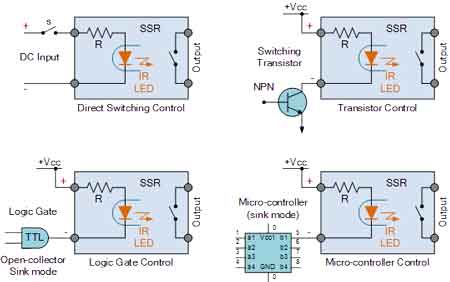
Electrical Safety Certification Explained

NFPA 70e Training
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 6 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our OSHA 3875 Fact Sheet – Electrical PPE for Power Industry Workers

- Follow rules for rubber gloves, arc-rated PPE, and inspection procedures
- Learn employer obligations for testing, certification, and training
- Protect workers from arc flash and electrical shock injuries
Electrical safety certification ensures compliance with IEC standards, UL and CE marking through conformity assessment, type testing, risk assessment, insulation and grounding verification, reducing shock, fire, and arc-flash hazards for electrical equipment and industrial installations.
What Is Electrical Safety Certification?
It verifies products and systems meet safety standards via testing, risk controls, and documented compliance.
✅ Covers IEC/UL standards, CE marking, and national codes
✅ Requires type testing, insulation resistance, and dielectric strength
✅ Includes risk assessment, grounding verification, and labeling
Electrical safety certification forms the backbone of industry safety practices, protecting both lives and infrastructure. This certification confirms that systems and equipment comply with stringent standards, reducing the risks of fires, electric shocks, and other hazards. A deep understanding of this certification is indispensable for professionals such as electrotechnical engineers, safety experts, and facility managers. For many organizations, aligning with the principles of NFPA 70E certification streamlines documentation and audit readiness for safety programs.
Request a Free Training Quotation
Electrotechnical inspection approval is a critical requirement for industrial electricians, as it ensures that systems and installations adhere to stringent safety standards. This certification plays a key role in minimizing risks like shocks, fires, and system malfunctions, protecting both individuals and infrastructure. For industrial electricians, understanding the intricacies of these certifications is vital to maintaining workplace safety and regulatory compliance. Organizations can meet regulatory requirements while prioritizing a safe working environment by following established guidelines like the NFPA 70E standard and engaging in NFPA 70E training. Supervisors should verify that curricula align with NFPA 70E training requirements to ensure task-appropriate qualifications.
The Role of Standards in Certification
Standards like the NFPA 70E standard define the framework for safety, offering guidelines for preventing accidents and reducing downtime. These standards emphasize maintaining safe work environments and controlling electrotechnical risks, such as arc flashes. Following these protocols is crucial not only for certification but also for fostering a proactive safety culture. Beyond definitions, NFPA 70E provides practical guidance for implementing risk assessments and energized work permits effectively.
Sign Up for Electricity Forum’s Arc Flash Newsletter
Stay informed with our FREE Arc Flash Newsletter — get the latest news, breakthrough technologies, and expert insights, delivered straight to your inbox.
How Certification Benefits Organizations
Certifications bring numerous advantages. They help businesses meet regulatory compliance, which is often a prerequisite for obtaining insurance. Additionally, certified systems experience fewer breakdowns, improving operational efficiency and reducing downtime. Employees working on certified systems are less likely to encounter life-threatening incidents, boosting morale and trust. These benefits are amplified when staff receive ongoing electrical safety training that reinforces procedures and hazard recognition.
The Core of Electrotechnical Safety Certification
At its essence, inspection approval guarantees that systems are evaluated, installed, and maintained according to established benchmarks. The certification process involves assessments by qualified inspectors who issue reports verifying compliance. These certifications provide peace of mind to industries where workers are not exposed to electrotechnical hazards and systems function reliably. Certifications align with guidelines from bodies like the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), underscoring their importance in minimizing workplace incidents. Auditors frequently look for documented completion of NFPA 70E arc flash training as part of competency evidence during evaluations.
Why Training Matters
Achieving electrotechnical safety certification involves more than testing systems—it requires a culture of informed practices. Electrotechnical safety training programs, such as those focused on the NFPA 70E standard, equip professionals with the knowledge to implement safe work procedures. A comprehensive training course includes identifying risks, using personal protective equipment (PPE), and understanding arc flash boundaries. Such training is not limited to engineers; it extends to all personnel who interact with systems. Organizations often schedule periodic NFPA 70E training to refresh PPE selection, approach boundaries, and job briefing practices.
Common Certifications and Their Scope
There are multiple types of certifications depending on the application and environment. For instance, certifications like the Electrotechnical Installation Certificate (EIC) are used for new systems, while the Electrotechnical Installation Condition Report (EICR) applies to older systems. Both serve different purposes but share the goal of ensuring safe and reliable operations. Regular inspections, often required for certifications, reveal hidden faults before they become critical. Complementary to installation documents, arc flash training certification helps ensure personnel can maintain compliance between inspection cycles.
It validates that equipment and systems adhere to established safety standards, minimizing risks such as electrotechnical fires, shocks, and system malfunctions. This certification is vital for protecting lives, maintaining workplace efficiency, and meeting legal obligations. By adhering to recognized guidelines like the NFPA 70E standard and incorporating comprehensive training, organizations can create safer workplaces and uphold the integrity of their electrotechnical infrastructure.