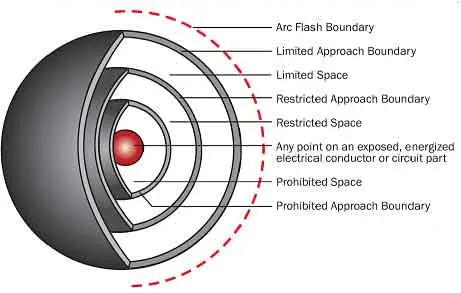
Arc Flash PPE
By R.W. Hurst, Editor

CSA Z462 Arc Flash Training - Electrical Safety Essentials
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 6 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our OSHA 4474 Fact Sheet – Establishing Boundaries Around Arc Flash Hazards

- Understand the difference between arc flash and electric shock boundaries
- Learn who may cross each boundary and under what conditions
- Apply voltage-based rules for safer approach distances
Arc flash PPE protects electrical workers from arc flash and shock hazards. Proper personal protective equipment—arc-rated clothing, face shields, gloves, and helmets—helps ensure compliance with NFPA 70E and OSHA electrical safety standards.
What is Arc Flash PPE?
Arc flash PPE (Personal Protective Equipment) safeguards workers from thermal, electrical, and shock hazards.
? Protects against burns and electrical injuries during arc flash events
? Ensures NFPA 70E and OSHA compliance for electrical safety
? Includes arc-rated clothing, gloves, face shields, and protective gear
Arc Flash PPE is mandatory personal protective equipment designed to safeguard electrical workers from severe injuries caused by electrical explosions. In high-risk work environments, personal protective equipment includes arc-rated (AR) arc flash protection, face shields, flash-suit hoods, rubber insulating gloves, and long-sleeved shirts and pants engineered to withstand intense heat and incident energy. NFPA 70E and CSA Z462 safety standards define the required levels of protection based on calculated exposure risk, measured in cal/cm². Whether you're selecting gear for 8 or 40 cal/cm² scenarios, understanding proper PPE requirements, types of PPE, and flame-resistant clothing options is essential to ensure compliance and prevent life-threatening injuries.
Request a Free Training Quotation
Selecting the right arc-rated clothing begins with understanding the requirements outlined in NFPA 70E-compliant gear standards. Workers must wear garments made from flame-resistant fabric that can withstand exposure to high incident energy without melting or igniting. The most common configuration includes a shirt and pants, but depending on the task, other types of personal protective equipment may be required to ensure full-body coverage. Personal protective equipment for electrical hazards must be matched to the energy level and task complexity, with proper labelling and documentation to support compliance.
Sign Up for Electricity Forum’s Arc Flash Newsletter
Stay informed with our FREE Arc Flash Newsletter — get the latest news, breakthrough technologies, and expert insights, delivered straight to your inbox.
Understanding Arc Flash PPE Requirements
The foundation of electrical safety is understanding requirements under NFPA 70E and CSA Z462. Clothing must be selected to match either the incident energy (measured in cal/cm²) or the task-based protection category. For example, exposure to energy greater than 40 cal/cm² requires specialized protective flame-resistant suits with multi-layer protection and a properly rated flash suit hood.
Visit: NFPA 70E PPE Requirements
Materials: Nomex, Kevlar, and FR Cotton
Choosing arc flash protection requires understanding material strengths. Nomex, a flame-resistant fiber, delivers lightweight safety at 12 cal for PPE Category 2 tasks like panel work, meeting NFPA 70E standards. It resists heat and ignition, making it ideal for face shields and suits. Kevlar blends add durability, boosting 40 cal/cm² gear for Category 4 hazards, protecting against intense electrical explosions. FR cotton, treated for flame resistance, offers breathability at 8–12 cal/cm² for Category 1–2 roles, but it’s less durable and heavier. Nomex balances versatility, Kevlar excels in ruggedness, and FR cotton suits budget-conscious teams. Each meets ASTM F1506 for reliability. For hazard-specific gear, visit our arc flash PPE categories, or explore arc flash clothing for non-suit options like flame-resistant shirts.
Case Study: How Arc Flash PPE Saved Lives
During a 2024 outage, a technician servicing a 480V panel experienced an electrical explosion with a 25 cal/cm² rating. Equipped with NFPA 70E-compliant gear—a 40 cal/cm² suit, flame-resistant face shield, and gloves—they avoided injury. The PPE Category 4 suit absorbed the arc’s heat, while the shield, meeting ASTM F1506, blocked debris. This incident highlights the life-saving role of arc-flash protection. Post-event, the team mandated 12 cal gear checks for lower-risk tasks to reinforce compliance. High-hazard solutions are detailed in our 40 cal arc flash suit.
Conducting an Arc Flash Hazard Assessment
A hazard assessment ensures arc flash protection matches risks:
-
List Equipment: Identify incident-prone systems (e.g., 480V panels).
-
Estimate Energy: Use IEEE 1584 for cal/cm² (e.g., 12 cal for low voltage).
-
Measure Distance: Closer workers need higher ratings (e.g., 25 cal/cm²).
-
Choose Gear: Select PPE Category gear, like 40 cal/cm² suits, per NFPA 70E.
-
Document: Log for compliance.
Flame-resistant face shields and gloves complete the system. For visuals, see our arc flash PPE requirements chart, or explore arc flash PPE requirements.
Arc Flash PPE Categories and Required Gear
Personal protective equipment is organized into four categories based on the severity of the hazard:
-
Category 1 may include long-sleeved shirts and shirt-and-pants combinations with minimum ratings of 4 cal/cm².
-
Category 4 addresses exposure above 40 cal/cm², requiring full-body suits and additional insulation.
Each category has specificarc flash protection clothing requirements. Learn more:
Implementing an Arc Flash PPE Program
An effective PPE program implementation begins with accurate energy level analysis to determine the appropriate hazard risk category for each task. This ensures that worker exposure limits are not exceeded and that the selected gear meets the required thermal protective performance. Organizations must also align their strategies with current electrical safety compliance standards, such as NFPA 70E and CSA Z462, to avoid liability and enhance protection. Choosing between daily wear vs task-based clothing depends on the frequency and intensity of exposure, with task-based solutions often required for higher-risk operations that demand enhanced insulation and coverage.
Choosing the Right Flash Suit
Suits come in various ratings and configurations to match different risk levels. Suits rated for 40 cal/cm² or higher typically feature layered materials, face shields, and flash suit hoods for complete coverage.
Electricity Today T&D Magazine Subscribe for FREE

- Timely insights from industry experts
- Practical solutions T&D engineers
- Free access to every issue
Explore options:
Arc Flash PPE Performance and Material Standards
Not all personal protective equipment is created equal. High-quality AR fabrics must remain flame-resistant even after repeated washings and regular use. The work environment—such as humidity, temperature, and proximity to energized parts—can impact how PPE performs under stress.
Review key insights: PPE Performance
Additional Arc Flash PPE
Personal protective equipment includes more than just clothing. Proper types extend to:
-
Rubber insulating gloves for voltage protection
-
Face shields and balaclavas for facial safety
-
Safety glasses, hard hats, and hearing protection, depending on job-specific risks
Learn what PPE includes in a comprehensive gear set:
Meeting Compliance Through PPE Programs
Selecting and wearing arc-flash protective clothing is only part of the solution. Employers must train staff, audit usage, and regularly maintain and inspect gear. Your company's flash protection strategy should align with NFPA 70E mandates, including proper documentation of PPE requirements by task and location.
Arc Flash PPE Compliance Checklist
Ensure safety with arc-rated PPE:
-
? Verify NFPA 70E labels (12 cal–40 cal/cm²).
-
? Inspect flame-resistant gear for damage.
-
? Match PPE category to hazards.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is arc flash protection?
Arc flash protection uses flame-resistant gear, suits, face shields, and gloves to protect against incident energy. Rated at 12 cal for PPE Category 1 or 40 cal/cm² for Category 4, it meets NFPA 70E for safety up to 40,000°F. Learn levels at arc-rated PPE categories.
How does a face shield meet NFPA 70E?
A 12 cal/cm2 face shield, per ASTM F1506, protects PPE Category 2 workers from heat, ensuring NFPA 70E compliance. It pairs with hoods for coverage. See arc flash safety gear for accessories.
Why test Arc Flash PPE?
Testing per ASTM F1506 confirms gear withstands AF. Check ppe performance for testing details.
Explore More Arc Flash Topics:
Explore our Arc Flash Training Programs or contact us to Request a Free Training Quotation for group safety sessions and PPE consultation.