The need for new sources of power to be developed is the increasingly devastated state of the world's environment. Using fossil fuels (gas, coal, and oil) produce a great deal of pollution and toxic waste products which pollute the earth's biosphere. Oil, coal and natural gas produce toxic smoke that sends pollutants into the air and causes global warming. For these reasons it is going to be necessary to shift to sources in the future in order to maintain a sustainable enviroment and world economy.
Alternative Information from the Electricity Forum
The purpose of this section of our website is to offer technical information relating to the renewable industry. Our intention on these pages is to provide useful renewable electricity energy information on the various forms of sources and technologies and where the industry is heading.
Why Alternative Energy?
For years, governments worldwide have been trying to initiate laws and regulation to reduce toxic greenhouse gases (such as carbon dioxide) and implement programs (such as wind and solar) to replace fossil fuels. But why?
Global Warming
Despite their harmful gas-producing properties, coal and oil naturally come from the environment. However, these sources run out and what's worse, when they're used, they emit greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions into the air, and, overtime, as GHGs buildup, blankets the planet. It sounds harmful, but in reality, can be quite deadly.
Carbon dioxide, among other harmful greenhouse gases, causes Earth's average surface temperature to increase. Hot temperatures are ideal on a hot beach, but, the right temperatures are necessary if animal and plant life are to thrive. And, these hot temperatures have been steadily increasing year-by-year (known as global warming) and have already compromised Earth's environment. In fact, animals are already looking for new habitats and the sea level is slowly rising due to melting ice in the Arctic and Antarctica (North and South Poles).
The melting ice in the North and South Poles can speed-up global warming because the Arctic ice protects Earth’s from absorbing 100 per cent of the sun’s intense heat. The sun is the Earth's main source of energy, but without protection, the planet would not be able to sustain life. Clouds, like ice, help to reflect 30 per cent of the suns rays, which keeps the planet at the right temperature while the remaining 70 per cent warms the Earth.
But, greenhouse gas emissions act like an invisible wrapper that traps the sun’s heat and causes the planet to warm up. This increased heat melts the north and south ice caps thus taking away some of Earth’s protection from the sun thus causing wildfires, heat waves, flooding, droughts and much worse – all because of global warming. In fact, studies conducted from satellite images show that the polar ice cap in the Arctic is melting at least nine percent every ten years, which means by the end of the 21st century, there could be no more summer ice in the Arctic.
Alternative Energy Vs. Renewable Energy
There is a marked difference between the terms. This refers to any form of energy which is an alternative to the traditional fossil fuels, like oil, natural gas and coal. Renewable energy, on the other hand, refers to forms of power that are renewed by the natural processes of the Earth, such as solar energy or wind energy.
Forms Of AE
Solar power is generated from solar energy, which can be converted through the use of solar power or photovoltaic cells. Sunlight is easy to harness and free, but it can be difficult to generate large quantities of solar power forom large scale solar power plants. However, there are several solar power plant projects in existence around the world, but mostly in locations where there are many "solar days" in the year.
Solar power is environmentally "friendly", as it produces no pollution or waste byproduct. Solar panels come in various shapes and sizes and can be used on a small scale by mounting solar power panels on residential rooftops or they can be installed (usually on the ground) on a large scale for electricity production in "solar farms". Solar power is most commonly intended for on-site local electricity generation on commercial buildings.
Wind power is very popular. Wind power technology has grown enormously in various places in world and is becoming a feasible source of power production. Wind power has a lot of potential as a business and economic model for many countries. Wind power, however, is vulnerable to weather conditions, but in certain locations like coastal offshore areas and at high altitudes, there is a steady source of wind energy that can be converted into wind electricity. Wind power is harnessed through the spinning of wind turbine blades, which are turned by the wind to generate electricity. Wind power can be used both for electricity generation on a large scale with multiple turbines to form what is called a wind farm, or in other words a wind power plant, or, more infrequently, on a smaller scale for home electricity generation.
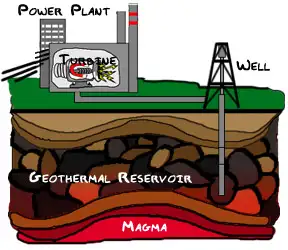
Geothermal power is created by tapping into the energy drawn in the form of heat from the planet’s core and using that heat to produce steam, which in turn can be used to turn turbines and generate electricity. This is accomplished by absorbing the heat from the earth's crust and that heat is used to boil water which evaporates to turn turbines, producing the electricity. The feasibility of geothermal power technology is great because thermal heat is available at no cost (station operation is the only expense). However, the main disadvantage to this technology is that the locations where geothermal heat is easily available are limited and change based on tectonic movement and the arrangement of the surface of the Earth. Geothermal power is renewable and does not pollute, and there are places in many parts of the world, such as Iceland, where geothermal power is in great supply.
A highly developed form of hydroelectric power. Hydroelectric power comes from dams which harness the power of rivers. The falling water from a higher level (head) to a lower level passes through turbines at the dam's base, turning electricity-generating turbines. There are many hydroelectric dams in existence, and hydroelectric power from these dams is a highly developed technology. There are many hydroelectric dams everywhere in the world. Hydroelectric power is a clean, green technology which produces no pollution. Unfortunately, most of the lakes and rivers that could easily be exploited with hydroelectric have been dammed already, so the future of hydroelectric power lies in the development of less appealing sites. There are a number of hydroelectric projects in existence, in Africa, Asia and elsewhere.