Understanding DC Voltage Drop Calculation
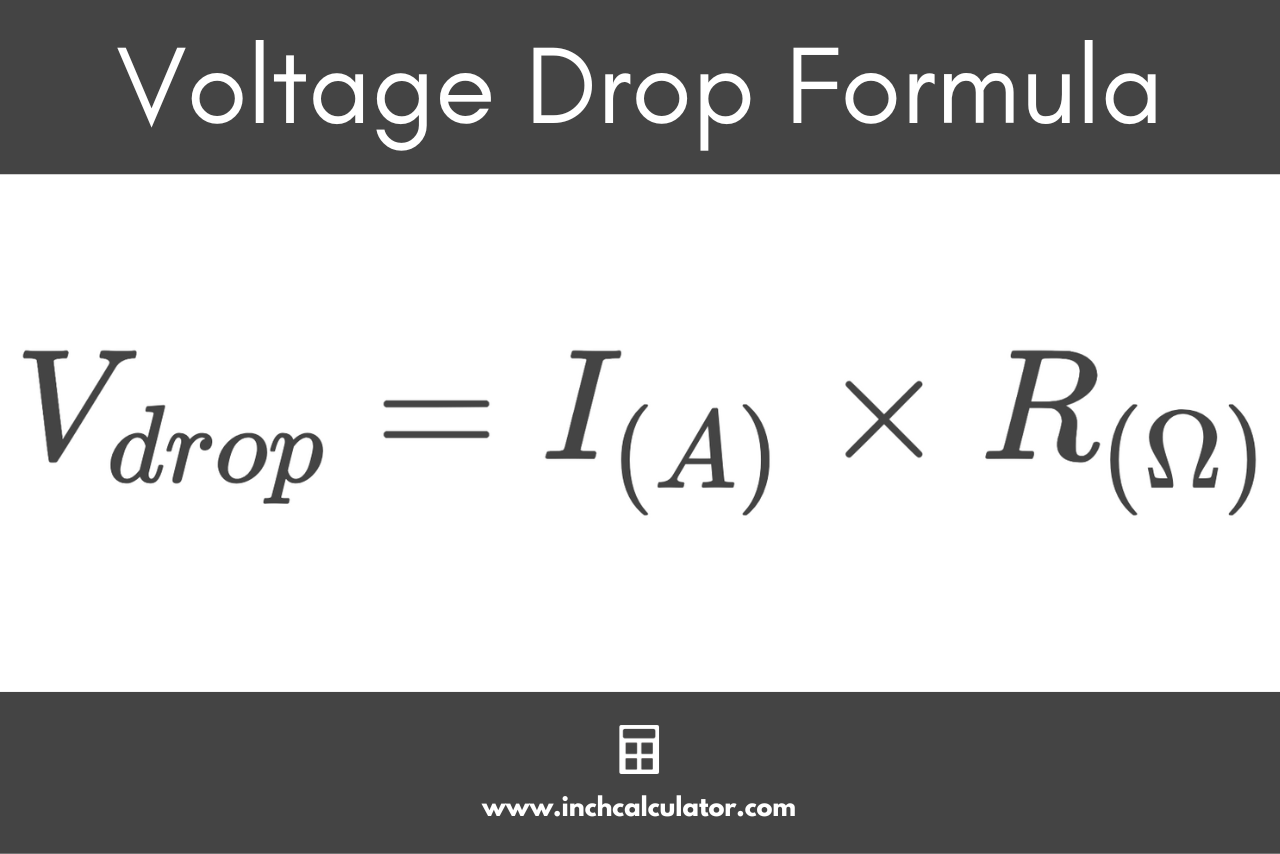
Short Circuit Study & Protective Device Coordination
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.
- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our OSHA FS3529 Fact Sheet – Lockout/Tagout Safety Procedures

- Learn how to disable machines and isolate energy sources safely
- Follow OSHA guidelines for developing energy control programs
- Protect workers with proper lockout devices and annual inspections
DC voltage drop calculation determines energy lost through resistance in a DC circuit. It’s critical for efficient design, proper wire sizing, and ensuring devices receive the right voltage without performance issues, especially in long wiring runs.
Power Quality Analysis Training
Request a Free Power Quality Training Quotation
What is "DC voltage drop calculation"?
DC voltage drop calculation determines the voltage loss along a DC circuit due to conductor resistance.
✅ Ensures proper voltage reaches devices
✅ Helps size conductors to minimize losses
✅ Prevents system inefficiencies and malfunctions
Learn more about voltage dropping and its impact on power quality.
DC Voltage Drop Calculation - In electrical design, calculating voltage drop is essential, particularly in direct current (DC) systems. Voltage drop refers to the loss of electrical potential as current flows through a conductor, typically caused by resistance. This energy loss can impact system performance, especially in circuits with long wiring runs or undersized conductors. Need a quick estimate? Try our voltage drop calculator for fast DC system planning.
How do you calculate voltage drop in a DC circuit?
To calculate voltage drop in a DC circuit, you can use the formula:
V drop = I × R
Where V drop is the voltage drop, I is the current in amperes, and R is the conductor’s resistance in ohms. Resistance is influenced by factors such as wire length, wire size (gauge), and material. A voltage drop calculator can be used to quickly determine losses, taking into account wire length and size. For more accurate calculations, some tools also account for the effects of temperature and other variables. Want the full math? Visit our voltage drop formula guide for detailed equations and examples.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the acceptable percentage for DC voltage drop?
The acceptable percentage of voltage drop depends on the type of circuit. Typically, for power and lighting circuits, a voltage drop of no more than 3% is ideal. According to the National Electric Code (NEC), the total system voltage drop, including branch circuits and feeders, should not exceed 5%. Maintaining low voltage drops ensures devices receive enough electrical potential to function properly without significant energy loss. For an overview of the general principles of voltage drop across AC and DC systems, read our article.
Electricity Today T&D Magazine Subscribe for FREE

- Timely insights from industry experts
- Practical solutions T&D engineers
- Free access to every issue
How does wire length and size affect DC voltage drop?
Wire length and wire gauge are key factors in determining the voltage drop in a circuit. As wire length increases, so does resistance, leading to a higher voltage drop. Similarly, smaller wire sizes (thinner wires) have more resistance than larger ones. Wire size, often measured in circular mils, plays a crucial role in minimizing voltage loss. By selecting wires with a larger cross-sectional area, you can reduce resistance and minimize energy loss, particularly in circuits designed to carry larger loads over longer distances.
What is the difference between voltage drop in AC and DC circuits?
Voltage drop occurs in both AC and DC circuits, but the difference lies in the factors contributing to it. In DC systems, voltage drop is purely a function of resistance, whereas in AC systems, both resistance and reactance must be considered. Reactance occurs due to the presence of inductance and capacitance in the circuit. Therefore, calculating voltage drop in an AC system is more complex, as it involves factors such as phase angle and impedance. However, the same basic principles of wire size, material, and length apply to both AC and DC systems.
How can you minimize voltage drop in a DC system?
To minimize voltage drop in DC systems, several approaches can be used. First, reducing wire length in the design will naturally reduce resistance. Second, using the correct wire gauge based on the load and distance is critical. A voltage drop calculator helps determine the optimal wire size for a specific system. Ensuring clean, proper connections throughout the circuit also plays a role in minimizing energy loss. For circuits carrying single-phase loads or mixed AC and DC systems, maintaining balance using methods like zig-zag transformers can improve overall efficiency.
DC Voltage Drop Calculation
In North America, electrical systems follow guidelines established by the National Electric Code to ensure safety and performance. By using proper voltage drop formulas and selecting the appropriate wire length, gauge, and material, engineers can optimize the performance of DC circuits. Tools like voltage drop calculators facilitate the design of systems that minimize energy loss and ensure reliable operation. These methods help maintain efficient power delivery while meeting regulatory requirements.
Related Pages