Ground Grid Testing of Substation Cost Sheet
By R.W. Hurst, Editor
Substation Relay Protection Training
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our OSHA 4475 Fact Sheet – Being Aware of Arc Flash Hazards

- Identify root causes of arc flash incidents and contributing conditions
- Apply prevention strategies including LOTO, PPE, and testing protocols
- Understand OSHA requirements for training and equipment maintenance
A ground grid testing of substation cost sheet outlines testing expenses for grid resistance, soil resistivity, and step/touch voltage. This essential document helps estimate costs, ensure safety, and meet IEEE 80 standards for substation grounding performance.
What Is Ground Grid Testing of Substation Cost Sheet?
A ground grid testing of the substation cost sheet details the financial and technical aspects of evaluating substation grounding systems.
✅ Helps plan cost-effective testing for substation ground systems
✅ Covers equipment, labor, testing methods, and project variables
✅ Supports regulatory compliance and electrical safety standards
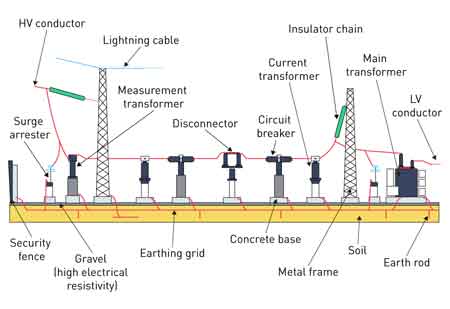
A reliable substation ground system is crucial for ensuring safety, protecting equipment, and meeting regulatory requirements. Without proper grounding, electrical faults can generate dangerous step voltage and touch voltage conditions that pose a threat to workers and infrastructure. Ground grid assessment verifies that the system is capable of safely dissipating fault current into the earth. This article provides a detailed overview of assessment methods, associated costs, and factors influencing project budgets—with an emphasis on cost-effective planning for substations of all sizes.
Electrical Transformer Maintenance Training
Substation Maintenance Training
Request a Free Training Quotation
Introduction to Ground Grid Testing
Ground grid evaluation is a critical process for ensuring that the grounding network in a substation performs its function under real-world fault conditions. The goal is to ensure the ground system can carry high currents into the earth without creating unsafe surface voltages. Key industry standards such as IEEE 80 and IEEE 81 provide the basis for evaluating these systems.
-
IEEE Std 80 outlines design criteria and safety limits for step and touch voltages in substation ground systems.
-
IEEE Std 81 describes proper procedures for measuring soil resistivity and ground impedance during field testing.
If you need a broader understanding of how substations function, visit our page on what is an electrical substation.
FREE EF Electrical Training Catalog
Download our FREE Electrical Training Catalog and explore a full range of expert-led electrical training courses.

- Live online and in-person courses available
- Real-time instruction with Q&A from industry experts
- Flexible scheduling for your convenience
Ground Grid Testing of Substation Cost Sheet – Example Table
| Substation Size | Testing Methods | Estimated Cost Range | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small | Soil Resistivity + Continuity Testing | $5,000 – $10,000 | Suitable for compact substations or remote sites with simple layouts. |
| Medium | Current Injection + Ground Integrity Testing | $10,000 – $20,000 | Ideal for suburban substations with moderate fault current exposure. |
| Large | Comprehensive (CIT, Soil, Continuity) | $20,000 – $40,000 | Best for high-voltage substations needing full compliance verification. |
Detailed Cost Breakdown
A thorough cost sheet for ground grid evaluation includes verification methodology, labor and equipment expenses, and ancillary charges. Engineers and planners must know how to control these costs through proper scheduling and method selection to deliver a cost-effective grounding analysis.
Assessment Methods
The selection of verification techniques depends on substation layout, soil conditions, and project goals. Common procedures include:
-
Current Injection Verification (CIT): This method applies controlled current to simulate fault scenarios, measuring step voltage, touch voltage, and ground potential rise.
-
Soil Resistivity Measurement: Helps determine how effectively the earth can dissipate current—an essential step in ground grid design or upgrade planning.
-
Continuity and Integrity Inspection: Confirms the performance of buried ground conductors and interconnections, including grounding rods and bonding points.
Substations with digital relays or automated systems benefit most from comprehensive analysis, especially during substation automation projects.
Equipment Costs
Testing requires specialized hardware, which may be rented or purchased depending on testing frequency:
-
Purchase: Advanced ground testers, such as the DV Power GGT200, can cost over $10,000, making them a viable investment for high-volume or in-house testing programs.
-
Rental: Renting a substation earth tester is a cost-effective alternative for periodic testing, usually priced between $50 and $80 per day.
Labor Costs
Technician costs represent a significant portion of any testing budget. Rates are influenced by location, project scale, and required qualifications:
-
Technician Rates: Specialists in grid testing typically charge $100 to $250/hour.
-
Duration: Testing a simple site may take one day, while testing complex systems with multiple grounding rods, transformers, or breakers may take several days.
For substations with aging infrastructure or inadequate documentation, refer to our resource on electrical substation maintenance.
Miscellaneous Costs
Additional expenses should be planned for in your cost sheet:
-
Travel and Logistics: Includes mobilization of test personnel and shipping of equipment, especially when working on tie substations or remote sites.
-
Analysis and Reporting: Post-test analysis and compliance reporting typically cost $1,000 to $3,000, depending on the level of detail required.
Sample Cost Sheets
These sample budgets provide approximate costs by substation size:
Small Substation
-
Method: Soil Resistivity + Continuity Evaluation
-
Estimated Cost: $5,000 – $10,000
Medium Substation
-
Method: Current Injection + Ground Integrity Inspection
-
Estimated Cost: $10,000 – $20,000
Large Substation
-
Method: Comprehensive Assessment (CIT, Soil, Continuity)
-
Estimated Cost: $20,000 – $40,000
For a breakdown of equipment typically included in these estimates, visit our guide on electrical substation components.
MISO Transmission Cost Estimate Guide
The MISO Transmission Cost Estimation Guide, a comprehensive planning resource developed to help utilities, engineers, and project developers estimate costs for transmission-related projects, including substation upgrades and ground grid testing.
Published by the Midcontinent Independent System Operator (MISO), a not-for-profit organization that manages the electric grid across 15 U.S. states and the Canadian province of Manitoba, the Ground Grid Testing of Substation Cost Sheet provides a standardized approach to forecasting costs in large-scale electrical infrastructure projects. MISO is responsible for ensuring grid reliability, coordinating electricity transmission, and operating the wholesale energy market across a broad region of North America.
This guide can help readers understand typical labor and equipment rates, identify key cost drivers, and develop cost-effective budgets that align with regulatory expectations. It’s a valuable tool for promoting transparency, consistency, and informed decision-making in the planning and execution of substation and transmission projects.
Factors Influencing a Ground Grid Testing of Substation Cost Sheet
Many conditions outside the test itself can affect the total project cost and complexity:
-
Soil Conditions: Difficult or high-resistance soil may require deeper grounding rods or expanded ground grid layouts.
-
Substation Age and Configuration: Older facilities often need more thorough inspection due to undocumented modifications or degradation of ground conductors.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Utilities in urban or industrial zones often face more rigorous inspection criteria, particularly for substation ground systems serving critical infrastructure or prone to substation explosions.
Whether you're commissioning a new substation or maintaining aging infrastructure, a good Ground Grid Testing of Substation Cost Sheet is key to ensuring safety, performance, and compliance. By understanding the cost structure of various methods, labour, and site logistics, you can develop a more accurate and cost-effective budget that supports reliability and long-term integrity.
Sign Up for Electricity Forum’s Electrical Substations Newsletter
Stay informed with our FREE Electrical Substations Newsletter — get the latest news, breakthrough technologies, and expert insights, delivered straight to your inbox.
If you’re looking for technical training or planning support, explore our electrical substation training programs or consult with our substation maintenance training team.
Related Articles