Power System Analysis and Design
By R.W. Hurst, Editor
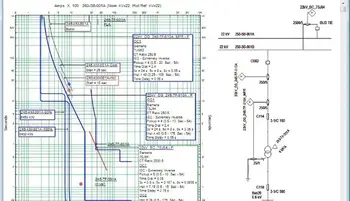
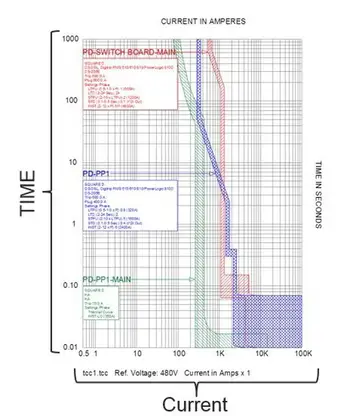
Short Circuit Study & Protective Device Coordination
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.
- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our NFPA 70E Fact Sheet – 2024 Electrical Safety Edition

- Understand how NFPA 70E works with NEC and NFPA 70B standards
- Clarify the shared responsibility between employers and employees
- Learn how NFPA 70E supports OSHA compliance
Power system analysis and design ensure the reliable, efficient operation of electrical networks. It encompasses load flow, fault analysis, and system optimization to ensure stable performance in power generation, transmission, and distribution.
What is Power System Analysis and Design?
Power system analysis and design are critical disciplines within electrical engineering, ensuring the efficient, reliable, and safe operation of electrical systems.
✅ Ensures reliable and efficient power delivery across grid components
✅ Involves load flow, short circuit, and stability studies
✅ Guides system upgrades, protection, and fault mitigation strategies
The intricate networks that deliver electricity from generation sources to consumers are the backbone of modern society. The field of analysis and design is dedicated to understanding, optimizing, and ensuring the reliability of these complex systems. As we transition towards renewable energy sources and grapple with increasing demand, the importance of this discipline grows exponentially. This article will examine key aspects of analysis, including the primary categories, components, principles, and methods, as well as the common software tools employed in the field. Power system engineering brings all of these principles together in a comprehensive discipline that supports the planning, development, and maintenance of modern power systems.
Visit our Power System Analysis and Design Training Page
The Pillars of Power System Analysis and Design
At its core, an analysis is divided into three key categories:
-
Steady-State Analysis: Examining the system's behaviour under normal operating conditions, engineers utilize tools like load flow studies to determine voltage levels, power flows, and losses within the grid. This information is crucial for efficient power delivery and identifying potential bottlenecks. A foundational aspect of steady-state system analysis is load flow analysis, which helps engineers model voltage profiles and power flows across complex grids.
-
Fault Analysis: Unexpected events such as short circuits, equipment failures, or lightning strikes can disrupt power flow and cause widespread outages. Fault analysis techniques, such as symmetrical components and Thevenin equivalent circuits, help engineers predict and mitigate the impact of these disturbances. Effective protection planning relies on precise short circuit current calculation to assess fault levels and equipment withstand ratings.
-
Stability Analysis: Maintaining the delicate balance between power generation and consumption is paramount. Stability analysis assesses the system's ability to withstand disturbances and return to a stable operating state, preventing cascading failures and blackouts.
Sign Up for Electricity Forum’s Electrical Engineering Newsletter
Stay informed with our FREE Electrical Engineering Newsletter — get the latest news, breakthrough technologies, and expert insights, delivered straight to your inbox.
Main Components
A typical system consists of six main components:
-
Generation: Facilities and equipment used to produce electricity, such as power plants and renewable energy sources.
-
Transmission: High-voltage lines and substations that transport electricity over long distances from generation sites to distribution networks.
-
Distribution: Lower-voltage networks that deliver electricity from transmission systems to end-users.
-
Loads: Devices and systems that consume electrical power, including residential, commercial, and industrial loads.
-
Protection Systems: Equipment and protocols designed to detect and isolate faults to protect the system and ensure safety.
-
Control Systems: Systems that monitor and regulate the operation of the power grid to maintain stability and efficiency. Learn how phase rotation meters are used to verify correct motor and transformer connections in three-phase systems.
Principles and Practices of Power System Analysis
Electrical Engineers rely on fundamental principles and sophisticated software tools to analyze and design electrical systems:
-
Ohm's Law and Kirchhoff's Laws form the basis for understanding electrical circuits.
-
Power equations are used to calculate power flow and losses in transmission lines.
-
The per-unit system simplifies calculations by normalizing values.
-
Software like ETAP, PSS/E, and PSCAD enable complex modeling and simulation, aiding engineers in making informed decisions.
To understand how voltage and current interact in real-world applications, explore our explanation of the 480 voltage power and current formula.
Performing Load Flow Analysis
Load flow analysis, also known as power flow analysis, involves solving a set of nonlinear algebraic equations to determine the steady-state operating condition. The key steps include:
-
Modelling the System: Representing components, such as generators, loads, transmission lines, and transformers, using appropriate mathematical models.
-
Formulating Equations: Developing the power flow equations based on Kirchhoff's laws and power equations.
-
Solving Equations: Using numerical methods, such as the Newton-Raphson method, to solve the power flow equations and determine the voltage magnitudes and angles at each bus in the system.
Common Methods for Fault Analysis
Fault analysis involves studying the effects of faults to design protective measures. Common methods include:
-
Symmetrical Components: A technique for analyzing unbalanced faults by decomposing them into balanced components.
-
Short Circuit Analysis: Determining the currents that flow during fault conditions to design protective devices.
-
Time-Domain Simulations: Using software tools to simulate fault conditions and study the dynamic response.
Advanced static var compensator technology improves voltage stability and reactive power control in modern grids.
Designing a Stable and Reliable Network
Designing an electrical system for stability and reliability involves several considerations:
-
Redundancy: Incorporating multiple pathways for power flow to ensure reliability in case of component failures.
-
Protection Schemes: Designing protective devices and systems to detect and isolate faults quickly.
-
Dynamic Stability Analysis: Studying the system's response to disturbances to ensure it can return to a stable operating state.
Software Tools for Power System Analysis and Design
Several software tools are commonly used for power system analysis and design:
-
ETAP (Electrical Transient Analyzer Program): A comprehensive tool for load flow, fault analysis, and stability studies.
-
PSS/E (Power System Simulator for Engineering): Widely used for power flow, stability, and dynamic simulations.
-
DIgSILENT PowerFactory: A powerful tool for analyzing and designing complex electrical systems.
These tools enable engineers to model, simulate, and analyze electrical systems with high accuracy, facilitating efficient and reliable design and operation. If you're building a career in this field, our hands-on power system training programs offer in-depth instruction on analysis tools and software.
Additionally, the rise of distributed energy resources (DERs), such as rooftop solar panels and electric vehicles, is transforming the traditional centralized grid into a more decentralized network. This requires new approaches to power system analysis and design, including the development of microgrids and the integration of advanced power electronics.
The Role of Advanced Technologies in Power System Analysis and Design
The digital revolution is transforming the power industry, with technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and big data analytics assuming an increasingly significant role in power system analysis and design. These tools can be used to optimize grid operation, predict and prevent equipment failures, and enhance overall system resilience.
Test Your Knowledge About Electrical Engineering!
Think you know Electrical Engineering? Take our quick, interactive quiz and test your knowledge in minutes.
- Instantly see your results and score
- Identify strengths and areas for improvement
- Challenge yourself on real-world electrical topics
Moreover, the advent of high-voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission is enabling the efficient transmission of electricity over long distances, facilitating the integration of remote renewable resources and enhancing grid interconnection.
Related Articles








