Electrical Room
By R.W. Hurst, Editor

NFPA 70e Training
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 6 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our NFPA 70E Fact Sheet – 2024 Electrical Safety Edition

- Understand how NFPA 70E works with NEC and NFPA 70B standards
- Clarify the shared responsibility between employers and employees
- Learn how NFPA 70E supports OSHA compliance
An electrical room is a dedicated space for housing switchgear, panels, and transformers. It enables safe power distribution and centralized control in buildings, ensuring code compliance, proper ventilation, and fire safety for industrial power systems.
What is an Electrical Room?
An electrical room is a dedicated space designed to house power distribution equipment, such as switchgear, transformers, and circuit breakers.
✔️ Contains switchgear, circuit breakers, and panels
✔️ Provides centralized control of power systems
✔️ Must meet fire, ventilation, and access safety codes
An electrical room typically manages a facility’s power distribution, ensuring safe operations, providing maintenance access, and protecting systems against overloads or environmental hazards.
Request a Free Training Quotation
Key Elements of Electrical Room Design
Designing an electrical room requires striking a balance between functionality, safety, and long-term maintenance accessibility. Poor design can lead to cramped spaces, overheated equipment, and an increased risk of accidents.
Adequate Space and Clearance
Adequate working clearances around equipment are mandatory for safe operation and emergency response. The NEC 110.26 defines minimum space requirements depending on voltage and operating conditions.
-
Maintain at least three feet of clear working space in front of panels and switchgear.
-
Ensure unobstructed door swings and easy access to disconnect switches and circuit breakers.
-
Provide emergency egress pathways that are wide enough to allow for quick evacuation.
Electrical rooms operating large systems should also consider their power quality needs to protect sensitive electronic equipment.
Electrical Room Ventilation and Environmental Control
Heat buildup inside an enclosure can significantly reduce the lifespan of sensitive equipment. Proper ventilation and climate control systems help maintain safe operating temperatures and control humidity.
-
Install mechanical ventilation or dedicated cooling systems where necessary.
-
Monitor humidity levels to prevent condensation, which can cause short circuits or corrosion.
For electrical rooms housing critical loads, integrating electrical generators and UPS systems can further safeguard operational continuity during power disruptions.
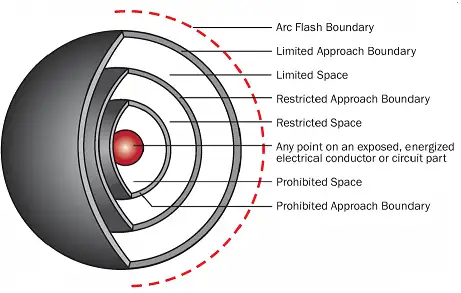
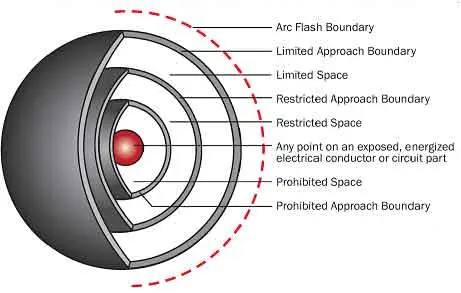
Test Your Knowledge About Arc Flash!
Think you know Arc Flash? Take our quick, interactive quiz and test your knowledge in minutes.
- Instantly see your results and score
- Identify strengths and areas for improvement
- Challenge yourself on real-world electrical topics
Electrical Room Lighting and Accessibility
Good lighting supports safe work practices by allowing personnel to read equipment labels, settings, and safety signage easily. Select energy-efficient, shadow-free lighting and ensure fixtures are positioned to minimize dark spots.
Accessibility is equally important. Maintain clear, signed pathways, and avoid storing non-conductive materials that can obstruct exits or access to control panels.
Discover how to minimize hazards in confined spaces with our comprehensive guide on safety tips.
Electrical Room HVAC Design
Proper climate control is essential for maintaining the optimal performance of power distribution equipment. Without HVAC systems, heat buildup from active power distribution can damage sensitive components and reduce the system's lifespan. Electrical rooms typically house high-energy equipment that generates substantial heat, making ventilation or dedicated cooling systems essential for maintaining a comfortable working environment. Regular HVAC maintenance ensures that the room or space remains within acceptable operating temperatures.
Electrical Room Fire Suppression Systems
Electrical rooms require specialized fire protection solutions due to the presence of energized equipment. Standard water-based sprinkler systems are often unsuitable, as water can cause additional hazards. Instead, fire suppression systems such as clean agent systems (like FM-200 or Novec 1230) are recommended to extinguish fires without damaging distribution equipment. Proper installation and regular testing of these systems are key components of maintaining a safe working environment.
Electrical Room Cable Management Best Practices
Efficient cable management within an electrical room ensures safe operation, minimizes maintenance issues, and promotes improved airflow. Cables should be neatly routed in trays, separated by voltage class where necessary, and clearly labelled for easy identification. Poor cable management can obstruct access to critical distribution panels, increasing the risk of overheating. Investing in proper cable pathways protects both personnel and equipment.
Emergency Lighting Requirements
In the event of a power outage or emergency, electrical rooms must have reliable backup lighting to ensure safe evacuation and facilitate emergency operations. Emergency lighting systems should be tied to backup generators or UPS systems to ensure continuous illumination. This is particularly important where facilities typically house critical distribution equipment that must be shut down or isolated in the event of an emergency.
Electrical Room Safety Protocols
Electrical rooms are high-risk areas if proper safety protocols are not followed. Implementing robust safety protocols is crucial for protecting both workers and equipment.
Controlled Access and Personnel Training
Access to electrical rooms should be restricted to authorized personnel who are trained in electrical safety practices. Visitors and unauthorized employees must be prohibited unless supervised.
Post clear signage at all access points, warning of potential hazards and the requirement for personal protective equipment (PPE) where applicable.
Proper Equipment Labeling
Clear, permanent labels identifying voltage levels, circuit functions, and hazard warnings must be affixed to all panels and equipment. Electrical rooms that contain energized components should also display arc flash labels where necessary.
Proper labeling ensures faster troubleshooting, safer maintenance, and better emergency response.
Emergency Response Preparedness
An effective emergency plan should be in place, including:
-
Emergency shut-off procedures.
-
Clearly marked exits and backup lighting.
-
Regular fire extinguisher inspections and fire suppression system checks.
Facilities should also regularly verify NEC 250-122 grounding and bonding systems to ensure fault currents are safely directed away from personnel and equipment.
Preventive Maintenance
Regular maintenance enhances reliability, lowers repair costs, and prolongs equipment life.
Routine Inspections
Schedule inspections at least once a year, or more frequently in high-risk or high-usage environments. Inspections should focus on:
-
Signs of overheating, discoloration, or arcing.
-
Physical damage or loose connections.
-
Performance of ventilation and environmental controls.
Utilize tools such as thermal imagers and infrared cameras to promptly identify hidden faults.
Sign Up for Electricity Forum’s Arc Flash Newsletter
Stay informed with our FREE Arc Flash Newsletter — get the latest news, breakthrough technologies, and expert insights, delivered straight to your inbox.
Preventive Maintenance Plans
Establish a preventive maintenance schedule tailored to your facility's needs. Core activities should include:
-
Cleaning dust and contaminants from equipment and ventilation systems.
-
Testing protective relays, ground fault systems, and emergency lighting.
-
Lubricating mechanical components where required.
Maintenance staff should always follow lockout tagout procedures before performing any service.
For facilities with motor control centers, maintaining electric motors and drives (VFDs) is critical to keeping motors operating efficiently.
Comprehensive Documentation
All inspections, tests, and repairs must be thoroughly documented. Good record-keeping:
-
Supports predictive maintenance planning.
-
Provides proof of regulatory compliance.
-
Helps track emerging trends and repeated issues.
Discover incident energy analysis as a proactive approach to enhancing safety and maintenance planning.
Compliance with Standards and Regulations
Facilities must comply with various regulatory codes and standards to ensure the safety of personnel and the reliability of operations.
-
NFPA 70E and CSA Z462: Provide requirements for assessing risks, training workers, and selecting appropriate PPE.
-
OSHA Standards: Mandate safe design, operation, and maintenance of systems under 29 CFR 1910 Subpart S.
Facilities operating transformers inside rooms must also be familiar with transformer fuse protection to ensure safe isolation of faults.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What equipment is typically found in an electrical room?
Rooms typically contain switchgear, motor control centers, circuit breakers, transformers, uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems, and backup generators.
How often should an electrical room be inspected?
Perform inspections at least annually. Critical facilities with continuous operations should conduct quarterly or even monthly inspections.
How does poor ventilation affect an electrical room?
Without proper ventilation, equipment can overheat, leading to thermal breakdown, increased maintenance costs, and a higher risk of equipment failure.
What training is required for electrical room personnel?
Personnel must complete safety training, which includes topics such as PPE selection, arc flash awareness, and safe lockout/tagout procedures.
Register for one of our Electricity Forum electrical courses to ensure compliance and maintain worker safety.
Related Resources
Explore more from our Industrial Power System Library: