What Is a VFD?
By R.W. Hurst, Editor
Motor Control Training
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our NFPA 70E Fact Sheet – 2024 Electrical Safety Edition

- Understand how NFPA 70E works with NEC and NFPA 70B standards
- Clarify the shared responsibility between employers and employees
- Learn how NFPA 70E supports OSHA compliance
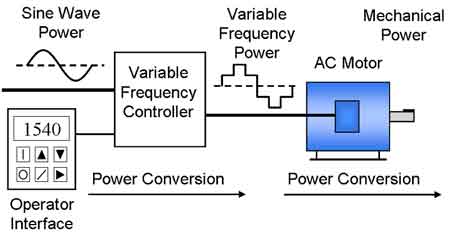
A Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) controls motor speed and torque by adjusting frequency and voltage. VFDs improve energy efficiency, reduce electrical stress, and extend equipment life in industrial, commercial, and HVAC applications.
What Is a VFD?
A VFD is an electronic device that provides precise control over the speed and torque of AC electric motors, making them highly energy efficient and cost-effective.
✅ A VFD is an electronic device that regulates AC motor speed and torque.
✅ It works by varying the input frequency and voltage supplied to the motor.
✅ A VFD is used for energy savings, process control, and reducing wear on equipment.
Electric Motor Testing Training
Request a Free Training Quotation
Variable frequency drives are electronic devices that provide precise control over the speed and torque of AC electric motors, making them highly energy-efficient and cost-effective. When precise speed control is needed in HVAC or industrial systems, consider the role of a variable frequency drive (VFD) in optimizing AC motor performance.
A VFD works by varying the frequency and voltage of the power supplied to the motor. They use pulse width modulation (PWM) techniques to generate high-frequency voltage pulses with varying pulse widths. They are utilized in a wide range of industrial and commercial applications, enabling precise control over the speed and torque of electric motors, which leads to significant energy savings and process improvements.
In addition, it offers several advantages over traditional motor control methods, such as mechanical speed control and fixed-speed drives, including energy efficiency, precise control, soft start, reduced maintenance, and improved safety. With its ability to precisely control the speed and torque of electric motors, a VFD has become an essential component of modern power systems. To understand how speed regulation fits into broader motor systems, see our guide on electric motor control, which covers the fundamentals of managing torque, current, and direction.
FREE EF Electrical Training Catalog
Download our FREE Electrical Training Catalog and explore a full range of expert-led electrical training courses.

- Live online and in-person courses available
- Real-time instruction with Q&A from industry experts
- Flexible scheduling for your convenience
VFD Basics
An AC drive, also known as a frequency converter, is an electronic device that controls the speed of an AC electric motor by varying the frequency and voltage of the power supplied to the motor. The VFD consists of three main components: a rectifier, a DC bus, and an inverter.
The rectifier converts AC voltage from the mains into DC voltage, which is then filtered and stored in the DC bus. The inverter then converts the DC voltage back into an AC voltage of varying frequency and voltage, which is supplied to the motor. By adjusting the frequency of the AC voltage supplied to the motor, the motor's speed can be controlled. If you’re just starting to explore the field, our overview of how electric motors work offers a solid foundation for understanding speed modulation principles.
How Does a VFD Work?
A VFD works by varying the frequency of the AC voltage supplied to the motor. It is a device that controls the speed of the motor. The speed of an AC motor is directly proportional to the frequency of the AC voltage supplied to it. Therefore, by varying the frequency of the AC voltage supplied to the motor, the speed of the motor can be controlled to match the speed of the motor. An insulated gate bipolar transistor IGBT manages the sine wave of single-phase motors.
A VFD uses pulse width modulation (PWM) techniques to vary the frequency of the AC voltage supplied to the motor. The inverter in the VFD generates a series of high-frequency voltage pulses with varying pulse widths. The average voltage and frequency of the AC voltage supplied to the motor can be controlled by varying the width of these pulses.
The control system also provides precise control over the motor's acceleration and deceleration, which is critical in many industrial applications. The DC bus in the VFD also serves as a buffer to smooth out fluctuations in the power supply, thereby ensuring a stable power supply to the motor.
Applications of VFDs
The VFD is utilized in a wide range of industrial and commercial applications, enabling precise control over the speed and torque of electric motors, resulting in significant energy savings and process improvements. Some of the main applications of VFDs are:
-
HVAC Systems: A VFD is used in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems to control the speed of fans and pumps, resulting in significant energy savings.
-
Industrial Automation: A VFD is used in various industrial automation applications, such as conveyor systems, cranes, and mixers, to provide precise control over the speed and torque of electric motors.
-
Renewable Energy Systems: The VFD utilizes renewable energy sources, such as wind turbines and solar panels, to regulate the speed of the generator or motor and optimize power output.
-
Electric Vehicles: A VFD is used in electric vehicles to control the speed of the motor and improve energy efficiency, resulting in a longer driving range and reduced energy consumption.
Advantages
VFD technology offers several advantages over traditional motor control methods, such as mechanical speed control and fixed-speed drives. Some of the main advantages of VFDs are:
-
Energy Efficiency: They can save significant amounts of energy by matching the motor's power consumption to the application's demand.
-
Precise Control: They provide precise control over the speed and torque of electric motors, resulting in improved process control and reduced wear and tear on equipment.
-
Soft Start: They provide a soft start for electric motors by gradually ramping up the speed and torque, resulting in reduced stress on the motor and its mechanical components.
-
Reduced Maintenance: They can reduce the maintenance requirements of electric motors by providing more precise control over the speed and torque of the motor
-
Improved Safety: They can improve the safety of industrial applications by providing precise control over the speed and torque of electric motors, reducing the risk of accidents and injuries.
Sign Up for Electricity Forum’s Motors and Drives Newsletter
Stay informed with our FREE Motors and Drives Newsletter — get the latest news, breakthrough technologies, and expert insights, delivered straight to your inbox.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the benefits of using a VFD?
A VFD offers several benefits, including energy efficiency, precise control over motor speed, soft start and stop capabilities, reduced maintenance requirements, and enhanced safety. VFDs can save energy by matching the motor's power consumption to the application's demand. They also provide precise control over the speed and torque of the motor, resulting in improved process control and reduced wear and tear on equipment. In addition, VFDs' soft start and stop feature reduces stress on the motor and mechanical components, while the improved safety is due to precise control over motor speed and torque.
How does a VFD control motor speed?
A VFD controls the speed of a motor by varying the frequency of the AC voltage supplied to the motor. The speed of an AC motor is directly proportional to the frequency of the AC voltage supplied to it. Therefore, by varying the frequency of the AC voltage supplied to the motor, the motor's speed can be controlled. The VFD uses pulse width modulation (PWM) techniques to vary the frequency of the AC voltage supplied to the motor. For deeper insight into how motor structure affects control strategies, visit our page on electric motor design and its influence on speed and torque behavior.
What types of motors can be controlled by a VFD?
A VFD can control the speed of various types of motors, including induction motors, permanent magnet motors, and synchronous motors.
How do you choose the right VFD for your application?
Choosing the right one for your application involves several factors, including the motor's power rating, the type of motor, the load requirements, the ambient temperature, and the operating environment. It is also essential to consider the features and specifications, such as the control method, PWM frequency, voltage and current ratings, and overload capacity.
What are the VFD maintenance requirements?
VFDs have relatively low maintenance requirements, but following the manufacturer's guidelines for maintenance and troubleshooting is essential. Regular maintenance can include inspecting the VFD for signs of wear or damage, cleaning and replacing filters, checking and tightening electrical connections, and testing the motor control under load conditions. It is also recommended to have the VFD serviced by a qualified technician on a periodic basis. Enhancing system performance goes beyond speed adjustment—proper electric motor maintenance ensures long-term reliability and efficiency.
Related Articles