Italy : Enel Green Power and Sapio sign an agreement to supply green hydrogen produced by NextHy in Sicily
Electrical Testing & Commissioning of Power Systems
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
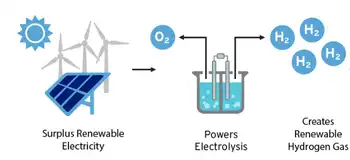
Sicily Green Hydrogen accelerates decarbonization via renewable energy, wind farm electrolysis, hydrogen storage, and distribution from Enel Green Power and Sapio at the NextHy industrial lab in Carlentini and Sortino Sicily hub.
Key Points
Sicily Green Hydrogen is an Enel-Sapio plan to produce hydrogen via wind electrolysis for industrial decarbonization.
✅ 4 MW electrolyzer powered by Carlentini wind farm
✅ Estimated 200+ tons annual green H2 production capacity
✅ Market distribution managed by Sapio across Sicily
This green hydrogen will be produced at the Sicilian industrial plant, an innovative hub that puts technology at the service of the energy transition, echoing hydrogen innovation funds that support similar goals worldwide
Activating a supply of green hydrogen produced using renewable energy from the Carlentini wind farm in eastern Sicily is the focus of the agreement signed by Enel Green Power and Sapio. The agreement provides for the sale to Sapio of the green hydrogen that will be produced, stored in clean energy storage facilities and made available from 2023 at the Carlentini and Sortino production sites, home to Enel Green Powers futuristic NextHy innitiative. Sapio will be responsible for developing the market and handling the distribution of renewable hydrogen to the end customer.
In contexts where electrification is not easily achievable, green hydrogen is the key solution for decarbonization as it is emission-free and offers a potential future for power companies alongside promising development prospects, commented Salvatore Bernabei, CEO of Enel Green Power. For this reason we are excited about the agreement with Sapio. It is an agreement that looks to the future by combining technological innovation and sustainable production.
Sapio is strongly committed to contributing to the EUs achievement of the UN SDGs, commented Alberto Dossi, President of the Sapio Group, and with this project we are taking a firm step towards sustainable development in our country. The agreement with EGP also gives us the opportunity to integrate green hydrogen into our business model, as jurisdictions propose hydrogen-friendly electricity rates to grow the hydrogen economy, which is based on our strong technological expertise in hydrogen and its distribution over 100 years in business. In this way we will also be able to give further support to the industrial activities we are already carrying out in Sicily.
The estimated 200+ tons of production capacity of the Sicilian hub is the subject of the annual supply foreseen in the agreement. Once fully operational, the green hydrogen will be produced mainly by a 4 MW electrolyzer, which is powered exclusively by the renewable energy of the existing wind farm, and to a lesser extent by the state-of-the-art electrolysis systems tested in the platform. Launched by Enel Green Power in September 2021, NextHys Hydrogen Industrial Lab is a unique example of an industrial laboratory in which production activity is constantly accompanied by technological research. In addition to the sectors reserved for full-scale production, there are also areas dedicated to testing new electrolyzers, components such as valves and compressors, and innovative storage solutions based on liquid and solid means of storage: in line with Enels open-ended approach, this activity will be open to the collaboration of more than 25 entities including partners, stakeholders and innovative startups. The entire complex is currently undergoing an environmental impact assessment at the Sicily Regions Department of Land and Environment.
It is an ambitious project with a sustainable energy source at its heart that will be developed at every link in the chain: thanks to the agreement with Sapio, in fact, at NextHy green hydrogen will now not only be produced, stored and moved on an industrial scale, but also purchased and used by companies that have understood that green hydrogen is the solution for decarbonizing their production processes. In this context, this experimental approach that is open to external contributions will allow the Enel Green Power laboratory team to test the project on an industrial scale, so as to create the best conditions for a commercial environment that can make the most of all present and future technologies for the generation, storage and transport of green hydrogen, including green hydrogen microgrids that demonstrate scalable integration. It is an initiative consistent with Enels Open Innovability spirit: meeting the challenges of the energy transition by focusing on innovation, ideas and their transformation into reality.











