Quality of Electricity
Substation Grounding Training
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our OSHA 3875 Fact Sheet – Electrical PPE for Power Industry Workers

- Follow rules for rubber gloves, arc-rated PPE, and inspection procedures
- Learn employer obligations for testing, certification, and training
- Protect workers from arc flash and electrical shock injuries
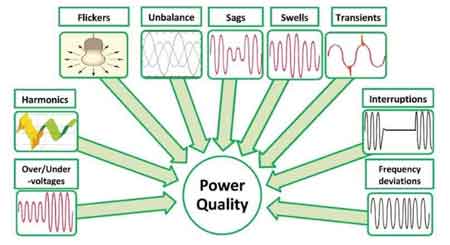
Quality of electricity measures how stable and reliable power is. It affects equipment life, energy costs, and performance. Good quality power has consistent voltage and frequency, low harmonics, and minimal interruptions or distortions in the electrical supply.
What is "quality of electricity"?
Quality of electricity describes how stable, clean, and reliable the electrical power is in a system.
✅ Ensures voltage and frequency remain within optimal limits
✅ Reduces harmonics, flicker, and transients that harm equipment
✅ Improves energy efficiency and extends system life
The quality of electricity refers to the stability and consistency of the electrical supply in terms of voltage, frequency, and waveform. In modern electrical systems, maintaining a high standard is critical to ensuring that electrical equipment functions properly without interruption or damage. Poor quality can cause serious issues, particularly in systems with sensitive electronic equipment that requires precise electrical regulation. In this article, we examine the factors that affect the quality of electrical supply, its impact on systems, and strategies for mitigating related issues. To understand how voltage consistency affects power quality, see our guide on what is power quality.
Power Quality Analysis Training
Request a Free Power Quality Training Quotation
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the quality of electricity, and why is it important for electrical systems?
It is essential because it directly impacts the reliability and performance of electrical systems and supply networks. A high-quality electrical supply ensures that equipment operates efficiently, reducing the risk of malfunctions, breakdowns, or damage. Consistent voltage levels, stable frequency, and a clean voltage waveform are crucial for maintaining system performance, especially in environments with sensitive electronic equipment. Poor electrical performance often stems from low power factor; learn more in our article on how to calculate power factor.
What factors determine the quality of electricity?
Several factors influence electrical quality, including voltage sags, voltage drops, harmonic distortion, and PF. The standard supply frequency in many countries is fundamental 60 Hz, but issues can arise when the frequency deviates or when harmonic frequencies, such as 180 Hz, interfere with the system. Harmonic distortion results from nonlinear loads, which generate unwanted frequencies that distort the voltage waveform. Another key factor is power factor (PF), which measures how effectively electricity is being utilized. Maintaining an optimal PF is crucial for ensuring efficient operation of systems. Voltage sags and drops are common issues that degrade power quality; our article on voltage drops explains why they matter.
FREE EF Electrical Training Catalog
Download our FREE Electrical Training Catalog and explore a full range of expert-led electrical training courses.

- Live online and in-person courses available
- Real-time instruction with Q&A from industry experts
- Flexible scheduling for your convenience
How can poor PQ impact industrial and commercial equipment?
Poor PQ can have significant consequences for industrial and commercial operations. PQ issues, such as voltage sags, harmonic voltage distortion, and fluctuations in the supply, can lead to malfunctions or damage to electrical equipment. Sensitive equipment, such as computers, servers, and other electronics, is particularly susceptible to these disturbances. Over time, PQ problems can reduce the lifespan of machinery, increase maintenance costs, and lead to unplanned downtime, ultimately affecting overall productivity. Harmonics can distort waveforms and damage sensitive equipment; visit our page on power quality and harmonics to learn more about this topic.
What are common issues that degrade the PQ and how can they be mitigated?
Common PQ problems include voltage drops, harmonic distortion, and unstable frequency. These issues are often caused by sudden changes in load, equipment failures, or external disturbances, such as lightning. Harmonic distortion, for instance, is introduced by nonlinear loads such as variable-frequency drives or LED lighting. To mitigate these problems, devices such as voltage regulators can stabilize voltage fluctuations, while harmonic filters reduce unwanted harmonic frequencies. Additionally, installing surge protection devices and ensuring that electrical equipment is properly rated for the system's capacity can help prevent issues from occurring. Tools like a power quality analyzer help identify voltage fluctuations, harmonics, and waveform distortions in real time.
What tools or devices are used to monitor?
Several tools are available to monitor and improve the PQ in systems. PQ analyzers are commonly used to assess system performance by measuring parameters such as harmonic distortion, power factor (PF), and voltage stability over extended periods of time. Voltage regulators are crucial for maintaining a stable voltage level, particularly in systems susceptible to voltage sags and drops. Harmonic filters, capacitors, and advanced monitoring systems can also be used to mitigate the effects of harmonic distortion and ensure a high-quality supply for both electrical systems and equipment. One effective strategy for improving electrical efficiency is power factor correction, which minimizes reactive power losses.
Maintaining a high-quality electrical supply is crucial for the safe and efficient operation of systems. Various factors, such as harmonic distortion, voltage sags, and PF, play a significant role in determining the stability and reliability of electrical systems. By using tools like voltage regulators and harmonic filters, and regularly monitoring the system, PQ can be preserved, protecting both the system and the electrical equipment connected to it. For a deeper look at disturbances like flicker and waveform instability, see our detailed guide on power quality voltage flicker.
Related Articles