Arc Flash Categories by Voltage Chart
NFPA 70e Training
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 6 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our OSHA 4474 Fact Sheet – Establishing Boundaries Around Arc Flash Hazards

- Understand the difference between arc flash and electric shock boundaries
- Learn who may cross each boundary and under what conditions
- Apply voltage-based rules for safer approach distances
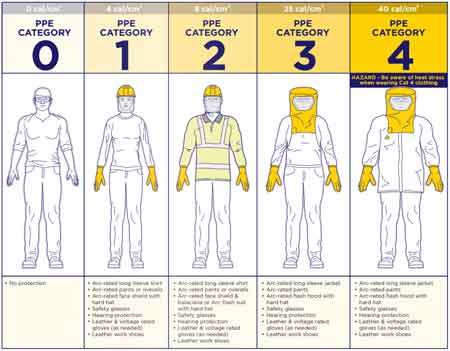
Arc flash categories by voltage chart shows required PPE levels based on system voltage and incident energy. This guide helps electrical workers select appropriate protection according to NFPA 70E standards, reducing shock and arc flash risks in industrial and commercial settings.
What are the Arc Flash Categories by Voltage Chart?
An arc flash categories by voltage chart provides critical safety guidance for selecting personal protective equipment (PPE) based on system voltage and potential incident energy.
✅ Identifies PPE categories by system voltage and task risk level
✅ Aligns with NFPA 70E and CSA Z462 standards
✅ Supports safe work practices and compliance for electrical safety
For a foundational overview of arc flash risks, see our main arc flash guide, which covers causes, hazards, and safety strategies.
This chart categorizes different voltage levels and their associated risks, guiding workers and safety professionals in selecting the appropriate level of protection. Higher voltage levels generally correspond to higher energy releases during an arc event, which means more extensive PPE is necessary. By understanding how categories are influenced by voltage, fault current, and the clearing time of protective devices, professionals can accurately classify hazards and ensure safety in potentially dangerous environments using the voltage chart. Learn how arc flash boundary calculations are influenced by voltage, fault current, and PPE requirements to ensure accurate risk classification.
Request a Free Training Quotation
In electrical safety, understanding the correlation between voltage levels and categories is essential to ensuring proper protection for workers. The potential hazards associated with working on or near energized equipment vary depending on the voltage present, and selecting the correct personal protective equipment (PPE) is crucial for minimizing risk.
Test Your Knowledge About Arc Flash!
Think you know Arc Flash? Take our quick, interactive quiz and test your knowledge in minutes.
- Instantly see your results and score
- Identify strengths and areas for improvement
- Challenge yourself on real-world electrical topics
Arc Flash Categories by Voltage Chart
| System Voltage | Typical Equipment | Incident Energy (cal/cm²) | PPE Category | Required PPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| < 240V | Control panels, lighting panels | < 1.2 | Category 0/1 | FR shirt & pants, safety glasses, hearing protection |
| 240–480V | Motor control centers, switchgear | 1.2 – 8 | Category 2 | FR clothing (min 8 cal/cm²), arc-rated face shield, gloves, hearing protection |
| 480–600V | Large breakers, transformers | 8 – 25 | Category 3 | Arc-rated coveralls, flash hood, gloves, hard hat, face and neck protection |
| 600–1000V | Substation gear, bus ducts | 25 – 40 | Category 4 | Arc-rated suit (≥40 cal/cm²), full-body protection, gloves, hood, balaclava |
| > 1000V | Utility gear, high-voltage gear | Site-specific analysis | Engineering req. | Custom PPE based on incident energy, detailed arc flash study required |
Arc Flash Boundary Table by Incident Energy
See the Arc Flash Boundary Table by Incident Energy for a detailed breakdown of PPE levels at specific energy thresholds.
| Incident Energy (cal/cm²) | Minimum Arc Flash Boundary | PPE Category | Required PPE Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.2 cal/cm² | 18 inches (typical) | Category 1 | FR shirt and pants, safety glasses, and hearing protection |
| 4 cal/cm² | 24 inches | Category 2 | FR clothing (8 cal/cm² min), arc-rated face shield, leather gloves |
| 8 cal/cm² | 36 inches | Category 3 | Arc-rated coveralls, balaclava, hard hat, face shield |
| 25 cal/cm² | 48 inches | Category 4 | Arc-rated full suit, arc-rated hood, gloves, full-body protection |
| 40+ cal/cm² | >60 inches (engineered) | Special Analysis | Suit rated ≥40 cal/cm², insulated tools, work only if absolutely necessary |
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the different arc flash categories based on voltage levels?
Arc flash categories are classified according to the potential energy release during an electrical fault. The higher the voltage, the greater the likelihood of a severe arc event. Categories range from Category 1 to Category 4, with each representing an escalating level of risk and requiring increasingly protective gear. Low-voltage systems, typically operating at voltages below 240 volts, often fall into Category 1 or 2. These systems present a lower energy release and require less protection. As the voltage increases, so does the potential danger, placing the system in higher categories.
Categories 3 and 4 are typically reserved for systems with higher voltage, where the risk of a more severe arc is present. These categories require extensive protection, including flame-resistant clothing, gloves, and face shields. The exact category for a specific task will depend not only on the voltage but also on other factors, such as the available fault current and the distance from the energy source. To ensure proper protection for each hazard category, refer to our detailed Arc Flash PPE Requirements Chart, which outlines the specific clothing and equipment required by incident energy level.
How does voltage impact the arc flash category assigned to a task?
The relationship between voltage and the assigned category is direct but not absolute. As voltage levels rise, the energy that can be released during an electrical explosion increases. However, voltage is not the only factor that determines the hazard level. The available fault current and clearing time of protective devices also play a significant role.
For example, a system operating at 480 volts may fall into a higher category than one operating at 240 volts, but if the available fault current is low, the overall energy release might still place it in a lower category. The combination of voltage, fault current, and protective device clearing time will dictate the category, making the use of a voltage chart essential for accurate classification. To dive deeper into voltage-specific hazards, our 480V arc flash guide explains how moderate voltage levels can still pose serious risks if not properly assessed.
What PPE is required for each arc flash category by voltage level?
PPE is designed to provide protection against the thermal energy released during an arc event. Each category corresponds to a specific level of PPE, which includes clothing and equipment rated for the hazard. For Category 1, basic PPE, such as flame-resistant shirts, pants, and safety glasses, is typically required. As the categories increase, so does the protection level. Explore the differences between Category 1 PPE and Category 4 suits like the 40 cal arc flash suit to understand how protective gear scales with risk.
For Category 2, additional PPE, such as arc-rated gloves and a face shield, may be necessary. In Categories 3 and 4, full-body protection is required, including arc-rated coveralls, gloves, helmets, and face shields. The voltage chart and the corresponding hazard category for the task at hand should guide the choice of PPE.
How do you determine the arc flash category using a voltage chart?
A voltage chart provides a visual reference for determining the appropriate arc flash category based on the system’s operating voltage. It helps in evaluating the potential energy release and selecting the correct PPE. The chart is typically organized by voltage levels, with different columns or sections indicating the corresponding category. To use the chart, identify the operating voltage of the system and then cross-reference it with the available fault current and protective device clearing time to determine the appropriate category.
It is important to remember that the voltage chart is not a stand-alone tool; it must be used in conjunction with a thorough hazard assessment. Other variables, such as the proximity of workers to the energized equipment, must also be considered when assigning a category.
Sign Up for Electricity Forum’s Arc Flash Newsletter
Stay informed with our FREE Arc Flash Newsletter — get the latest news, breakthrough technologies, and expert insights, delivered straight to your inbox.
Are higher voltage systems always in higher arc flash categories?
While higher voltage systems generally pose a greater risk, they are not always assigned to higher categories. The actual category is determined by the total energy released during an arc event, which is influenced by factors beyond just voltage. Systems with high voltage but low fault current might be placed in a lower category than systems with lower voltage but high fault current.
Thus, it is essential to conduct a full analysis of all the factors involved, including voltage, available fault current, and the clearing time of protective devices, when determining the category.
Understanding arc flash categories by the voltage chart is crucial for protecting workers from electrical hazards. By using a voltage chart and considering all relevant factors, such as fault current and the clearing time of protective devices, organizations can accurately determine the appropriate category for each task. Selecting the correct PPE based on these categories is vital for ensuring the safety of personnel working with energized equipment. Discover common mistakes in assessments with our article on the 10 most frequent arc flash analysis errors and how to avoid them.
Related Articles








