How are arc flash and electric shock protection boundaries determined?
By R.W. Hurst, Editor
CSA Z462 Arc Flash Training - Electrical Safety Essentials
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 6 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our OSHA 4475 Fact Sheet – Being Aware of Arc Flash Hazards

- Identify root causes of arc flash incidents and contributing conditions
- Apply prevention strategies including LOTO, PPE, and testing protocols
- Understand OSHA requirements for training and equipment maintenance
Arc flash and electric shock protection boundaries are determined using NFPA 70E. Key factors include system voltage, fault current, and clearing time. These values define safe distances to prevent injury from arc blast, thermal exposure, and electrical shock.
How Are Arc Flash and Electric Shock Protection Boundaries Determined?
Arc flash and shock boundaries are calculated to reduce electrical injury risk:
✅ Based on NFPA 70E formulas, considering voltage and fault current
✅ Establishes Limited, Restricted, and Arc Flash boundaries
✅ Helps workers choose the correct PPE and safety practices
Establishing these critical safety zones involves assessing various factors to protect personnel from hazards.
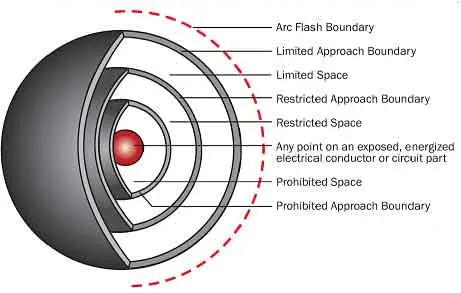
Shock Protection Boundaries: Defined by NFPA 70E, these include:
-
Limited Approach Boundary: The distance from an exposed energized conductor within which a shock hazard exists. Only qualified personnel should cross this boundary, and unqualified workers must be supervised.
-
Restricted Approach Boundary: A closer distance near energized parts where there is an increased risk of shock due to arc-over combined with inadvertent movement. Only qualified workers using appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and insulated tools are permitted within this boundary.
-
Arc Flash Boundary: This boundary is determined based on the potential incident energy of an arc flash event. It represents the distance at which the incident energy equals 1.2 cal/cm², the threshold for a second-degree burn. Factors influencing this boundary include system voltage, available fault current, and the duration of the arc. Detailed calculations, often guided by standards like IEEE 1584, are performed to establish this boundary accurately.
Understanding and accurately determining these boundaries are essential steps in mitigating hazards and ensuring workplace safety. To fully understand how protection zones are calculated, see our guide on arc flash boundary and how it relates to safe working distances.
Sign Up for Electricity Forum’s Arc Flash Newsletter
Stay informed with our FREE Arc Flash Newsletter — get the latest news, breakthrough technologies, and expert insights, delivered straight to your inbox.
Arc Flash and Shock Protection Boundaries – Summary Table
| Boundary Type | Definition | Who May Enter |
|---|---|---|
| Limited Approach Boundary | Distance where a shock hazard exists. | Unqualified workers with supervision; qualified workers. |
| Restricted Approach Boundary | Closer distance with increased shock risk due to arc-over potential. | Qualified workers with proper PPE and insulated tools. |
| Arc Flash Boundary | Distance where incident energy equals 1.2 cal/cm² (second-degree burn threshold). | Any worker wearing PPE rated for calculated energy level. |
Implementing Safety Measures
Establishing and adhering to arc flash and shock protection boundaries is essential for maintaining a safe working environment. Here are some practical steps:
-
Conduct Regular Risk Assessments: Regularly assess the workplace to identify potential arc flash and shock hazards. Update the boundaries and safety measures as needed.
-
Provide Training: Ensure that all employees, especially those working within the restricted approach boundary, receive comprehensive training on safety and the use of PPE.
-
Equip with Proper PPE: Provide workers with appropriate PPE based on the incident energy levels and voltage ratings of the systems they work with. Learn more about PPE requirements and how they’re matched to calculated boundaries in our detailed arc flash PPE category guide.
-
Use Clear Signage: Clearly mark the arc flash boundaries and shock protection boundaries with signs and floor markings to alert workers to the potential hazards.
-
Enforce Safety Protocols: Implement strict safety protocols, including the use of work permits for tasks within the restricted approach boundary, and ensure that unqualified personnel are escorted by a qualified person when necessary.
Understanding and implementing arc flash and shock protection boundaries is crucial for ensuring workplace safety. By determining these boundaries based on incident energy levels and voltage ratings, and by providing proper PPE and training, employers can significantly reduce the risk of serious injuries. Regular risk assessments and strict adherence to safety protocols further enhance workplace safety, protecting workers from the potentially devastating effects of arc flashes and shocks. Learn how factors like voltage and fault current shape calculations in our resource on arc flash boundary calculation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is the Primary Factor That Determines the Boundary?
The primary factor determining the protection boundary is the incident energy, measured in calories/cm². This energy level is calculated based on the potential arc flash hazard, which considers factors such as fault current, arc duration, and distance from the arc source. NFPA 70E tables set the boundary at the distance where the incident energy drops to 1.2 calories/cm², the threshold for second-degree burns. Explore step-by-step methods in our 7 steps to arc flash analysis, helping ensure accurate boundary assessments.
What Is the Most Important Criterion for Choosing PPE for Arc Flash or Shock?
The most important criterion for choosing PPE for arc flash or shock protection is the voltage rating and incident energy level. The PPE must be rated to withstand the maximum potential incident energy of the arc flash and the system's voltage. Properly rated PPE includes arc-rated clothing, gloves, face shields, and other protective gear designed to protect against specific levels of incident energy and voltage. Use our online arc flash calculator to estimate incident energy and determine approach limits based on system data.
Which Three Factors Does an Arc Flash Risk Assessment Determine?
An arc flash risk assessment is crucial for determining several key factors that ensure workplace safety:
-
Incident Energy Calculation: The assessment calculates the incident energy (calories/cm²) at various distances from the equipment. This helps establish the arc flash boundaries and determine the appropriate PPE. See how incident energy defines burn risk thresholds in our arc flash boundary table by incident energy.
-
Protection Boundaries: The assessment defines the boundaries within which different safety measures must be implemented. This includes the protection boundary where incident energy is 1.2 calories/cm², the limited approach boundary, and the restricted approach boundary.
-
Appropriate Safety Measures: The assessment identifies the necessary safety measures, including the required PPE levels and safety protocols that qualified workers must follow when working within these boundaries.
For instance, a worker exposed to 1.2 calories/cm² of incident energy during an arc flash event is at risk of sustaining severe injuries. This threshold is significant because it represents the minimum amount of thermal energy that can cause human skin to receive second-degree burns. According to NFPA 70E and IEEE 1584, arc flash boundaries are established based on this energy level to ensure personnel safety. Proper personal protective equipment (PPE) is essential to prevent these injuries, as unprotected exposure beyond this limit can lead to serious burns and long-term tissue damage. For a full overview of electrical arc flash hazards, visit our arc flash channel page which connects all relevant safety resources.
FREE EF Electrical Training Catalog
Download our FREE Electrical Training Catalog and explore a full range of expert-led electrical training courses.

- Live online and in-person courses available
- Real-time instruction with Q&A from industry experts
- Flexible scheduling for your convenience







