3 Phase Power Explained
By R.W. Hurst, Editor
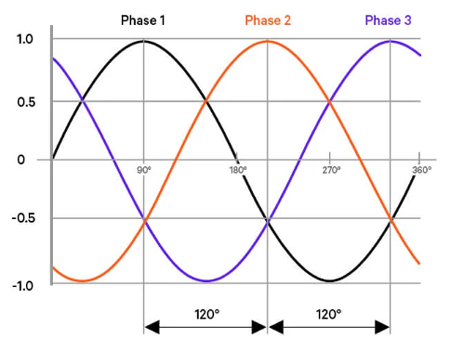
3 phase power is a type of AC electrical power using three alternating currents. Common in industrial and commercial settings, it provides consistent voltage, increased efficiency, and reduced conductor size compared to single-phase systems. Ideal for motors and heavy loads.
What is: 3 phase power?
3 phase power is a method of electrical distribution using three alternating currents, commonly used in commercial and industrial systems.
-
✅ Delivers consistent voltage for high-voltage equipment
-
✅ Reduces energy loss and increases transmission efficiency
-
✅ Supports large motors and heavy electrical loads reliably
It is is the dominant form of electricity distribution in industrial and commercial environments. Unlike single-phase, which uses one alternating voltage waveform, 3 phase systems deliver electricity through three separate waveforms, each 120 degrees out of phase with the others. This design creates a more stable and efficient energy flow, making it ideal for serving motors, heavy equipment, and large facilities. Where single systems experience periodic voltage dips, it provides near-constant energy delivery, significantly improving performance and reducing stress on electrical components.
The advantages of this balanced power delivery system go beyond stability. It is also more efficient in terms of conductor usage. For the same amount of current and voltage, a 3 phase system can transmit approximately 1.73 times more energy than a single-phase system. This means that businesses can use smaller, lighter conductors to deliver the same or even greater amounts of energy, resulting in reduced infrastructure costs and energy losses. For a deeper understanding of electrical stability in 3 phase systems, refer to our Power Quality overview, which explains voltage balance, waveform integrity, and load management.
How 3 Phase Systems Are Configured
In practice, they are wired in one of two main configurations: Wye (Y) or Delta (Δ). Each has specific advantages and is selected based on the application and infrastructure requirements.
The Wye configuration connects each of the three phase conductors to a common neutral point. This allows for both line-to-line and line-to-neutral voltages, giving it greater flexibility in mixed-load environments. Wye systems are common in commercial buildings and utility-scale distribution systems because they can serve both high-voltage equipment and standard single-phase outlets.
By contrast, the Delta configuration connects each phase conductor end-to-end, forming a closed loop with no neutral. This design is more compact and cost-effective when loads are present, such as in many industrial facilities. Delta systems are also more resilient to phase failure—if one phase fails, the system can often continue running at reduced capacity, which is not typically possible with Wye systems.
To summarize the key differences:
-
Wye (Y):
-
Provides both 3-phase and single-phase
-
Uses four wires (three phases and one neutral)
-
Ideal for applications with mixed voltage requirements
-
-
Delta (Δ):
-
Pure 3-phase distribution with three wires
-
Better fault tolerance
-
More efficient for heavy, balanced loads
-
If you're interested in understanding the differences between real, reactive, and apparent power, our guide on Apparent Power and Apparent Power vs. Real Power breaks down the essential distinctions. To calculate energy flow accurately in your setup, use our interactive Power Factor Calculator or our dedicated Apparent Power Calculator.
Electrical Behavior and Energy Calculations
A core feature of 3 phase electricity is its ability to deliver consistent torque and energy without the oscillations seen in single-phase systems. This consistency is especially important for electric motors, which operate more smoothly and efficiently when served by electricity.
From a mathematical standpoint, energy in a balanced 3 phase system is calculated using the formula:
P = √3 × V × I × PF
Where:
-
Pis total power (watts), -
Vis the line-to-line voltage, -
Iis the current, and -
PFis the power factor.
This equation highlights the energy advantage. The √3 multiplier (~1.732) represents the phase offset and indicates that a 3 phase system can deliver significantly more energy than a single-phase system for the same voltage and current. Grounding plays a vital role in power quality and safety—review our sections on Electrical Grounding and Grounding and Bonding to ensure code compliance.
Real-World Applications and Benefits
3 phase power is the backbone of industrial operations worldwide. It serves the machinery in manufacturing plants, the HVAC systems in commercial buildings, and the data centers that run the internet. Due to its efficiency and energy density, it’s also used in high-voltage transmission lines and backup systems, such as large-scale UPS.
The specific benefits include:
-
✅ Stable and continuous energy delivery, reducing vibrations and wear in electric motors
-
✅ Material efficiency, requiring less copper or aluminum for wiring
-
✅ Smaller and more efficient equipment, including motors and transformers
-
✅ Greater scalability for large buildings and industrial operations
These benefits combine to lower both operational costs and long-term maintenance needs, which is why 3 phase systems are the standard for any serious energy infrastructure. Facilities managing non-linear loads can learn how to mitigate waveform distortion with our guide on Power Quality and Harmonics.
In modern electrical engineering, alternating current (AC) is the foundation of most power distribution systems due to its efficiency in transmitting electricity over long distances. Among the various configurations, 3 phase electricity systems are the most effective because they deliver constant power, minimizing voltage fluctuations and improving performance in industrial applications. Unlike single-phase power, which suffers from dips between cycles, setups deliver power smoothly and continuously. This consistent delivery is especially beneficial for heavy machinery and motors, which rely on steady torque. A key component in many systems is the neutral wire, which enables both line-to-line and line-to-neutral connections, providing flexibility in voltage options. Compared to single-phase configurations, balanced power delivery systems with a neutral wire provide superior load balancing and energy efficiency.
Challenges and Power Quality Concerns
Despite its advantages, 3 phase power does come with some challenges. The most notable is the system complexity. These installations require more careful design, specialized equipment, and more rigorous safety standards. In Wye configurations, an imbalance or a broken neutral conductor can cause voltage fluctuations and damage to equipment. Delta configurations, while more fault-tolerant, can make troubleshooting more difficult in complex systems.
Another issue is power quality, particularly when nonlinear loads (such as variable-speed drives or LED lighting systems) are present. These loads introduce harmonics—distortions in the waveform—that can create overheating, interference, and reduced efficiency.
To maintain optimal quality, engineers often implement solutions like:
-
✅ Power factor correction capacitors to improve energy efficiency
-
✅ Harmonic filters to smooth out waveform distortions
-
✅ Active monitoring systems that detect and correct imbalances in real-time
These measures are crucial in modern facilities, where sensitive electronics and high-performance machinery coexist.
When 3 Phase Isn't Available
In some rural or older urban areas, utility providers may only deliver single-phase systems. To work around this limitation, businesses and homeowners sometimes install converters that generate artificial 3 phase electricity from single-phase supply. These include:
-
Static converters, which are compact and inexpensive but limited in performance
-
Rotary converters, which are more reliable and better suited for motor loads
-
Variable frequency drives (VFDs), which can simulate 3 phase electricity while also controlling motor speed and torque
Each option comes with trade-offs in terms of cost, complexity, and efficiency. For detailed calculations related to balanced systems, visit our Three Phase Power Calculation page, which includes formulas, worked examples, and load factor insights.
Historical and Technical Context
The origins of 3 phase power can be traced back to the late 19th century. Innovators such as Nikola Tesla, Galileo Ferraris, and Mikhail Dolivo-Dobrovolsky recognized the limitations of direct current (DC) and single-phase alternating current (AC) systems. Their combined efforts laid the foundation for modern power, which today serves as the electrical standard in nearly every country for industrial infrastructure.
Different countries use varying standards for wiring colors, voltage levels, and grounding methods. For example, North America often uses a high-leg delta system for mixed-load facilities, while European countries standardize around 400V/230V Wye systems.
3 phase electricity is more than just a technical enhancement—it's a foundational system that enables our modern, electrified world. Its advantages in efficiency, stability, and equipment performance make it indispensable for everything from factories to high-rises. While it requires more planning and design than single-phase alternatives, the return on investment is clear: lower energy losses, reduced material costs, and better equipment longevity.
In a world increasingly dependent on energy-hungry technologies, this kind of power remains the most reliable, scalable, and efficient choice for serious electrical infrastructure.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is 3 phase used for?
It is commonly used in industrial and commercial applications where large amounts of electricity are needed to operate heavy machinery, HVAC systems, motors, and high-power equipment. It’s ideal for facilities that require consistent voltage and reliable energy delivery.
How does 3 phase differ from single phase?
The key difference lies in the number of alternating currents used. Single-phase systems utilize a single AC waveform, resulting in voltage dips between cycles. In contrast, 3 phase power uses 3 synchronized waveforms 120 degrees apart, delivering smoother, continuous power.
Why is 3 phase more efficient?
It is more efficient because it delivers constant power with less energy loss, allows for smaller conductors, and reduces the need for starting equipment in electric motors. This results in lower transmission losses and greater cost savings in both wiring and operation.
Related Articles











