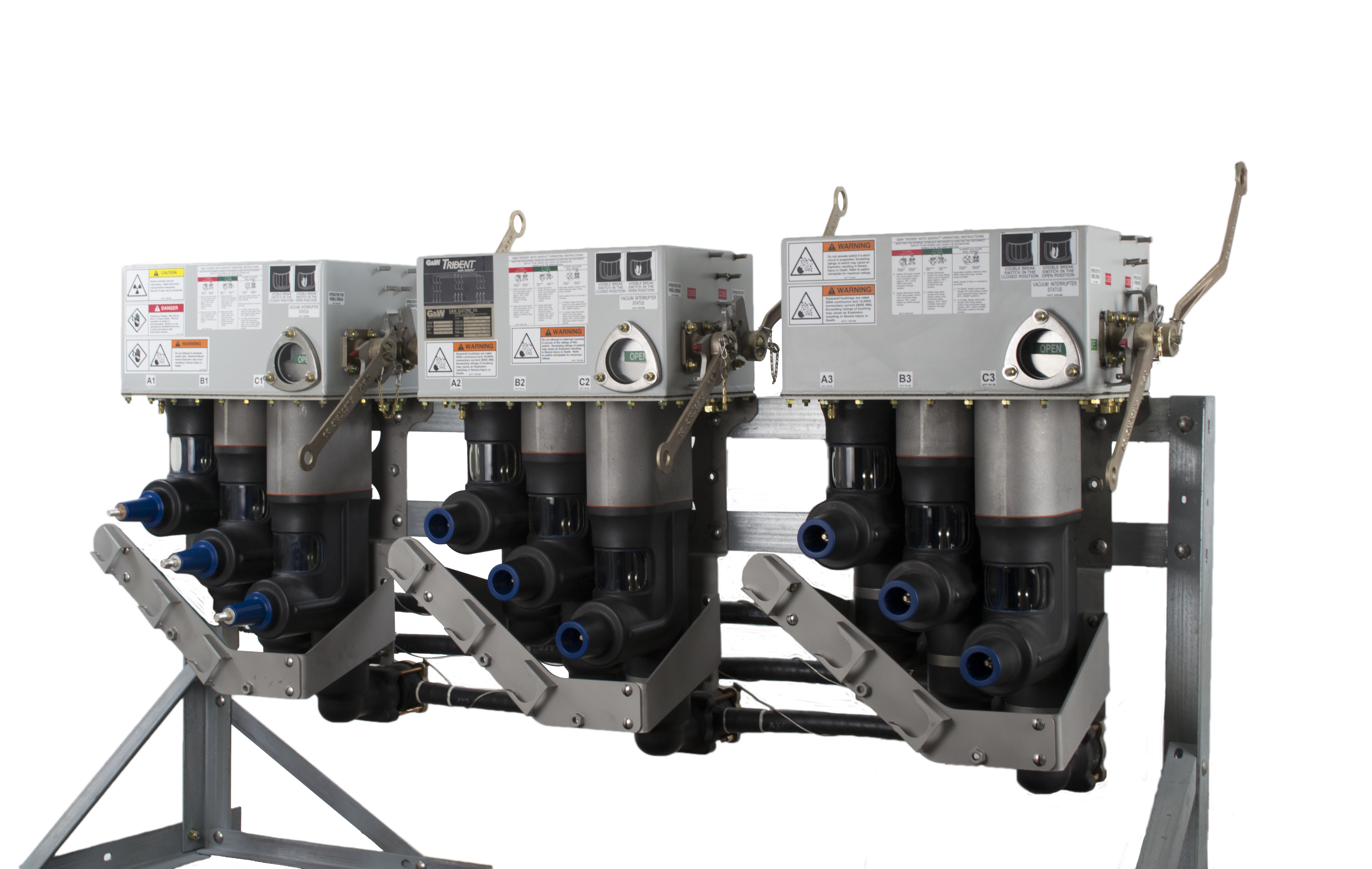
Electrical Substation Maintenance: Protecting Assets

Substation Relay Protection Training
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our OSHA 3875 Fact Sheet – Electrical PPE for Power Industry Workers

- Follow rules for rubber gloves, arc-rated PPE, and inspection procedures
- Learn employer obligations for testing, certification, and training
- Protect workers from arc flash and electrical shock injuries
Electrical substation maintenance involves testing, inspection, and diagnostics to prevent failures, reduce power outages, and extend equipment life. It enhances system reliability, supports compliance, and uses real-time data to detect early signs of wear or malfunction.
What is Electrical Substation Maintenance?
plays a vital role in ensuring the safety, reliability, and performance of modern power systems. Substations manage voltage levels, regulate power flow, and distribute electricity efficiently. Without proper inspection and servicing, substation equipment is more likely to fail—leading to power outages, equipment damage, and expensive downtime.
✅ Electrical substation maintenance is the routine inspection, testing, and servicing of equipment like transformers, circuit breakers, and protective relays to ensure system reliability and safety.
✅ It detects early signs of wear or failure using tools such as infrared thermography, power factor testing, and data analytics to prevent unplanned outages.
✅ Maintenance supports regulatory compliance, improves power flow and asset performance, and extends the life of critical infrastructure.
Electrical Transformer Maintenance Training
Substation Maintenance Training
Request a Free Training Quotation
By adopting proactive maintenance strategies supported by real-time monitoring, data analytics, and asset management tools, utilities can reduce the risk of faults, extend the life of high-voltage equipment, and maintain continuous service. Effective inspection and testing practices are best understood in the context of what an electrical substation is, since maintenance directly supports safe and reliable grid operations.
Why Substation Maintenance Matters
Routine substation maintenance is essential for:
-
Preventing equipment failures that can trigger widespread power outages
-
Improving safety and compliance with Department of Energy and utility standards
-
Supporting the reliability of transformers, circuit breakers, and protective relays
-
Enhancing overall grid stability and asset performance
Substations are high-voltage environments with complex systems. Maintenance efforts must target key assets like electrical substation transformer, circuit breaker in substation, and substation protection to ensure safe operation.
Electricity Today T&D Magazine Subscribe for FREE

- Timely insights from industry experts
- Practical solutions T&D engineers
- Free access to every issue
Condition Monitoring and Testing
Detecting early signs of equipment degradation is the cornerstone of a successful substation maintenance strategy. Key diagnostic tests include:
-
Power factor testing: Assesses insulation condition on transformers and switchgear
-
Dissolved gas analysis: Detects gases in transformer oil that indicate internal faults
-
Infrared thermography: Locates overheating in conductors and connections
-
Partial discharge testing: Identifies weaknesses in insulation systems
-
Transformer turns ratio (TTR) tests: Validate transformer winding conditions
These tests help identify performance declines early, thereby reducing the risk of failure and allowing for planned maintenance.
Preventive and Predictive Maintenance
There are two core approaches to substation upkeep:
-
Preventive maintenance includes routine inspections and scheduled servicing of equipment, such as substation components, to catch wear before it leads to breakdowns.
-
Predictive maintenance uses advanced tools like SCADA systems, thermal imaging, and load flow analysis to predict failures based on equipment behavior. This strategy relies heavily on real-time data analytics and management software.
Together, they support condition-based interventions that optimize costs and improve system reliability.
Asset Management and Lifecycle Optimization
Substations must be managed as part of a broader asset lifecycle strategy. Through continuous monitoring and diagnostics, utility companies can:
-
Schedule upgrades before critical failures
-
Extend the useful life of aging infrastructure
-
Reduce long-term capital expenditures
Substation automation plays a crucial role in gathering performance data and feeding it into modern asset management systems. This integration allows planners to align maintenance with long-term investment goals.
Safety and Compliance
Substations are inherently hazardous. Maintenance helps enforce substation grounding requirements and ensures fault detection systems operate properly. This protects personnel and ensures compliance with regulatory guidelines, such as those from the Department of Energy and OSHA.
Proper maintenance of protective devices and grounding systems reduces the risk of arc flash events and improves emergency response preparedness.
Role of Technology in Modern Substation Maintenance
Technology is transforming substation maintenance through:
-
Real-time condition monitoring: Sensors and SCADA deliver up-to-the-minute performance data
-
Digital twins: Simulate equipment behaviour to optimize servicing schedules
-
Automated fault alerts: Notify teams of failures before they escalate
-
AI-powered analytics: Enhance decision-making for predictive repairs
These tools enable teams to address failures more quickly and allocate resources more efficiently.
To learn more about how technology supports maintenance strategies, visit our digital substation page.
FAQs
What types of equipment are included in substation maintenance?
Transformers, circuit breakers, protective relays, switches, and grounding systems are key. These components regulate voltage, isolate faults, and protect the grid.
How does maintenance reduce outages?
Maintenance detects faults early, helping avoid unplanned outages. It improves electrical substation reliability and extends equipment life.
How is technology changing maintenance practices?
Digital tools, such as remote sensors, SCADA, and AI, now monitor systems in real-time. This enables faster, more targeted servicing and smarter long-term planning.
What standards apply to substation maintenance?
The Department of Energy and IEEE establish guidelines for inspections, safety testing, and the performance of power assets.
Where can I learn more?
Enroll in our substation maintenance training to build your skills in diagnostics, testing, and compliance.
Related Articles