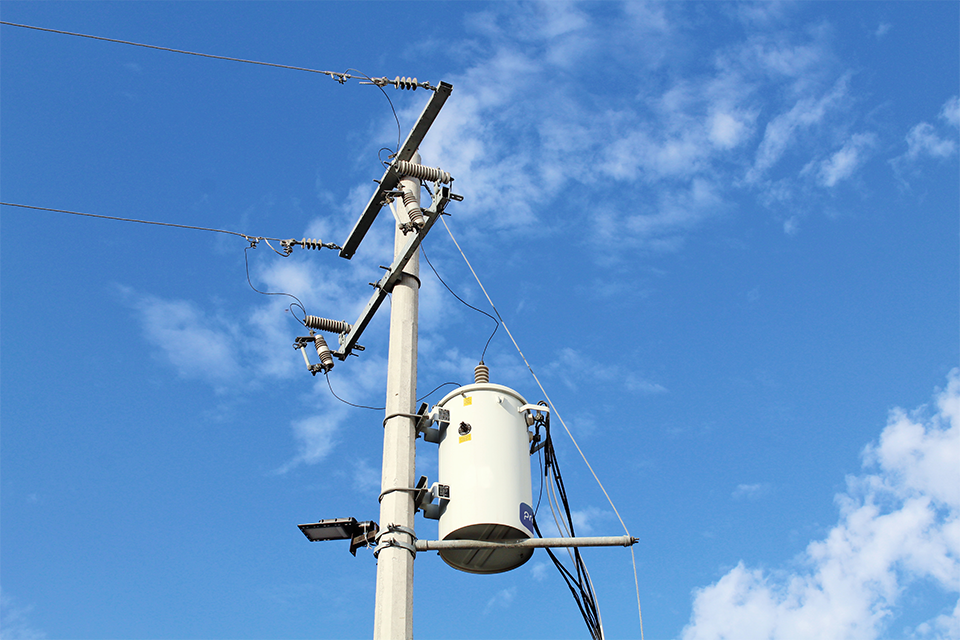
Power Pole Transformer And T&D

Power Transformer Maintenance Training
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our NFPA 70E Fact Sheet – 2024 Electrical Safety Edition

- Understand how NFPA 70E works with NEC and NFPA 70B standards
- Clarify the shared responsibility between employers and employees
- Learn how NFPA 70E supports OSHA compliance
A power pole transformer steps down high-voltage electricity from distribution lines to usable levels for homes and businesses. Mounted on utility poles, these transformers play a key role in electrical power distribution, ensuring safe, efficient energy delivery.
What is a Power Pole Transformer?
A power pole transformer is a distribution transformer mounted on a utility pole. It converts high-voltage electricity to lower voltages for safe residential and commercial use.
✅ Steps down utility line voltage for household use
✅ Mounted on power poles for efficient distribution
✅ Ensures safe, reliable electricity delivery
It is a vital piece of equipment in distribution transformer networks, responsible for stepping down high-voltage electricity into lower, manageable voltages for safe and effective use in various systems. Understanding how electrical pole equipment operates is crucial for safety, performance, and system reliability. Let’s explore the components and applications of these devices to support maintenance, installation, and troubleshooting for industrial electricians.
Electrical Transformer Maintenance Training
Substation Maintenance Training
Request a Free Training Quotation
Mounting and Installation
Mounted on utility poles, often wood or concrete, these devices are elevated to improve safety and delivery efficiency. The pole-mounted transformer setup is ideal for outdoor distribution, reducing contact risks while providing easy access to power lines in both urban and rural environments. Positioned high above ground, they not only enhance accessibility for power lines but also minimize risks associated with tampering or accidental contact. This design makes them a cornerstone of outdoor primary and secondary local distribution systems, where reliability and durability are paramount.
Types and Configurations
Power pole transformers are available in single-phase and three-phase configurations. Single-phase power transformers are commonly used in rural areas, whereas three-phase transformer types predominate in industrial and urban zones, where higher power demands are typically found.These variations highlight the versatility of this electrical equipment in adapting to the unique demands of the grid.
Electricity Today T&D Magazine Subscribe for FREE

- Timely insights from industry experts
- Practical solutions T&D engineers
- Free access to every issue
Voltage Step-Down Process
These transformers use a magnetic core and primary and secondary windings to reduce voltage. High-voltage input enters the primary winding, inducing a lower voltage in the secondary winding. The principles of step-down transformers follow standard transformer operation, enhanced by materials such as silicon steel to reduce energy loss.
One of the critical functions of the grid device is stepping down the voltage for safe and efficient use. This process involves the primary windings, which receive high-voltage electricity, and the secondary windings, which output the lower, usable voltage. By incorporating materials like silicon steel into their cores, these devices optimize magnetic fields, thereby minimizing energy losses during the transformation process. This focus on efficiency is especially important, given that these devices are continuously energized, demanding a design that prioritizes both performance and longevity.
Applications in Power Distribution
In the broader context of electricity distribution, these devices play a crucial role in delivering electricity to end-users. They form an essential link in the power grid, enabling the seamless flow of electricity from generation stations through the distribution network to homes, offices, and small industries. Without grid devices, the high voltage carried by transmission lines would be incompatible with the needs of everyday electrical devices, underscoring their importance in the modern world. To understand how these components fit into the broader network, explore our page on electrical power transformers.
Efficiency and Design Considerations
Transformer cores must be designed for continuous use and minimal loss. Transformer losses due to heat and magnetic field fluctuation are reduced through the use of specialized materials and advanced construction techniques. Additionally, these devices are engineered to perform optimally under varying loads, ensuring consistent delivery even during fluctuations in demand. This reliability is critical in maintaining the stability of the grid.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does a power pole transformer do?
A power pole transformer is a crucial component of the electrical distribution system, reducing the high voltage of electricity carried by lines to a lower, usable voltage suitable for homes, businesses, and other facilities. For example, it typically steps down the voltage from several thousand volts to the standard 120/240 volts used in residential areas.
How does a power pole transformer work?
The core and coil design allows magnetic induction between windings, creating a lower output voltage. This process follows the principles described in our guide on how transformers work.
What are the common types of power pole transformer?
These include single-phase and three-phase models, oil-filled transformer or dry-type transformers, each suited to different environments and load needs.
Single-phase transformers are used in residential areas or small businesses and step down the voltage for single-phase distribution systems. Three-phase devices are commonly used in industrial and commercial settings and are specifically designed for three-phase electrical distribution. They are installed directly on utility poles for overhead distribution systems, while pad-mounted transformers are often used in areas where power lines are underground but can serve the same function as pole-mounted transformers. Oil-filled devices utilize insulating oil for both cooling and insulation, making them more durable for high-voltage applications. In contrast, dry-type devices use air for cooling and are typically employed in lower-voltage or indoor settings.
What are the signs of failure?
Signs of a failing power pole transformer include overheating, which may be indicated by visible smoke or signs of melting insulation. Unusual noises, such as humming, buzzing, or clicking sounds that are louder or different from normal operation, can also be a warning. Physical damage, such as cracks, bulges, or oil leaks on the device casing, along with electrical interruptions, frequent outages, or irregular voltage delivery, are clear indicators. A burning smell or fluctuating voltage, such as lights dimming or flickering in nearby buildings, may signal internal failure or overheating.
Sign Up for Electricity Forum’s Utility Transformers Newsletter
Stay informed with our FREE Utility Transformers Newsletter — get the latest news, breakthrough technologies, and expert insights, delivered straight to your inbox.
What is the lifespan and maintenance?
Typically lasting 25–40 years, these devices require regular inspections, transformer testing, oil analysis, and load checks for optimal performance.
Maintenance includes routine inspections for physical damage, leaks, and corrosion, as well as oil testing for oil-filled devices to detect contamination, moisture, or breakdown products. Cleaning to remove debris, dirt, or bird nests from the device and its surroundings is important. Thermal scanning can identify hotspots that may indicate overloading or internal faults, while load monitoring ensures the device is not overloaded beyond its rated capacity. Preventive repairs should address minor issues promptly to prevent larger failures. Regular maintenance and monitoring maximize the lifespan and reliability of grid devices.
Related Articles