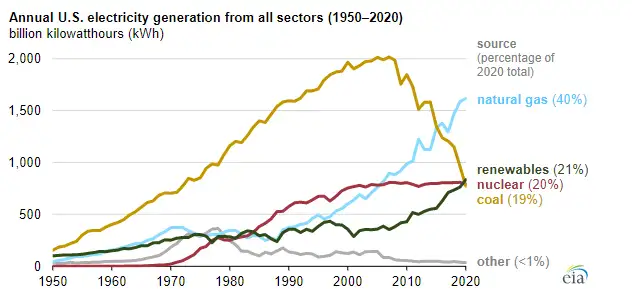
Renewables Projected to Soon Be One-Fourth of US Electricity Generation

CSA Z463 Electrical Maintenance -
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 6 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
U.S. Renewable Energy Forecast 2024 will see wind and solar power surpass one-fourth of electricity generation, EIA projects, as coal declines, natural gas dips, and clean energy capacity, grid integration, and policy incentives expand.
Key Points
EIA outlook: renewables at 26% of U.S. power in 2024, led by wind and solar as coal declines and gas share dips.
✅ Wind and solar hit 18% combined, surpassing coal's 17%.
✅ Natural gas dips to 37% as demand rebounds modestly.
✅ Coal plant closures accelerate amid costs, emissions, and age.
Renewable energy is poised to reach a milestone, after a record 28% in April this year, as a new government report projects that wind, solar and other renewable sources will exceed one-fourth of the country’s electricity generation for the first time, in 2024.
This is one of the many takeaways from the federal government’s Short Term Energy Outlook, a monthly report whose new edition is the first to include a forecast for 2024. The report’s authors in the Energy Information Administration are expecting renewables to increase in market share, while natural gas and coal would both decrease.
From 2023 to 2024, renewables would rise from 24 percent to 26 percent of U.S. electricity generation; coal’s share would drop from 18 percent to 17 percent; gas would remain the leader but drop from 38 percent to 37 percent; and nuclear would be unchanged at 19 percent.
It was a big deal in 2020 when generation from renewables passed coal for the first time in 130 years over a full year. Coal made a comeback in 2021 and then retreated again in 2022 as renewables surpassed coal in generation. The ups and downs were largely the result of fluctuations in electricity demand during and then after the Covid-19 pandemic.
The new report indicates that coal doesn’t have another comeback in the works. This fuel, which was the country’s leading electricity source less than a decade ago, is declining as many coal-fired power plants are old and economically uncompetitive. Coal plants continue to close, and developers aren’t building new ones because of concerns about high costs and emissions, a trend underscored when renewables became the second-most prevalent source in 2020 across the U.S.
The growth in renewable energy is coming from wind and solar power, with wind responsible for about one-third of the growth and solar accounting for two-thirds, the report says, and combined output from wind and solar has already exceeded nuclear for the first time in the U.S. Other renewable sources, like hydropower and biomass, would be flat.
In fact, the growth of wind and solar is projected to be so swift that the combination of just those two sources would be 18 percent of the U.S. total by 2024, which would surpass coal’s 17 percent.
A key variable is overall electricity consumption. EIA is projecting that this will fall 1 percent in 2023 compared to 2022, due a mild summer. Then, consumption will increase 1 percent in 2024.
If demand was rising more, then natural gas power would likely gain market share because of gas power plants’ ability to vary their output as needed to respond to changes in demand.
I asked Eric Gimon, a senior fellow at the think tank Energy Innovation, what he thinks of these latest numbers.
He said wind and solar have gotten so big that it almost makes sense to track them as their own categories as opposed to lumping them into the larger category of renewables. He expects that the government will do this sometime soon.
Also, he thinks the projected increases for wind and solar, while substantial, are still smaller than those resources are likely to grow.
“My experience over the last 10 years is that the EIA tends to have flattish forecasts,” he said, meaning the federal office has underestimated the actual growth.
Some energy analysts have criticized EIA for being slow to recognize the growth of renewables. But much of the criticism is about the Annual Energy Outlook, which has numbers going out to mid-century, even as the U.S. is moving toward 30% from wind and solar by the end of the decade. The Short Term Energy Outlook, with numbers going one year into the future, has been more reliable.
Gimon said EIA is “kind of like your conservative uncle” in its forecasts, so it’s notable that the office expects to see a significant uptick in wind and solar.
Even so, he thinks the latest Short Term Energy Outlook should be read as the lower end of the range of potential increase for wind and solar.
For him to be right, the wind and solar industries will need to figure out solutions to the challenges they’ve been having in obtaining parts; they will need to make progress in dealing with local opposition to many projects and in having enough interstate power lines to deliver the electricity. And, new policies like the Inflation Reduction Act will need to have their desired effect of encouraging projects through the use of tax incentives.
It’s not much of a stretch to imagine that clean energy industries will make some progress on all of those fronts.