California's Looming Green New Car Wreck

Protective Relay Training - Basic
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
California Gas Car Ban 2035 signals a shift to electric vehicles, raising grid reliability concerns, charging demand, and renewable energy challenges across solar, wind, and storage, amid rolling blackouts and carbon-free power mandates.
Key Points
An order ending new gasoline car sales by 2035 in California, accelerating EV adoption and pressuring the power grid.
✅ 25% EV fleet could add 232.5 GWh/day charging demand by 2040
✅ Solar and wind intermittency strains nighttime home charging
✅ Grid upgrades, storage, and load management become critical
On September 23, California Gov. Gavin Newsom issued an executive order that will ban the sale of gasoline-powered cars in the Golden State by 2035. Ignoring the hard lessons of this past summer, when California’s solar- and wind-reliant electric grid underwent rolling blackouts, Newsom now adds a huge new burden to the grid in the form of electric vehicle charging, underscoring the need for a much bigger grid to meet demand. If California officials follow through and enforce Newsom’s order, the result will be a green new car version of a train wreck.
In parallel, the state is moving on fleet transitions, allowing electric school buses only from 2035, which further adds to charging demand.
Let’s run some numbers. According to Statista, there are more than 15 million vehicles registered in California. Per the U.S. Department of Energy, there are only 256,000 electric vehicles registered in the state—just 1.7 percent of all vehicles, a share that will challenge state power grids as adoption grows.
Using the Tesla Model3 mid-range model as a baseline for an electric car, you’ll need to use about 62 kilowatt-hours (KWh) of power to charge a standard range Model 3 battery to full capacity. It will take about eight hours to fully charge it at home using the standard Tesla NEMA 14-50 charger, a routine that has prompted questions about whether EVs could crash the grid by households statewide.
Now, let’s assume that by 2040, five years after the mandate takes effect, also assuming no major increase in the number of total vehicles, California manages to increase the number of electric vehicles to 25 percent of the total vehicles in the state. If each vehicle needs an average of 62 kilowatt-hours for a full charge, then the total charging power required daily would be 3,750,000 x 62 KWh, which equals 232,500,000 KWh, or 232.5 gigawatt-hours (GWh) daily.
Utility-scale California solar electric generation according to the energy.ca.gov puts utility-scale solar generation at about 30,000 GWh per year currently. Divide that by 365 days and we get 80 GWh/day, predicted to double, to 160 GWh /day. Even if we add homeowner rooftop solar, and falling prices for solar and home batteries in the wake of blackouts, about half the utility-scale, at 40 GWh/day we come up to 200 GW/h per day, still 32 GWh short of the charging demand for a 25% electric car fleet in California. Even if rooftop solar doubles by 2040, we are at break-even, with 240GWh of production during the day.
Bottom-line, under the most optimistic best-case scenario, where solar operates at 100% of rated capacity (it seldom does), it would take every single bit of the 2040 utility-scale solar and rooftop capacity just to charge the cars during the day. That leaves nothing left for air conditioning, appliances, lighting, etc. It would all go to charging the cars, and that’s during the day when solar production peaks.
But there’s a much bigger problem. Even a grade-schooler can figure out that solar energy doesn’t work at night, when most electric vehicles will be charging at homes, even as some officials look to EVs for grid stability through vehicle-to-grid strategies. So, where does Newsom think all this extra electric power is going to come from?
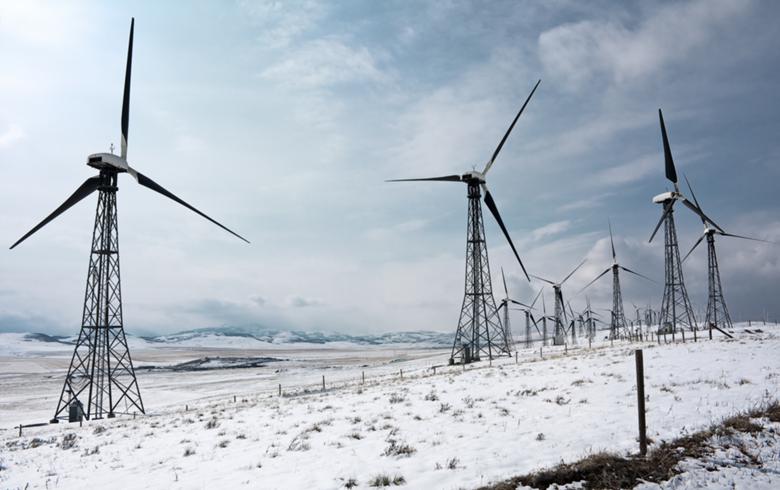
The wind? Wind power lags even further behind solar power. According to energy.gov, as of 2019, California had installed just 5.9 gigawatts of wind power generating capacity. This is because you need large amounts of land for wind farms, and not every place is suitable for high-return wind power.
In 2040, to keep the lights on with 25 percent of all vehicles in California being electric, while maintaining the state mandate requiring all the state’s electricity to come from carbon-free resources by 2045, California would have to blanket the entire state with solar and wind farms. It’s an impossible scenario. And the problem of intermittent power and rolling blackouts would become much worse.
And it isn’t just me saying this. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) agrees. In a letter sent by EPA Administrator Andrew Wheeler to Gavin Newsom on September 28, Wheeler wrote:
“[It] begs the question of how you expect to run an electric car fleet that will come with significant increases in electricity demand, when you can’t even keep the lights on today.
“The truth is that if the state were driving 100 percent electric vehicles today, the state would be dealing with even worse power shortages than the ones that have already caused a series of otherwise preventable environmental and public health consequences.”
California’s green new car wreck looms large on the horizon. Worse, can you imagine electric car owners’ nightmares when California power companies shut off the power for safety reasons during fire season? Try evacuating in your electric car when it has a dead battery.
Gavin Newsom’s “no more gasoline cars sold by 2035” edict isn’t practical, sustainable, or sensible, much like the 2035 EV mandate in Canada has been criticized by some observers. But isn’t that what we’ve come to expect with any and all of these Green New Deal-lite schemes?