Tesla’s lead battery expert hired by Uber to help power its ‘flying car’ service

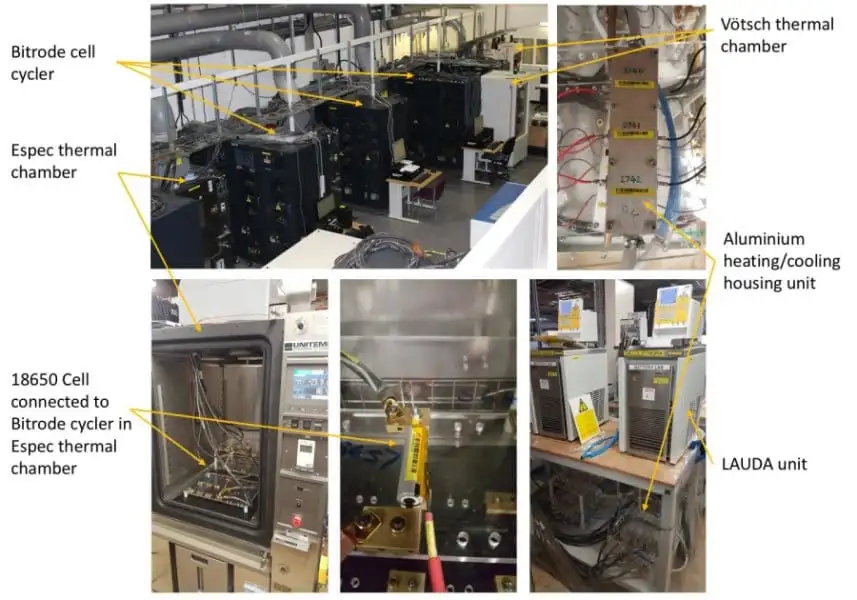
Protective Relay Training - Basic
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Uber Elevate eVTOL Batteries enable electric air taxis with advanced energy storage, lithium-ion cell quality, safety engineering, and zero-emissions performance for urban air mobility, ride-hailing aviation, and scalable battery pack development.
Key Points
Battery systems for Uber's electric air taxis, maximizing energy density, safety, and cycle life for urban air mobility.
✅ Ex-Tesla battery leader guides pack design and cell quality
✅ All-electric eVTOL targets zero-emissions urban air mobility
✅ Focus on safety, energy density, fast charge, and lifecycle
Celina Mikolajczak, a senior manager for battery pack development at Tesla, has been hired by Uber to help the ride-hail company’s “flying car” project get off the ground. It’s an important hire because it signals that Uber plans to get more involved in the engineering aspects of this outlandish-sounding project.
For six years, Mikolajczak served as senior manager and technical lead for battery technology, cell quality, and materials analysis. She worked with Tesla’s suppliers, tested the car company’s lithium-ion batteries for long-term use as the age of electric cars accelerates, oversaw quality assurance, and conducted “failure analysis” to drive battery cell production and design improvements. In other words, Mikolajczak was in charge of making sure the most crucial component in Tesla’s entire assembly line was top of the line.
Now she works for Uber — and not just for Uber, but for Uber Elevate, the absurdly ambitious air taxi service that hinges on the successful development of electric vertical take-off and landing (eVTOL) vehicles. There are practically zero electric planes in service today, and definitely none being used in a commercial ride-hail service. The hurdles to getting this type of service off the ground are enormous.
Her title at Uber is director of engineering and energy storage systems, and today marks her first week on the job. She joins Mark Moore, the former chief technologist for on-demand mobility at NASA’s Langley Research Center, who joined Uber almost a year ago to help lend a professional appearance to Elevate. Both serve under Jeff Holden, Uber’s head of product, who oversees the air taxi project.
Uber first introduced its plan to bring ride-sharing to the skies in a white paper last year. At the time, Uber said it wasn’t going to build its own eVTOL aircraft, but stood ready to “contribute to the nascent but growing VTOL ecosystem and to start to play whatever role is most helpful to accelerate this industry’s development.”
Instead, Uber said it would be partnering with a handful of aircraft manufacturers, real estate firms, and government regulators to better its chances of developing a fully functional, on-demand flying taxi service. It held a day-long conference on the project in Dallas in April, and plans to convene another one later this year in Los Angeles. In 2020, Uber says its aerial service will take off in three cities: LA, Dallas-Fort Worth, and Dubai.
UBER’S TAKING A MORE PROMINENT ROLE
Now, Uber’s taking a more prominent role in the design and manufacturing of its fleet of air taxis, which signals a stronger commitment to making this a reality — and also more of a responsibility if things eventually go south, as setbacks like Eviation's collapse underscore.
Perhaps most ambitiously, Uber says the aircraft it plans to use (but, importantly, do not exist yet) will run on pure battery-electric power, and not any hybrid of gasoline and electricity. Most of the companies exploring eVTOL admit that battery’s today aren’t light enough or powerful enough to sustain flights longer than just a few minutes, but many believe that battery technology will eventually catch up, with Elon Musk suggesting a three-year timeline for cheaper, more powerful cells.
Uber believes that in order to sustain a massive-scale new form of transportation, it will need to commit to an all-electric, zero-operational emissions approach from the start, even as potential constraints threaten the EV boom overall. And since the technology isn’t where it needs to be yet, the ride-hail company is taking a more prominent role in the development of the battery pack for its air taxi vehicles. Mikolajczak certainly has her work cut out for her.