Electrical Substation Articles | From Electricity Today Magazine
The IEC 61850 protocol has become the global standard for substation automation, enabling high-speed communication, interoperability, and streamlined integration of...
The integration of renewable energy sources (RES) into smart grid systems represents a fundamental shift in how energy is generated,...
A coalition of large energy consumers and ratepayer advocates has filed a complaint with the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC),...
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) has rejected a proposal from PJM Interconnection, one of the United States' largest regional...
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) recently hosted the Co-Located Load Conference, a significant event that focused on resource adequacy,...
Electrical Substation CHANNEL
Electrical Substation ARTICLES
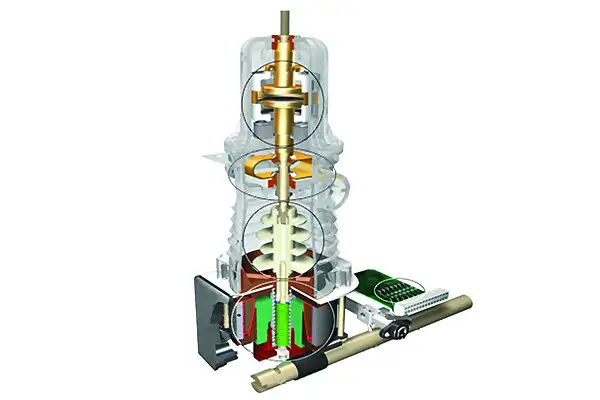
Safe Work Practices for Circuit Breakers
In our daily work lives, we often are required to reset...
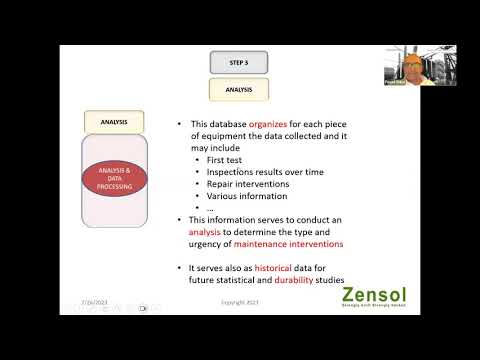
Gas Insulated Substation Explained
A Gas Insulated Substation (GIS) utilizes SF6 gas for insulation in...
Substation Explosion
A substation explosion can trigger a major power outage, release plumes...
Substation Focused on Environmental Design
One of the important trends in design of new overhead lines...
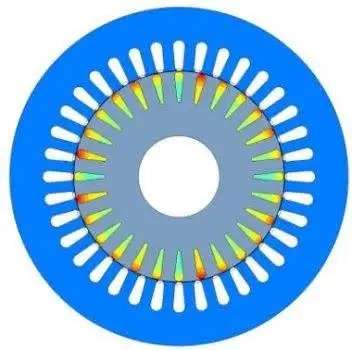
Substation Breaker - T&D Protection
A substation breaker is a critical device in electrical substations, designed...On-site Training Electrical Substation
Interested in Cost Effective, Professional On-site Electrical Electrical Substation Training?
We can present an Electrical Training Course to your electrical engineering and maintenance staff, on your premises, tailored to your specific equipment and requirements. Click on the link below to request a FREE quotation.
LIVE ONLINE ELECTRICAL TRAINING SCHEDULE
- MV & HV Circuit Breaker Maintenance Training
- Grounding and Bonding Training And The CE Code
- Arc Flash Analysis/Study
- Substation Maintenance Training
- Short Circuit Study & Protective Device Coordination
- Arc Flash Training - CSA Z462 Electrical Safety
- UPS Battery Testing and Maintenance Training
- NFPA 70e Training
- Lightning Protection Systems Training For Utility, Industrial, Commercial & Institutional power systems
- Power Transformer Maintenance Training
- Substation Relay Protection Training
- NFPA 70b Training - Electrical Maintenance
- Emergency Generators & Standby Power Systems
- Combined NFPA 70e LV Arc Flash And HV Electrical Safety
- Arc Flash Training - CSA Z462 Electrical Safety
- Fire Alarm Training
- 2024 CE Code - Changes and Fundamentals
- CE Code Calculations: Practical Applications and Advanced Techniques
- 2024 CE Code - Combined Course: Changes/Fundamentals and Calculations
- Energy Storage Systems Course
- High Voltage Safety Training
- NFPA 70e Training
Electrical Substation Videos
Electrical Substation Product Showcases
Electrical Substation Shared Media