-voltage systems remotely, lowering exposure risk.
-
Data-Driven Planning: Collected historical data feeds asset management, load forecasting, and predictive maintenance models.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Logging and reporting features help satisfy regulatory and auditing requirements.
Utility-Specific SCADA Use Cases
While SCADA has broad applications, it takes on specific roles in utility environments based on network topology, regulatory demands, and system goals. Its flexibility allows utilities to tailor the system to their operational needs, whether for outage response, distributed energy integration, or smart substation control.
-
Substation Automation: Monitor and control power transformers, circuit breakers, battery banks, and environmental systems.
-
Distribution Automation (DA): Use FLISR (Fault Location, Isolation, and Service Restoration) to minimize outage durations and reroute power in real time.
-
Load Management: Implement demand response strategies, peak shaving, and load forecasting based on real-time usage data.
-
Renewable Energy Integration: Monitor variable generation from solar and wind farms, ensuring safe grid interconnection and voltage control.
-
Black Start and Emergency Response: Provide visibility and control during total or partial grid outages, supporting fast recovery procedures.
Frequently Asked Questions - What is SCADA?
How is SCADA different from other utility control systems like EMS or DCS?
SCADA is designed for monitoring and controlling distributed field assets over wide geographic areas, such as substations and feeders. EMS (Energy Management Systems) are used at the transmission level for power flow modelling and balancing, while DCS (Distributed Control Systems) are typically confined to single-site process control, like in power plants or water treatment facilities.
Test Your Knowledge About Smart Grid!
Think you know Smart Grid? Take our quick, interactive quiz and test your knowledge in minutes.
- Instantly see your results and score
- Identify strengths and areas for improvement
- Challenge yourself on real-world electrical topics
Can SCADA systems be used with renewable energy sources like solar and wind?
Modern SCADA systems are essential for integrating renewable energy. They monitor generation output, voltage levels, and weather conditions, and help utilities manage intermittency, balance loads, and protect the grid from fluctuations caused by variable power sources.
Is SCADA secure from cyberattacks?
While SCADA systems are increasingly exposed to cybersecurity threats, best practices like network segmentation, secure protocols (e.g., DNP3-SA, IEC 62351), role-based access control, and regular vulnerability assessments can significantly reduce risk. Many utilities also deploy firewalls, VPNs, and intrusion detection systems to secure SCADA communications.
Related Articles








