How to Calculate Power Factor: A Step-by-Step
By R.W. Hurst, Editor
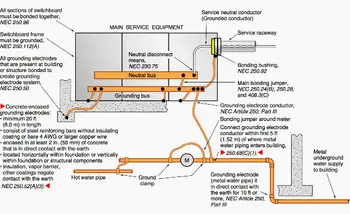
Grounding and Bonding and The NEC - Section 250
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.
- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our NFPA 70E Fact Sheet – 2024 Electrical Safety Edition

- Understand how NFPA 70E works with NEC and NFPA 70B standards
- Clarify the shared responsibility between employers and employees
- Learn how NFPA 70E supports OSHA compliance
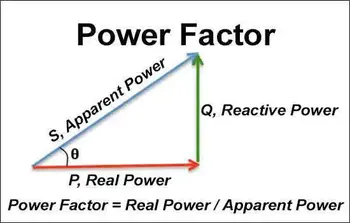
Calculate power factor by dividing real power (kW) by apparent power (kVA). This ratio indicates the efficiency with which electrical power is utilized. A power factor closer to 1 means better efficiency and reduced energy losses in electrical systems.
Power Quality Analysis Training
Request a Free Power Quality Training Quotation
How to calculate power factor?
Power factor calculation helps assess energy efficiency in AC power systems.
✅ Use the formula: Power Factor = Real Power (kW) ÷ Apparent Power (kVA)
✅ Indicates how effectively electrical power is converted into work
✅ Helps reduce energy losses and improve system performance
Calculating power factor involves dividing real power (in kW) by apparent power (in kVA). This simple formula helps businesses assess electrical efficiency, reduce waste, and optimize equipment performance for lower energy costs.
Understanding how to calculate power factor (PF) is essential for improving electrical system performance. By measuring the ratio of real power to apparent power (S), facility managers can pinpoint inefficiencies, identify equipment issues, and take corrective actions to minimize energy losses. Proper calculation ensures smoother operations, fewer penalties from utilities, and significant cost savings over time.
How to Calculate Power Factor
Knowing how to calculate PF is essential for understanding the efficiency of an electrical system. The calculation is simple once you know two key values: real power and S.
The Basic Formula
The standard formula for PF is:
PF = Real Power (kW) ÷ Apparent Power (S)
Real power is the energy actually consumed by equipment to perform work. S is the total energy supplied, combining both usable and non-usable components.
Step-by-Step Guide
-
Measure Real Power (kW):
Use a wattmeter to determine the real energy consumption. -
Measure S (kVA):
Measure voltage (V) and current (A), then calculate kVA using the formula:S (kVA) = (Voltage × Current) ÷ 1000
-
Apply the PF Formula:
Divide real power by S.
Practical Example
Suppose you measure the following in your system:
Electricity Today T&D Magazine Subscribe for FREE

- Timely insights from industry experts
- Practical solutions T&D engineers
- Free access to every issue
-
Real Power = 300 kW
-
Voltage = 400 V
-
Current = 500 A
First, calculate S:
(400 × 500) ÷ 1000 = 200 kVA
Now calculate PF:
300 ÷ 200 = 1.5 (which indicates an error; you cannot have a PF above 1)
Let's correct this:
(400 × 500) ÷ (1000 × √3) ≈ 346 kVA (for a 3-phase system)
Then:
300 ÷ 346 ≈ 0.87
Result: The PF is 0.87, meaning the system operates at 87% efficiency.
Need a faster way? Use our Power Factor Calculator to automate the calculation.
Why It Matters
Accurately calculating the power factor enables facilities to identify inefficiencies and correct them before they result in high energy costs or penalties.
Learn about techniques in Power Factor Correction.
Additional Tips
-
Always measure during peak load times for accuracy.
-
Use reliable measuring devices, such as clamp meters and digital analyzers.
-
If your calculated PF is below 0.9, improvements such as capacitor banks or Automatic Power Factor Controllers may be necessary.
For further reading on What is Power Factor? or how Capacitors Help Improve Efficiency, see our detailed guides.
Related Articles




