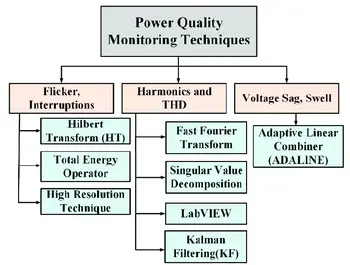
Power Quality Monitoring
By R.W. Hurst, Editor
Power Quality Analysis Training
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.
- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our OSHA 4475 Fact Sheet – Being Aware of Arc Flash Hazards

- Identify root causes of arc flash incidents and contributing conditions
- Apply prevention strategies including LOTO, PPE, and testing protocols
- Understand OSHA requirements for training and equipment maintenance
Power quality monitoring identifies voltage sags, swells, harmonics, and other disturbances in electrical systems. It ensures reliable operation, protects sensitive equipment, and improves energy efficiency in commercial, industrial, and utility electrical networks.
What is Power Quality Monitoring?
Power quality monitoring is a crucial process in electrical engineering that can help ensure a stable electrical supply and prevent equipment failure and downtime.
✅ Detects voltage anomalies, harmonics, and transients
✅ Prevents equipment damage and costly downtime
✅ Improves electrical system performance and energy efficiency
Poor power quality (PQ) can have serious consequences for facilities that depend on sensitive equipment and a reliable energy supply. When PQ issues arise, they are often linked to disturbances such as voltage sags, harmonics, or transients that affect overall efficiency. Monitoring these PQ parameters is essential for identifying the root causes of disruptions and preventing long-term damage. Left unchecked, problems can shorten equipment lifespan, increase energy costs, and lead to unexpected downtime. To address these challenges, many organizations use advanced PQ meters, which provide accurate data and insights that help engineers diagnose problems quickly and implement corrective solutions.
Power Quality Analysis Training
Request a Free Power Quality Training Quotation
Power quality monitoring is crucial for identifying and resolving issues such as voltage sags, harmonics, and other electrical disturbances that can impair system performance. By utilizing advanced analyzers with real-time diagnostics and data logging capabilities, facility managers can identify and rectify issues such as transients before they lead to equipment damage or downtime. This proactive approach not only ensures system reliability but also contributes to greater energy efficiency by maintaining optimal operating conditions across electrical networks.
FREE EF Electrical Training Catalog
Download our FREE Electrical Training Catalog and explore a full range of expert-led electrical training courses.

- Live online and in-person courses available
- Real-time instruction with Q&A from industry experts
- Flexible scheduling for your convenience
With the help of power quality measurement, electrical-related issues can be identified and rectified promptly, resulting in improved performance and extended equipment lifespan. Several types of equipment are used for power quality monitoring, including PQ analyzers, PQ meters, data loggers, and power quality monitoring systems. Regular monitoring is essential for maintaining the equipment's performance and extending its life by reducing the stress on the equipment due to poor PQ. Understanding the relationship between true, reactive, and apparent power is essential for accurate electrical system analysis and optimization.
The frequency of monitoring can depend on several factors, including the criticality of the equipment, its age, the type of supply, and environmental conditions. Power quality monitoring can be performed by electrical engineers or trained personnel with the necessary knowledge and expertise in electrical systems. The role of PQ monitoring in data centers is crucial. High-speed data logging is a critical aspect of PQ monitoring, enabling the early detection of energy-related issues and optimizing energy usage. Proper electrical grounding is a critical component of any PQ strategy, helping to protect systems from faults and surges.
Key Aspects and Benefits of Power Quality Monitoring
| Aspect | Key Insights | Practical Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Main Goal | Ensures stable electrical supply by identifying voltage fluctuations, harmonic distortion, and transient surges. | Reduces costly downtime and improves energy efficiency. |
| Core Benefits | - Detects electrical anomalies and disturbances- Prevents equipment damage and unplanned outages- Extends system lifespan through predictive maintenance | Lowers operational costs and optimizes energy consumption. |
| Monitoring Tools | Power quality analyzers, data loggers, PQ meters, and advanced diagnostic systems. | Provides real-time diagnostics and historical data for analysis. |
| Applications | Used in industrial plants, commercial facilities, and data centers for PF correction and reliability. | Protects sensitive electronic equipment and critical processes. |
| Key Parameters Measured | Voltage sags/swells, current variations, harmonics analysis, PF, frequency deviations, and transients. | Enables root-cause analysis of energy issues. |
| Critical Environments | Data centers require continuous monitoring and high-speed data logging to prevent outages. | Avoids costly downtime and ensures compliance with PQ standards. |
| High-Speed Data Logging | Captures fast disturbances that conventional meters miss, improving electrical system analysis. | Enables proactive fault detection and energy optimization. |
| Who Performs Monitoring | Electrical engineers, maintenance teams, or third-party monitoring services. | Ensures expert PQ assessment and fast problem resolution. |
| Frequency | Continuous or periodic monitoring, depending on equipment criticality, load type, and environment. | Balances cost-effectiveness with reliability. |
| Problems Detected | Voltage dips/swells, harmonics, frequency instability, and reactive power issues. | Prevents equipment overheating, failure, and excessive energy costs. |
The Role in Data Centers
Data centers are critical facilities that require an uninterrupted electrical supply to ensure continuous operation. Poor PQ can lead to data center downtime, resulting in significant financial losses. PQ measurement is, therefore, crucial in data centers to ensure that the electrical energy supplied is stable and reliable. PQ measurement can help detect and rectify energy-related issues that can cause equipment failure and downtime. The monitoring can also help identify areas for improvement in the electrical supply infrastructure and optimize energy usage. Additionally, PQ measurement can help data center managers comply with industry standards and regulations related to PQ. Installing an automatic power factor controller can greatly enhance energy efficiency by minimizing reactive electrical losses.
The Importance of High-Speed Data Logging
High-speed data logging is a crucial aspect of power quality monitoring, as it enables the capture and analysis of electrical signals at high speed and with high accuracy. Additionally, high-speed data logging enables the detection of transients and other rapidly changing PQ parameters that may be overlooked by conventional diagnostic equipment. High-speed data logging can also aid in the early detection of electrical-related issues and the optimization of energy usage, resulting in improved energy efficiency and lower energy costs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is it Important?
PQ measurement is a process that aims to identify and rectify energy-related issues that can cause equipment failure and downtime by monitoring and analyzing the electrical signals in an electrical system. It helps ensure that electricity is supplied consistently and reliably without interruptions or disturbances. It is crucial in various industries, such as data centers, where downtime can result in substantial financial losses. PQ measurement also helps maintain equipment performance and extend its life by reducing the stress on the equipment due to poor PQ. When issues arise, power quality troubleshooting can help pinpoint the root cause of flicker, distortion, or voltage imbalances across your facility.
What Types of Equipment are Used?
Several types of equipment are used for power quality monitoring, including PQ analyzers, PQ meters, data loggers, and PQ evaluation systems. PQ analyzers are handheld devices that measure and record various PQ parameters, including voltage, current, harmonics, and transients. PQ meters are used for long-term monitoring of PQ parameters and can be installed at a specific location to continuously monitor electrical signals. Data loggers are used for measuring voltage variations, current fluctuations, and other PQ parameters at high speed and with high accuracy. Ultimately, PQ diagnostics offer a comprehensive approach to PQ assessment, encompassing a range of sensors and analyzers that monitor various aspects of the electrical supply.
Electricity Today T&D Magazine Subscribe for FREE

- Timely insights from industry experts
- Practical solutions T&D engineers
- Free access to every issue
How Does It Help in Identifying and Solving Energy-Related Issues?
PQ measurement helps identify and solve electrical-related issues by detecting and analyzing the electrical signals in an electrical system. By monitoring PQ parameters, such as voltage, current, harmonics, and transients, PQ measurement can identify issues that can cause equipment failure and downtime. Once the problem is identified, appropriate measures can be taken to resolve the issue, such as installing PF correction equipment or reducing the system's load. PQ measurement can also help identify and solve energy-related issues that may take time, such as a gradual degradation of equipment due to poor PQ.
What Problems can be detected through Monitoring?
Several PQ issues can be identified through monitoring, including voltage sags, voltage swells, harmonics, transients, frequency fluctuations, and poor PF. Voltage sags are short-term drops in voltage levels that can cause equipment failure, while voltage swells are short-term increases in voltage levels that can damage equipment. Harmonics are non-sinusoidal components of a signal that can cause overheating and equipment failure. Transients are short-term variations in voltage levels that can cause equipment malfunctions or failures. Finally, frequency variations can cause equipment malfunction, and poor PF can lead to higher energy costs.
How Often Should Power Quality Monitoring be Performed?
PQ measurement should be performed regularly to ensure a stable electrical supply and prevent equipment failure and downtime. The frequency of monitoring can depend on several factors, including the criticality of the equipment, its age, the type of electrical supply, and environmental conditions. For instance, equipment in a data center may require constant monitoring to prevent downtime, while equipment in a less critical facility may require measurement at regular intervals.
PQ measurement can be performed by electrical engineers or trained personnel with the necessary knowledge and expertise in electrical systems. The responsibility of conducting PQ measurement can vary depending on the type of facility and the level of criticality. In some cases, the facility manager is responsible for monitoring; in others, this task is outsourced to a third-party provider.
Related Articles