NEC Ground Wire Size Chart Explained
Power Factor Training
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.
- Live Online
- 6 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our NFPA 70E Fact Sheet – 2024 Electrical Safety Edition

- Understand how NFPA 70E works with NEC and NFPA 70B standards
- Clarify the shared responsibility between employers and employees
- Learn how NFPA 70E supports OSHA compliance
NEC Ground Wire Size Chart provides standard wire sizing for grounding conductors in electrical systems. It ensures safe fault current paths, compliance with NEC codes, and reliable protection for residential, commercial, and industrial installations.
What is the NEC Ground Wire Size Chart?
The NEC Ground Wire Size Chart is a reference guide that specifies minimum grounding conductor sizes to ensure system safety and compliance.
✅ Defines correct ground wire sizing based on system capacity and fault current.
✅ Ensures electrical safety, proper bonding, and protection against shock hazards.
✅ Provides NEC-compliant sizing tables for residential, commercial, and industrial use.
Grounding and Bonding and the NEC 250 Training
Electrical Grounding and the CE Code Training
Request a Free Power Quality Training Quotation
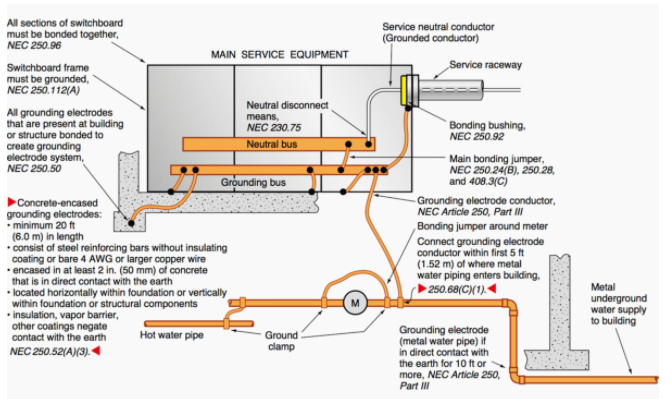
Grounding is a fundamental aspect of electrical safety, ensuring that fault currents are effectively carried away and reducing the risk of electric shock hazards and equipment damage. Understanding and utilizing the NEC ground wire size chart helps professionals comply with National Electrical Code (NEC) standards, prevent costly errors, and maintain the reliability of ac systems in electrical installations in residential, commercial, and industrial environments.
This essential knowledge safeguards both people and infrastructure while enhancing overall system performance. When designing electrical systems, especially branch circuits, it’s essential to ensure proper equipment grounding to maintain safety and comply with National Electrical Code (NEC) standards. Effective ground fault protection is achieved not only through the use of the right protective devices but also by installing a properly grounded electrode system.
Selecting the correct size for grounding conductors is critical to ensure the system can safely carry fault current during abnormal conditions. A well-designed grounding system supports both safety and system reliability across all electrical installations. For a comprehensive understanding of grounding principles, refer to our article on Electrical Grounding.
FREE EF Electrical Training Catalog
Download our FREE Electrical Training Catalog and explore a full range of expert-led electrical training courses.

- Live online and in-person courses available
- Real-time instruction with Q&A from industry experts
- Flexible scheduling for your convenience
NEC Ground Wire Size Chart (per NEC 250.122)
| OCPD Rating (Amps) | Copper Ground Wire | Aluminum Ground Wire |
|---|---|---|
| 15 or 20 | 14 AWG | 12 AWG |
| 30 | 10 AWG | 8 AWG |
| 40 or 60 | 10 AWG | 8 AWG |
| 100 | 8 AWG | 6 AWG |
| 200 | 6 AWG | 4 AWG |
| 300 | 4 AWG | 2 AWG |
| 400 | 3 AWG | 1 AWG |
| 500 | 2 AWG | 1/0 AWG |
| 600 | 1 AWG | 2/0 AWG |
| 800 | 1/0 AWG | 3/0 AWG |
| 1,000 | 2/0 AWG | 4/0 AWG |
| 1,200 | 3/0 AWG | 250 kcmil |
| 1,600 | 250 kcmil | 350 kcmil |
| 2,000 | 350 kcmil | 500 kcmil |
| Over 2,000 | Size per engineering judgment and NEC 250.122(F) |
Notes:
-
This chart applies to copper or aluminum EGCs in raceway or cable.
-
If the ungrounded conductors are upsized for voltage drop, EGCs must also be proportionally upsized (NEC 250.122(B)).
-
Always consult the latest NEC code or a licensed electrician for final design decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do I Determine the Correct Ground Wire Size Using the NEC Ground Wire Size Chart?
The conductor size required for an electrical system depends primarily on the rating of the overcurrent protection device (such as a circuit breaker) and the size of the conductors within the circuit. To determine the correct size, refer to NEC Table 250.122, which outlines the minimum size of conductors based on the amperage of the protective device.
For example, if a 100-amp breaker protects the circuit, the chart specifies a minimum conductor size of No. 8 copper or No. 6 aluminum. It's crucial to ensure that the conductor is large enough to handle potential fault currents safely, thereby protecting both the system and the people using it. For a deeper understanding of grounding and bonding practices in compliance with both CSA and NEC standards, refer to our comprehensive guide on Grounding and Bonding to CSA and NEC Standards.
What Factors Influence the Ground Wire Size According to the NEC Chart?
Several factors can affect the proper sizing of conductors:
-
Overcurrent Protection Device: The size of the device is the most important factor. Higher amperage circuits will require larger conductors to manage the associated fault currents.
-
Length of Run: If the distance between the circuit and the grounding electrode is significant, the conductor may need to be upsized to maintain effectiveness and minimize voltage drop.
-
Type of Installation: The conductor size may vary depending on whether it is used in a residential or commercial installation.
-
Material of the Conductor: Copper is more conductive than aluminum, which may allow for smaller copper conductors in certain applications.
Understanding these factors is essential for ensuring compliance with the Electrical Grounding Code and maintaining system safety.
What Is the Minimum Ground Wire Size for Residential Systems as per the NEC Chart?
For most residential applications, the NEC specifies minimum conductor sizes based on the amperage of the circuit's protective device. Common residential circuits, typically used for outlets and lighting, and rated at 15 or 20 amps, require No. 14 copper or No. 12 aluminum conductors.
However, larger appliances such as electric water heaters or central air conditioning units may require larger conductors. For instance, a 50-amp circuit would typically require No. 10 copper or No. 8 aluminum conductors.
Explore the intricacies of NEC Article 250 and its implications on grounding and bonding by reading our detailed analysis in Grounding and Bonding and The NEC - Section 250.
Does the NEC Ground Wire Size Chart Differ for Commercial vs. Residential Installations?
The same principles apply to both residential and commercial installations, but the actual conductor sizes differ due to the greater complexity and load requirements in commercial systems. Commercial systems may require larger ground rods and grounding conductors to handle higher fault currents and protect more extensive equipment setups.
For example, while residential systems usually involve lower amperage circuits, commercial buildings may require circuits capable of handling hundreds of amps. In such cases, the NEC chart will specify a larger conductor to manage the higher fault currents safely.
Enhance your knowledge of power quality and electrical grounding by downloading our Power Quality and Electrical Grounding Handbook Vol. 6, which offers in-depth insights into best practices and standards.
How Do Changes in Overcurrent Protection Devices Affect Ground Wire Size as per the NEC Chart?
Changes in the size of the overcurrent protection device will directly affect the required size of the conductor. For instance, if you upgrade from a 100-amp to a 200-amp breaker, the conductor size must also be increased accordingly. Failing to adjust the conductor size when upgrading the breaker can lead to unsafe conditions, as the conductor may not be able to handle the fault currents properly. Stay informed about the latest developments in electrical safety and grounding techniques by visiting our Electrical Grounding System, where we cover a range of topics pertinent to NEC compliance.
Test Your Knowledge About Power Quality!
Think you know Power Quality? Take our quick, interactive quiz and test your knowledge in minutes.
- Instantly see your results and score
- Identify strengths and areas for improvement
- Challenge yourself on real-world electrical topics
When making such changes, it is crucial to ensure that the grounding system complies with the current National Electrical Code (NEC) requirements. Consulting a licensed electrician or engineer is often necessary to ensure that the conductors meet safety standards and comply with relevant codes.
The NEC ground wire size chart is a critical tool for ensuring that electrical systems are properly grounded. By selecting the correct conductor size based on the rating of the overcurrent protection device, material type, and installation requirements, you can maintain a safe and reliable system. Whether working on a residential or commercial project, understanding conductor sizing is essential for ensuring compliance with the National Electrical Code and minimizing electrical hazards. For practical applications and case studies related to industrial electrical power systems, our Power Quality Channel provides valuable resources that complement the principles outlined in the NEC Ground Wire Size Chart.
Related Pages







