Is Voltage Dropping in Your Power System?
Substation Grounding Training
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our OSHA FS3529 Fact Sheet – Lockout/Tagout Safety Procedures

- Learn how to disable machines and isolate energy sources safely
- Follow OSHA guidelines for developing energy control programs
- Protect workers with proper lockout devices and annual inspections
Voltage dropping refers to a reduction in voltage as current flows through a circuit. It can lead to equipment inefficiency, overheating, and performance issues. Common causes include undersized wires, long cable runs, and aging infrastructure, all of which increase resistance.
Power Quality Analysis Training
Request a Free Power Quality Training Quotation
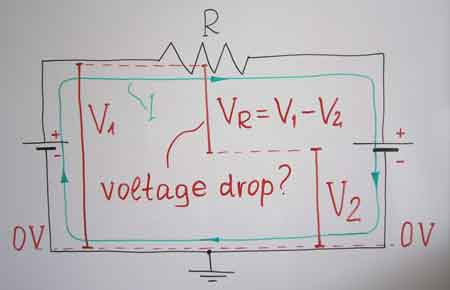
What is "Voltage Dropping"?
Voltage dropping is more than a minor inconvenience—it’s a power quality issue that affects the performance, safety, and efficiency of electrical systems. Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the root causes are essential for maintaining a reliable infrastructure. Learn how to identify and address wiring issues that contribute to voltage problems in our guide to the causes of voltage drop
✅ A gradual voltage reduction due to circuit resistance
✅ Causes flickering lights, motor failure, or overheating
✅ Signals power quality issues or poor wiring design
What Causes Voltage Dropping?
Voltage dropping typically results from resistance in conductors, poor connections, overloaded circuits, or aged infrastructure. As current flows through a conductor, part of the electrical energy is converted to heat, reducing the voltage available at the load. Key contributing factors include:
-
Undersized wiring or conductors
-
Long-distance cable runs without compensation
-
Corroded or loose terminals
-
High-resistance splices or connectors
-
Overloaded circuits or imbalanced phases
Environmental factors, such as temperature fluctuations and humidity, can also exacerbate the problem over time by increasing resistance and degrading materials. For hands-on troubleshooting, try our voltage drop calculator to quickly estimate the loss in your system.
Symptoms of Voltage Dropping in Electrical Systems
Voltage drops often manifest in subtle yet telltale ways. Common symptoms include:
-
Flickering or dimming lights
-
Motors that fail to start or run slower than normal
-
Heating devices that don’t reach full temperature
-
Intermittent resets or shutdowns in sensitive electronics
-
Unexpected tripping of breakers or protective devices
These symptoms are especially prominent during periods of peak load or in buildings with older wiring infrastructure. Left unaddressed, they can lead to long-term damage or premature failure of electrical equipment. Explore the voltage drop formula to gain a deeper understanding of how conductor size, distance, and load impact system performance. If you're working with DC circuits, see our in-depth article on DC voltage drop calculation.
Sign Up for Electricity Forum’s Power Quality Newsletter
Stay informed with our FREE Power Quality Newsletter — get the latest news, breakthrough technologies, and expert insights, delivered straight to your inbox.
How Voltage Dropping Affects Equipment and Infrastructure
When voltage consistently falls below the required operating level, electrical devices draw more current in an attempt to compensate for the shortfall. This overdraft can cause:
-
Overheating of motors and transformers
-
Reduced energy efficiency and higher operating costs
-
Shortened lifespan of sensitive devices
-
Increased risk of equipment failure and fire
In commercial and industrial facilities, voltage drops can disrupt production processes, interfere with automation systems, and increase downtime. For residential systems, it can damage appliances and lead to safety hazards.
Monitoring and Preventing Voltage Dropping
Effective monitoring is the first step toward preventing voltage dropping. Facilities should regularly inspect for:
-
Voltage fluctuations during load peaks
-
Signs of overheating at connections
-
Degradation in power-sensitive equipment
To mitigate voltage dropping, consider the following preventative strategies:
-
Use properly rated conductors for the application and load
-
Limit the length of wiring runs where possible
-
Regularly inspect and tighten electrical connections
-
Balance loads across phases in three-phase systems
-
Install voltage regulators or power conditioners for critical equipment
For systems with long cable runs or high current demands, a professional power quality assessment can help identify systemic causes and recommend corrective action. By monitoring system performance, maintaining wiring integrity, and applying preventative measures, facility managers and electricians can avoid costly downtime and keep equipment running at peak efficiency.
Related Pages




