What Is An Electrical Substation?

Substation Maintenance Training
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our OSHA 3075 Fact Sheet – Understanding Electrical Hazards in the Workplace

- Learn the effects of electric current on the human body
- Understand OSHA safety standards and protective devices
- Discover essential lockout/tagout and grounding practices
An electrical substation is a key facility in the power system where voltage levels are transformed, electricity is controlled, and energy is routed through transmission and distribution networks to ensure safe, efficient, and reliable power delivery.
What Is An Electrical Substation?
It is a key facility in the power grid that manages voltage and power flow to ensure electricity is transmitted and distributed safely. It:
✅ Transforms electricity from high voltage to lower levels for safe and efficient distribution.
✅ Routes and controls power through transmission lines, transformers, and switchgear.
✅ Enables safe and efficient system reliability, network stability, and grid protection.
Electrical Transformer Maintenance Training
Substation Maintenance Training
Request a Free Training Quotation
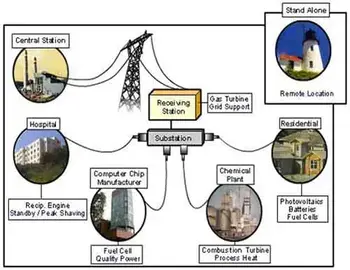
In a modern grid, power generators located at power plants initiate the electricity generation process, producing electricity that is delivered over high-voltage transmission lines. These lines connect to transmission substations, which step down voltage levels for regional delivery through the broader transmission system. As electricity moves closer to consumers, it enters a distribution substation, where the voltage is further reduced for safe delivery through the distribution network. This network ensures homes, businesses, and industries receive reliable power in the final distribution stage. The coordinated operation of distribution substations, transmission substations, and the entire transmission system is crucial for efficiently linking power generators with end-users across vast geographic areas. There are various types of substations. Each electrical substation is crucial in connecting a high-voltage transmission network voltage to a level suitable for local distribution.
Why Substations Are Essential
They are technical facilities and control hubs for the modern power system. They allow electricity to flow at the correct voltage, in the correct direction, and with built-in protection in case something goes wrong.
Sign Up for Electricity Forum’s Electrical Substations Newsletter
Stay informed with our FREE Electrical Substations Newsletter — get the latest news, breakthrough technologies, and expert insights, delivered straight to your inbox.
Proper functioning is essential to maintaining a stable and efficient energy supply. As a critical substation facility, it serves as a voltage conversion station, adjusting electricity levels to ensure safe transmission and distribution. Its role in the power grid involves routing electricity from high-voltage transmission lines to lower-voltage distribution networks, making it a central hub for power distribution. Without these facilities, managing the energy flow from generation sources to end-users would be impossible.
Key Functions:
-
Step up the voltage for transmission or step down for distribution
-
Switch circuits on or off during operation or maintenance
-
Detect and isolate faults automatically
-
Regulate load flow across the grid
-
Provide monitoring and control through remote systems
Transformers in Substations
Transformers are the heart of every substation. They change voltage levels between transmission and distribution systems, enabling long-distance transmission and safe end-use delivery. Without them, the grid would be unable to move electricity efficiently.
→ Learn more in our full guide on Electrical Substation Transformers.
What Equipment Is Inside?
Various specialized components work together inside a substation to manage and facilitate voltage transformation. These components must be precisely coordinated to ensure operational safety and efficiency.
Typical Components:
-
Transformers – Change voltage levels between transmission and distribution
-
Circuit Breakers – Interrupt power during faults
-
Disconnect Switches – Isolate equipment for maintenance
-
Busbars – Route current between incoming and outgoing lines
-
Protective Relays – Detect abnormal power delivery conditions
-
Control Systems – Monitor and automate switching and protection
For more details, read our guide on Circuit Breaker in Substation Explained.
Core Substation Components
Beyond transformers, substations rely on multiple interconnected devices, including switchgear, breakers, and protective relays. Each plays a crucial role in ensuring electricity flows safely and reliably. Explore the full list of devices in Electrical Substation Components.
Different Types
Substations are categorized by their roles in the power grid infrastructure. Each type has a specific purpose: stepping up or down in voltage, converting current, switching, and protection.
Common Types Include:
-
Transmission substations – Connect high-voltage systems and manage bulk power flow
-
Distribution substation – Deliver lower-voltage power to homes and businesses
-
Collector – Aggregate renewable energy sources
-
Converter – Convert AC to DC or vice versa for long-distance or specialized transmission
-
Switching – Reroute power without changing voltage
Learn more about how transmission substations step down voltage before distribution in our article What Is A Tie Substation.
Designing a Modern Substation
Design must consider space, safety, scalability, and the environment. The layout and physical structure vary depending on the site, voltage levels, and system requirements. Read more about engineering practices in Electrical Substation Design.
Design Priorities Include:
-
Proximity to load centers and transmission corridors
-
Flexible layouts (single, double, ring, etc.)
-
Secure fencing, barriers, and controlled access
-
Integration with digital controls and automation
-
Environmental compliance and aesthetic considerations
Learn more about layout trends in 3D Substation Design Utilizing AutoCAD.
How Substations Ensure Safety
Safety is non-negotiable when it comes to operation. Grounding systems, protective relays, and remote-control systems work together to protect personnel and prevent equipment damage.
Safety Systems Typically Include:
-
Grounding grids to prevent shock hazards
-
Arc flash protection for switchgear and circuit breakers
-
Insulation monitoring for cables and transformers
-
Fault detection with intelligent relays
-
Safety clearances and labeling for high-voltage zones
Visit Substation Grounding - Ensuring Safety, for more on how substations are grounded and safeguarded.
Maintaining Substation Reliability
Maintenance ensures they perform as intended over decades of service. Scheduled testing and equipment inspections help prevent unplanned outages and costly failures.
Typical Maintenance Tasks:
-
Infrared thermography for hotspots
-
Oil analysis for transformer health
-
Relay calibration and breaker timing tests
-
Physical inspections of busbars, insulators, and switches
-
Recordkeeping and remote diagnostic monitoring
Explore routine and advanced practices in Electrical Substation Maintenance.
Electricity Today T&D Magazine Subscribe for FREE

- Timely insights from industry experts
- Practical solutions T&D engineers
- Free access to every issue
Who Works in a Substation?
Operating and maintaining these stations requires skilled professionals who are trained in safety, transmission and distribution (T&D) systems, and protective equipment. Their job titles may include technicians, protection engineers, and linemen.
Workforce Roles Involve:
-
Monitoring equipment status and alarms
-
Performing safe lockout/tagout procedures
-
Testing and replacing relays, fuses, or breakers
-
Responding to faults or service disruptions
-
Coordinating with control centers during switching
To learn about classification and training pathways, see What Is Working On Substations As Lineman Classified As.
Training and Certification
Substation workers need both formal education and hands-on instruction to ensure safe operations. Courses often include T&D power system theory, protection systems, grounding, and digital control platforms.
Training Topics Often Cover:
-
Design fundamentals
-
High-voltage switching procedures
-
SCADA and protection relay logic
-
Ground resistance testing
-
PPE and all safety regulations
Find out what’s covered in our Electrical Substation Training Explained.
Emerging Technologies in Design
Digital substations are the future. Modern facilities increasingly rely on intelligent electronic devices (IEDS), digital relays, and fibre-optic communications. This shift allows real-time monitoring, remote fault location, and predictive maintenance.
Key Trends Include:
-
Integration with smart grid and SCADA systems
-
Digital relays replacing analog controls
-
Use of IEC 61850 for sub automation
-
Adoption of environmental design standards
-
Predictive analytics for condition-based maintenance
Explore innovation further in Substation Focused on Environmental Design.
They are far more than fenced yards with transformers—they are engineered hubs of precision, protection, and power control. They are essential for transforming electricity into a usable, safe form for the world to consume. From safety systems and advanced monitoring to renewable energy integration and digital transformation, they are the foundation of a modern, resilient transmission and distribution (T&D) grid.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an Electrical Substation – Role in the Power Grid & Electrical Distribution?
A substation is a facility in the power grid where voltage is transformed, electricity is routed, and flow is controlled to ensure safe, efficient distribution. The most critical component is the transformer, which enables long-distance transmission. Together with breakers, relays, and switchgear, substations maintain grid stability and reliable delivery to end-users.
What are the considerations in substation design?
Key factors include site location, voltage levels, the number of transformers and circuits, and safety clearances. Design must also account for environmental impacts, such as noise, electromagnetic fields, and visual disturbance, while ensuring scalability and compliance with relevant regulations.
What are the components of a substation?
Transformers, circuit breakers, switchgear, protective relays, busbars, and power lines all work together to efficiently and safely transform, route, and distribute electricity across the grid.
How is maintenance performed?
Maintenance includes inspecting, cleaning, testing, and repairing or replacing faulty equipment parts. Regular thermography, oil analysis, and relay calibration help prevent failures and ensure substations operate reliably.
How does a substation impact the environment?
Substations can create noise, electromagnetic fields, and visual impacts. To minimize effects, engineers use noise barriers, underground cabling, landscaping, and modern equipment that reduces emissions while meeting environmental standards.
Related Articles