Apparent Power Calculator
By R.W. Hurst, Editor
Power Factor Training
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.
- Live Online
- 6 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our OSHA 3875 Fact Sheet – Electrical PPE for Power Industry Workers

- Follow rules for rubber gloves, arc-rated PPE, and inspection procedures
- Learn employer obligations for testing, certification, and training
- Protect workers from arc flash and electrical shock injuries
Apparent power calculator for AC circuits computes VA and kVA using RMS voltage, current, and power factor, supporting single-phase and three-phase loads with real power, reactive power, and efficiency insights.
What Is an Apparent Power Calculator?
A tool that calculates apparent power (VA/kVA) from voltage, current, and power factor in single- or three-phase AC.
✅ Compute VA and kVA for single- or three-phase loads
✅ Inputs: RMS voltage, RMS current, optional power factor
✅ Supports delta/wye, line-to-line and line-to-neutral formulas
The apparent power calculator estimates total power in an AC circuit using voltage and current. It helps calculate volt-amperes (VA), assess power factor, and compare real, reactive, and apparent power values for designing efficient single-phase and three-phase electrical systems. For a concise overview of definitions and units, see the apparent power guide for additional context.
Power Quality Analysis Training
Request a Free Power Quality Training Quotation
An apparent power calculator is an essential online resource for electrical professionals performing AC circuit analysis. This tool helps determine total load (VA or kVA), actual work output (W), and stored energy (VAR), making it easier to assess circuit performance and optimize energy efficiency. Ideal for engineers, technicians, and electricians, it enables quick electrical load measurement while supporting power factor (PF) correction and facilitating system design improvements. Whether you’re analyzing industrial systems or troubleshooting facility equipment, a reliable kVA calculation tool is key to identifying inefficiencies and ensuring compliance with energy standards. Whether you're working on an industrial installation or analyzing residential loads, this calculator enables accurate electrical load measurement to optimize efficiency and reduce energy loss.
An effective kVA calculation tool is essential for anyone performing AC circuit analysis, as it provides accurate readings of VA, W, and VAR—the key metrics needed to understand total, real, and reactive energy flow. By using an online electrical calculator, engineers and technicians can quickly assess system performance, diagnose inefficiencies, and make informed decisions about energy usage. These tools support precise electrical load measurement, which is critical for balancing circuits and reducing energy waste. Whether managing industrial machinery or designing a commercial facility, understanding reactive load in AC systems helps ensure stability, efficiency, and compliance with energy standards.
Test Your Knowledge About Power Quality!
Think you know Power Quality? Take our quick, interactive quiz and test your knowledge in minutes.
- Instantly see your results and score
- Identify strengths and areas for improvement
- Challenge yourself on real-world electrical topics
If you need a refresher on fundamentals, this primer on real vs reactive power explains the concepts used by the calculator.
These measurements support accurate system analysis and help optimize electrical infrastructure for cost savings and efficiency. By understanding how voltage, current, and phase angle interact, engineers can make informed adjustments that improve overall performance.
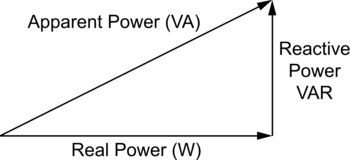
The calculator utilizes these formulas to calculate the AP, which represents the total energy in an AC circuit that encompasses both the real and reactive electrical components. The real power is the actual work performed by the circuit, while the reactive energy is the energy stored and released by the circuit's inductors and capacitors. The AP combines both energies and is measured in volt-amperes (VA) or kilovolt-amperes (kva). To review the math behind these relationships, consult the apparent power formula and verify your own calculations.
What is the Apparent Power Calculator, and how does it work?
The apparent power calculator uses basic input values—voltage, current, and optionally PF, to compute the total energy demand of an AC system. It is structured around the power triangle, which illustrates the relationship between VA, W, and VAR, enabling users to distinguish between real energy used and reactive load in AC systems. This simplifies complex calculations and supports both single-phase and three-phase setups. With accurate outputs and user-friendly steps, it’s one of the most practical tools for modern engineers. This tool is based on the triangle, which shows the relationship between real and reactive power. By inputting voltage, current, and energy factor, it calculates apparent energy using standard equations. Output values include real energy (W), reactive flow (VAR), and total system demand (VA). You can also determine the PF of your circuit to guide improvements. For PF derivations and variables, the power factor formula offers step-by-step detail.
How do I use the Apparent Power Calculator to calculate the energy in my circuit?
Using the apparent power calculator is a straightforward process. Begin by entering the voltage and current of your AC circuit. If known, include the PF for more accurate results. Then, select whether you're working with a single-phase or three-phase system. The calculator will compute and display three key values:
-
Apparent load in volt-amperes (VA or kVA)
-
Real output in watts (W)
-
Reactive demand in volt-amperes reactive (VAR)
This electrical calculator online helps streamline circuit analysis and can be used on-site or in the design phase to validate load requirements and optimize equipment selection. For quick PF checks, the power factor calculator provides instant results for comparison.
This information provides a clear picture of how much of the supplied electrical energy is being utilized for productive work versus how much is circulating without contributing to productivity. If you use a calculator, you can analyze circuit performance in real time.
To use the calculator:
-
Enter voltage (V)
-
Enter current (A)
-
Input PF(optional)
-
Select single-phase or three-phase
-
View output: kVA, kW, and kVAR
This process supports effective AC circuit analysis by delivering accurate data on system behavior.
What is the difference between real power, reactive power, and apparent power?
Understanding the relationship between different electrical quantities is crucial for system design. Real power represents usable energy that performs actual work and is measured in watts. Reactive energy is not consumed but instead circulates in the circuit to support magnetic and electric fields—it's measured in VAR. The combination of these two creates the apparent value, or the total demand placed on the system, measured in VA or kVA.
FREE EF Electrical Training Catalog
Download our FREE Electrical Training Catalog and explore a full range of expert-led electrical training courses.

- Live online and in-person courses available
- Real-time instruction with Q&A from industry experts
- Flexible scheduling for your convenience
By using a kVA calculation tool, you can visualize this relationship as an energy triangle—where real, reactive, and apparent components form a right-angle structure. This enables engineers to quickly identify whether the system is running efficiently or if adjustments, such as PF correction, are needed.
In AC systems:
-
Real output is the portion that performs useful functions, such as lighting or running a motor. It’s measured in watts.
-
Reactive demand is the portion used to build and collapse magnetic and electric fields in inductive or capacitive elements. It is measured in volt-amperes reactive (VAR).
-
Apparent load combines both and represents the total demand seen by the source, expressed in VA or kVA.
These three elements form the sides of the triangle, where the hypotenuse is apparent. For a deeper look into this relationship, see our article on apparent power vs real power.
Balancing Real and Reactive Components
In practical terms, active power represents the energy that completes tasks, while the reactive element enables voltage stability in the system. A high power factor (PF) ratio, indicating efficient usage, is characterized by a high ratio of real to total electrical flow. Using a calculator, engineers can assess the reactive energy factor of a circuit, identify sources of inefficiency, and take action to reduce waste. When this balance is optimized, the result is more real work delivered with less energy loss.
Why Improving PF Matters
Low PF results in inefficiencies, higher utility costs, and increased strain on components. A calculator for power factor can help you pinpoint weaknesses in your system. To correct these issues, devices such as automatic power factor controllers or capacitor banks may be installed to offset unnecessary reactive energy. To understand the metrics behind those corrections, see how power factor is calculated to interpret results correctly.
Single-Phase vs. Three-Phase Applications
This tool works with both single-phase and three-phase systems. In three-phase setups, calculations use a √3 multiplier to account for the vector nature of the voltage-current relationship. For reference, review the importance of energy accuracy in capacitive loads, where phase angles greatly impact energy flow.
Applications in Electrical Design and Maintenance
Whether diagnosing an energy quality issue or building a new panel, the calculator helps you quickly identify inefficiencies and improve your system’s performance. By combining this tool with insights from our article on apparent power in AC circuits, professionals can make data-driven decisions that lower costs and boost equipment longevity. For selection tradeoffs, reviewing apparent power vs real power helps align specs with load behavior.
Related Articles