NFPA 70E Arc Flash Table: Everything You Need to Know
By R.W. Hurst, Editor
CSA Z462 Arc Flash Training - Electrical Safety Essentials
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 6 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our OSHA 3075 Fact Sheet – Understanding Electrical Hazards in the Workplace

- Learn the effects of electric current on the human body
- Understand OSHA safety standards and protective devices
- Discover essential lockout/tagout and grounding practices
An NFPA 70E arc flash table helps determine when arc flash PPE is required. These tables outline hazard likelihood, PPE categories, and tasks that require protection, ensuring safer electrical work through standardized risk assessments and the selection of protective equipment.
Request a Free Training Quotation
What is the NFPA 70E Arc Flash Table?
The NFPA 70E is a standard that provides guidelines for electrical safety in the workplace. The arc flash table, part of the standard, determines the hazard level for a given electrical situation. In addition, the table provides information on arc flash boundaries, incident energy levels, and PPE category methods. Therefore, it is a crucial tool for determining the appropriate PPE and ensuring the safety of workers.
✅ Defines PPE Categories – Identifies the required personal protective equipment based on equipment type, voltage, and task. See how to use the Arc Flash Categories to identify PPE requirements for tasks based on voltage level and fault conditions.
✅ Assesses Risk Likelihood – Helps determine if an arc flash is likely to occur during specific tasks.
✅ Guides Safety Procedures – Supports compliance by outlining when and how to apply protection strategies.
Example: NFPA 70E Arc Flash Table
Here is an example based on NFPA 70E Table 130.7(C)(15)(a) (2024 edition), which illustrates when arc-rated personal protective equipment (PPE) is required for alternating current (AC) systems. This simplified version illustrates how the table helps select the right PPE Category based on equipment and task conditions:
| Equipment Type | Task Description | Arc Flash PPE Required? | PPE Category | Minimum Arc Rating (cal/cm²) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Panelboard (≤240V) | Opening hinged door | Yes | 1 | 4.0 |
| Panelboard (277/480V) | Testing or troubleshooting energized parts | Yes | 2 | 8.0 |
| Switchgear (480V, >25 kA fault) | Racking circuit breaker in or out | Yes | 4 | 40.0 |
| MCC (≤600V, <65 kA fault) | Operating handle (doors closed) | No | N/A | N/A |
This example shows that the task, equipment type, voltage level, and available fault current influence whether PPE is required and at what protection level. Always verify values with the latest NFPA 70E edition and system-specific data. To understand how boundary distances are determined based on incident energy, review our Arc Flash Boundary Table By Incident Energy article.
Electricity Today T&D Magazine Subscribe for FREE

- Timely insights from industry experts
- Practical solutions T&D engineers
- Free access to every issue
Arc Flash Categories by Voltage Chart
Here is a simplified version of the Arc Flash Categories by Voltage Chart, aligned with NFPA 70E guidance and commonly used voltage levels and tasks. This table includes typical PPE categories based on equipment type and voltage but should always be verified against the current NFPA 70E standard and a formal arc flash study. For further insight into how voltage and equipment type influence protection levels, see the Arc Flash Categories by Voltage Chart.
| Equipment Type | Voltage Range | Task Example | Arc Flash PPE Required? | PPE Category | Minimum Arc Rating (cal/cm²) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Panelboard (AC) | ≤240V | Opening hinged cover | Yes | 1 | 4.0 |
| Panelboard (AC) | 277/480V | Testing or troubleshooting energized parts | Yes | 2 | 8.0 |
| Motor Control Center (MCC) | ≤600V | Operating handle (doors closed) | No | N/A | N/A |
| Switchgear | 480V (>25 kA fault) | Racking a circuit breaker | Yes | 4 | 40.0 |
| Switchgear | 4.16 kV | Operating with doors open | Yes | 4 | 40.0+ |
| Transformer | 13.8 kV | Energized work on terminals | Yes | 4 | 40.0+ |
Arc Flash Boundaries
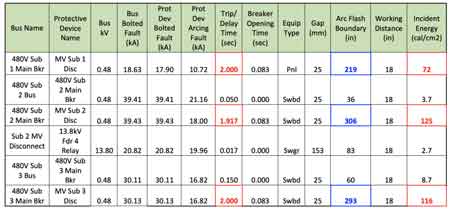
The arc flash boundary is the area around an electrical arc where a worker is at risk of serious injury. The NFPA 70E arc flash table provides information on the minimum distance required to ensure worker safety. The boundary is determined based on the incident energy level, which measures the heat energy released during an electrical arc. The higher the incident energy level, the larger the arc flash boundary.
For insights into the arc flash boundary as defined by NFPA 70E, visit our Arc Flash Boundary page.
Arc Flash Hazard
The arc flash hazard refers to the risk of injury or death resulting from an electrical arc. It is determined based on the incident energy level and the duration for which the electrical system is shut off. The incident energy level is a function of the fault current, the duration of the fault, and the distance from the arc. The hazard is assessed to determine the appropriate level of PPE needed to protect workers.
Visit Our NFPA 70E Arc Flash Training Page
Incident Energy Analysis Method
The incident energy analysis method determines an electrical system's incident energy level and arc flash boundary. It uses a series of equations and data inputs to calculate these. The method requires a detailed analysis of the electrical system and is typically performed by a qualified electrical engineer or technician. The incident energy analysis method is essential in ensuring worker safety, as it helps to identify potential arc flash hazards and determine the appropriate level of PPE needed. Learn how an Incident Energy Analysis can supplement the NFPA 70E table method for precise PPE selection.
PPE Category Method
The PPE category methods are used to determine the appropriate level of PPE for a given electrical system. The categories are based on the incident energy level and the working distance from the arc. The PPE category method provides a simple way to determine the appropriate level of PPE for workers in different electrical situations. The PPE categories are as follows:
| PPE Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Category 1 | Minimal PPE, such as safety glasses and gloves |
| Category 2 | Cotton clothing plus arc-rated PPE, such as a face shield and jacket |
| Category 3 | Cotton clothing plus arc-rated PPE plus flash suit hood |
| Category 4 | Cotton clothing plus arc-rated PPE plus flash suit hood plus additional gear like hard hat and safety glasses |
Working Distance
The working distance is the minimum distance required between workers and the electrical arc to ensure safety. It is determined based on the incident energy level and the PPE category. Therefore, the working distance is critical in determining the appropriate level of PPE and ensuring worker safety. Explore the full range of Arc Flash PPE Requirements to ensure compliance with NFPA 70E guidelines.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do I Use the NFPA 70E PPE Tables?
To use the tables, you need to know the incident energy level and the working distance for the electrical system you are working on. Once you have this information, you can use the tables to determine the appropriate level of PPE for your workers. The PPE categories are arranged based on incident energy level and working distance, making it easy to determine the appropriate level of protection for a specific task.
Which NFPA 70E Table Do I Use?
NFPA 70E Table 130.7(C)(15)(a) is used to determine if an arc flash hazard exists. The table provides information on the minimum incident energy level required to create one. If the incident energy level exceeds the threshold in the table, an arc flash hazard exists, and personal protective equipment (PPE) must be worn to protect workers.
FREE EF Electrical Training Catalog
Download our FREE Electrical Training Catalog and explore a full range of expert-led electrical training courses.

- Live online and in-person courses available
- Real-time instruction with Q&A from industry experts
- Flexible scheduling for your convenience
What is the NFPA 70E Table Method?
The NFPA 70E table method determines the incident energy level and arc flash boundary for a given electrical system. The method is based on tables that provide information on the incident energy level and arc flash boundary based on the type of equipment and the working distance. The tables offer a quick and straightforward way to determine the appropriate level of PPE for workers in different electrical situations.
What is the Table Method for Arc Flash?
The table method for arc flash uses the NFPA 70E arc flash table to determine the appropriate level of PPE for workers based on the incident energy level and working distance. It is a straightforward method for determining the necessary level of protection for a specific task.
What Are the Limitations of Using the NFPA 70E Table 130.7(C)(9)(a) for MCCs?
The NFPA 70E Table 130.7(C)(9)(a) provides information on the minimum PPE level required for workers working in motor control centers (MCCs). However, this table has some limitations. For example, the table does not account for the actual fault current or the protective device settings of the MCC, which can impact the incident energy level. Therefore, performing an incident energy analysis is crucial to determine the appropriate PPE level for working on Motor Control Centers (MCCs).
What Are the Limitations of Using the NFPA 70E Table 130.7(C)(9)(a) for MV Switchgear?
The NFPA 70E Table 130.7(C)(9)(a) is also used to determine the minimum PPE level required for workers working on medium-voltage (MV) switchgear. However, the table has some limitations. For example, the table does not consider the type of protective device used, such as a fuse or circuit breaker, which can affect the incident energy level. Therefore, performing an incident energy analysis is essential to determine the appropriate PPE level for working on MV switchgear.
Summary of Task Category Comparisons
Task category comparisons enable the comparison of workers' various tasks in different electrical situations. The comparisons allow for a quick and easy determination of the appropriate level of PPE required for a specific task. The comparisons are based on the incident energy level and the working distance, indicating the level of protection needed for a given task.
What is the Quick Check Method?
The Quick Check Method is a simplified approach for determining the appropriate level of PPE for a specific task. It is based on the type of task and the equipment being used, providing a quick and straightforward way to determine the required level of protection.
Our NFPA 70E Arc Flash Training course offers comprehensive instruction on PPE, incident energy, and hazard assessments.
Related Pages